Recognizing the Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis Early
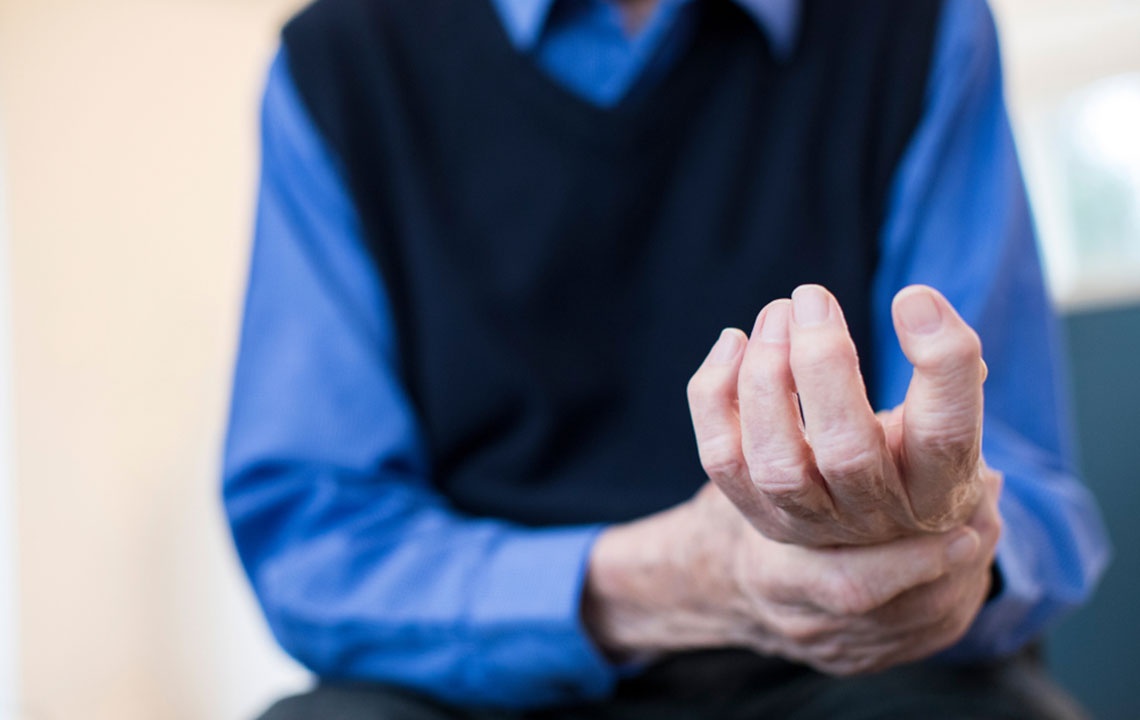
Rheumatoid arthritis affects millions annually, especially women, causing joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. Recognizing early symptoms like fatigue, tenderness, and deformity can lead to timely treatment, preventing permanent damage. This article highlights key signs to watch for and emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis for better outcomes.
Sponsored

Understanding the Signs and Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Each year, over 1.5 million individuals in the United States are diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, which is notably more common in women than in men. Predominantly affecting older adults, this joint disease can be identified early through specific symptoms. Recognizing these signs promptly can prevent severe damage. Read on to learn about key symptoms that indicate the presence of rheumatoid arthritis.
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing inflammation and tissue damage. Normally, the immune system defends the body against threats, but in this case, it targets joint tissues, leading to pain, swelling, and possible joint deformation.
This condition primarily affects the synovium—lining tissue inside joints that produces lubricating fluid, facilitating smooth movement. Persistent inflammation damages cartilage, bones, and joint tissues, resulting in instability and pain. Early diagnosis allows for interventions to restore joint function and prevent permanent damage.
Pay close attention to the following symptoms for early detection of rheumatoid arthritis:
Fatigue: Persistent tiredness often accompanies inflammation, disrupted sleep, medication side effects, or anemia, impacting mood, appetite, and daily activity.
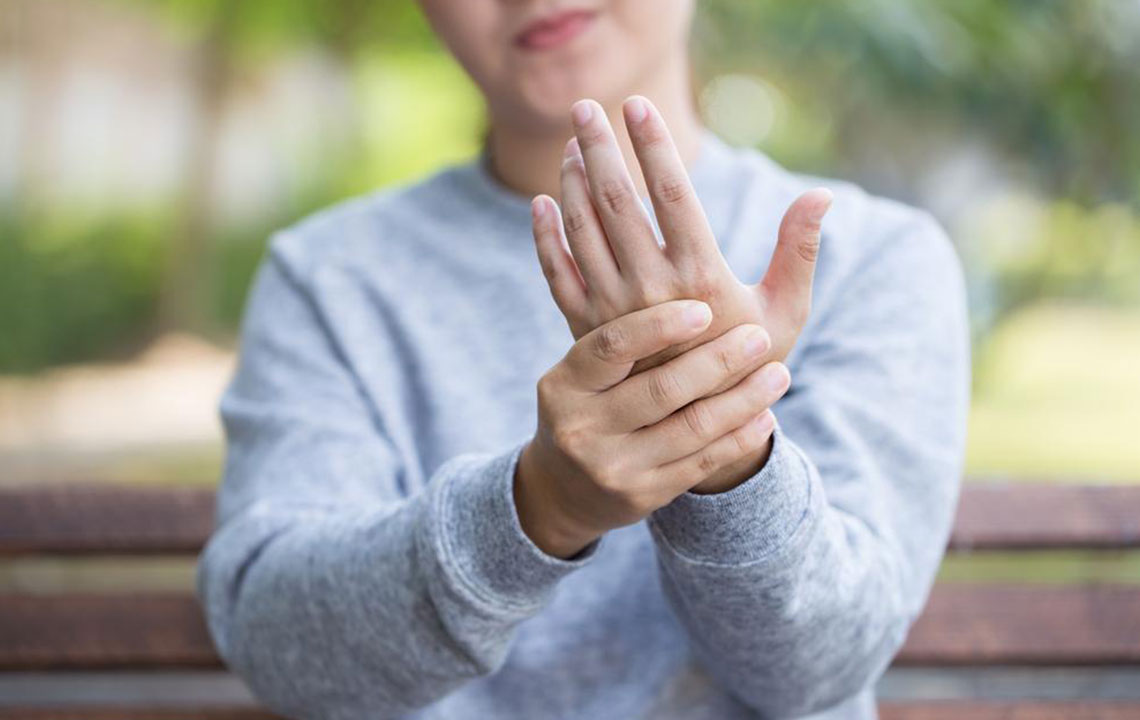
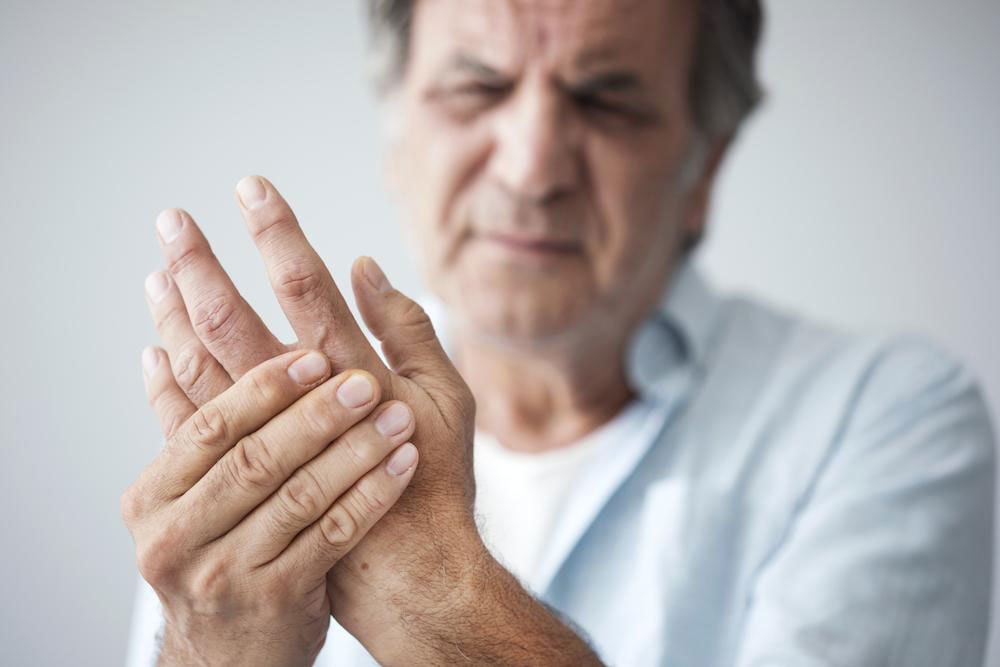
Joint Pain: Inflamed joint tissues lead to soreness and discomfort, which can persist even after the inflammation subsides or due to previous damage.
Joint Tenderness: Swollen tissues may irritate nerves, causing increased pain upon touch, often disturbing sleep.
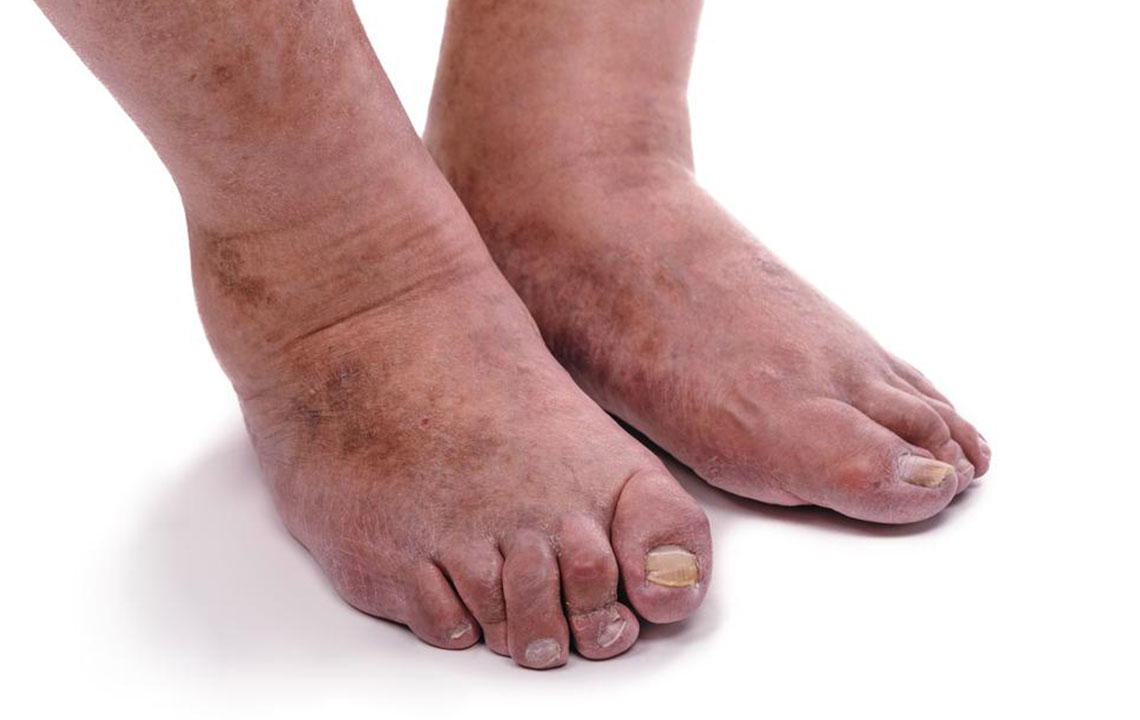
Swelling: Joints may become visibly swollen, reducing mobility and making routine tasks like removing rings difficult.
Redness and Warmth: Inflamed joints can appear red and feel warm, indicators of active inflammation, which typically lessen with treatment.
Limited Movement: Swelling and tissue damage restrict joint mobility; untreated, it can lead to irreversible stiffening.
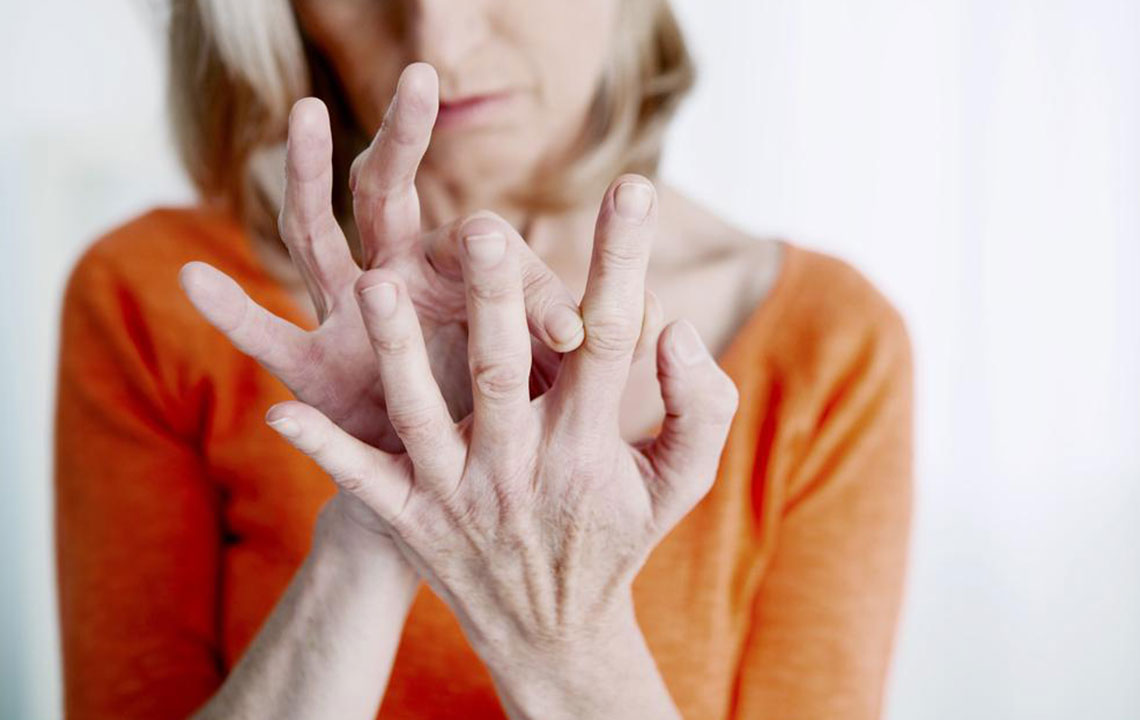
Joint Deformation: Chronic inflammation may cause structural changes, ligament laxity, and joint misalignment.
Numbness: Inflamed blood vessels can impinge nerves, resulting in tingling or numbness in extremities like wrists, elbows, and ankles.
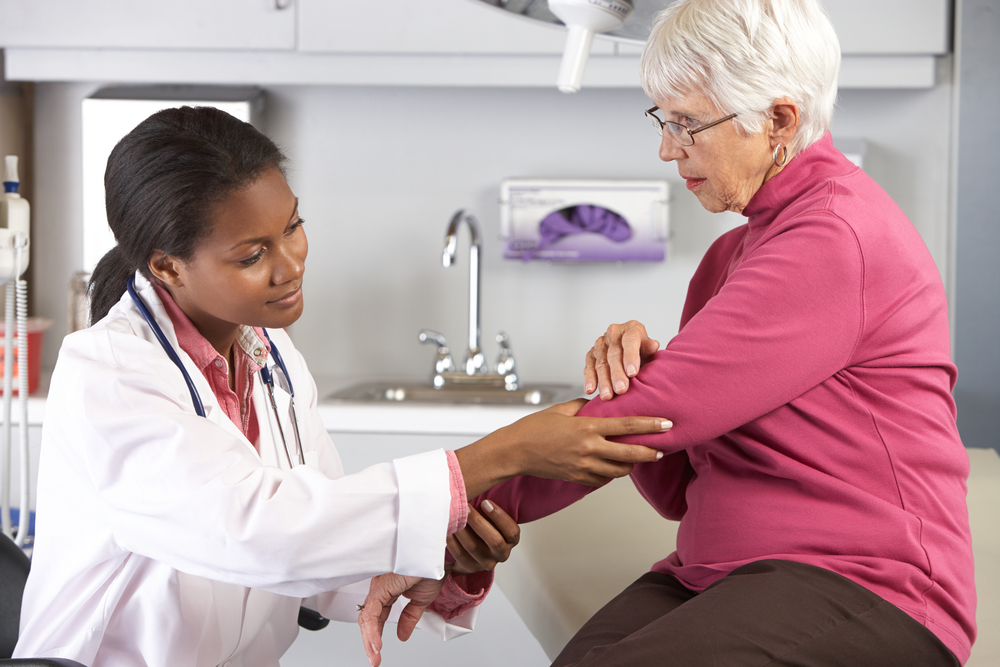
If you notice any of these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early intervention is vital to managing the disease effectively and avoiding long-term joint damage.