Effective Lifestyle Strategies for Managing Blood Glucose
Discover practical lifestyle and dietary strategies to effectively manage blood glucose levels and prevent diabetes. From exercise and portion control to low-GI foods and stress management, these simple tips can support long-term health. Always seek medical advice before making significant changes.
Sponsored

Proven Lifestyle Approaches to Regulate Blood Glucose Levels
Elevated blood sugar occurs when glucose isn't efficiently transported from the bloodstream into body cells. Without intervention, this can lead to diabetes.
Research indicates that nearly half of the population is either diabetic or pre-diabetic.
Luckily, simple adjustments in daily habits and diet can help maintain blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Below are practical lifestyle and nutritional tips to support diabetes management. Let’s explore them.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Physical activity is essential for overall health.
Consistent exercise helps reduce excess weight and enhances insulin effectiveness. This enables body cells to utilize blood sugar more efficiently. Additionally, muscle activity consumes glucose, aiding blood sugar control. Regular blood glucose monitoring can reveal how your body responds to various activities.
Limit Carbohydrate Consumption
Carbohydrates are converted into glucose, which insulin signals to be absorbed by cells. Excess carbs or insulin resistance cause blood sugar spikes. Adopting a low-carb diet can help keep levels stable and prevent high spikes.
Increase Dietary Fiber
Fiber slows carbohydrate digestion and sugar absorption, promoting steady blood sugar levels. A diet rich in soluble fiber, found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, is particularly effective for managing blood glucose.
Practice Portion Control
Managing portion sizes helps reduce calorie intake, support a healthy weight, and lower diabetes risk. Eating slowly and mindful portioning can prevent blood sugar surges.
Choose Low-GI Foods
Foods with a low glycemic index (under 55) cause smaller blood sugar increases. Incorporate options like leafy greens, nuts, legumes, fish, lean meats, quinoa, and sweet potatoes into your meals.
Manage Stress Levels
Stress triggers hormones like cortisol that raise blood sugar. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and breathing exercises can help reduce stress and support glucose control.
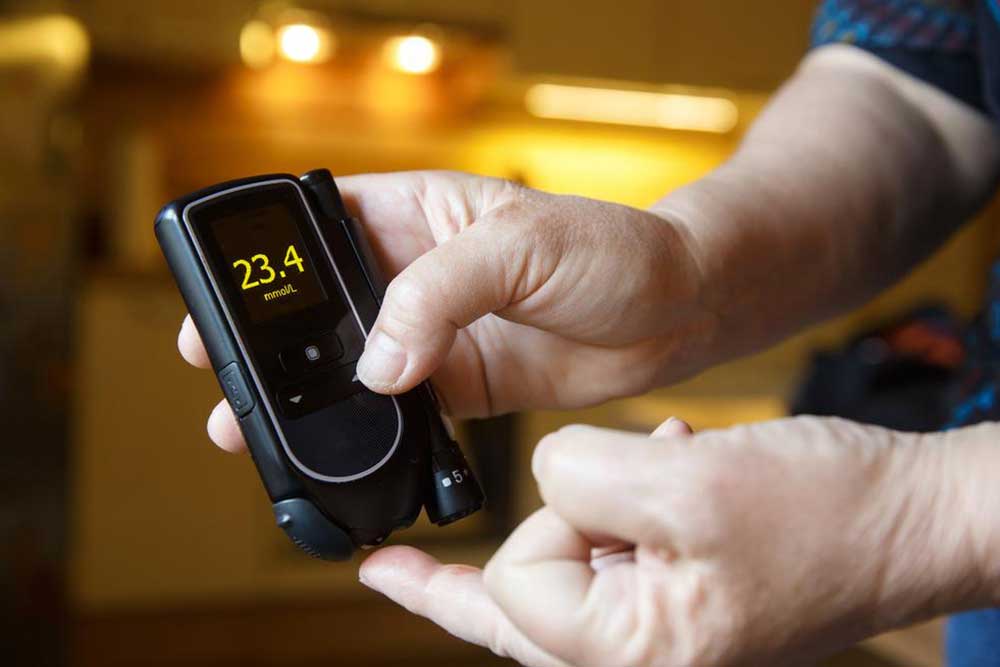
Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
Routine testing provides insights into how diet and activities impact blood sugar, enabling timely adjustments and medical consultations.
Prioritize Adequate Sleep
Sleeping at least 8 hours nightly supports blood sugar regulation. Sleep deprivation impairs insulin sensitivity, increases appetite, and raises cortisol levels, all of which contribute to elevated glucose.
Include Fenugreek Seeds
Fenugreek is a potent source of soluble fiber that enhances glucose tolerance and aids blood sugar management. A daily intake of 2-5 grams, added to food or brewed as tea, can be beneficial.
Implementing these lifestyle practices can significantly improve blood sugar stability. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting new routines or supplements, especially if on medication.