Foods to Include and Avoid During Diarrhea Recovery
Learn effective dietary guidelines for managing diarrhea. Discover which foods to include, such as bananas and chicken broth, and which to avoid, like fried foods and dairy. Following these tips can promote quick recovery, alleviate symptoms, and prevent complications. Seek medical advice if symptoms persist or worsen, especially with signs of dehydration or blood in stools.
Sponsored

Foods to Consider and Steer Clear of When Experiencing Diarrhea
Diarrhea is a common digestive issue characterized by frequent, loose stools. It occurs due to food allergies, bacterial infections, or consumption of poorly digested food. Sometimes, it also accompanies conditions like irritable bowel syndrome. Lasting for a few days, diarrhea can resolve naturally, but persistent or severe symptoms require medical attention.
Signs of Severe Diarrhea
Dehydration and high fever
Sharp stomach or rectal pain
Blood or mucus in stool
Persistent weakness and cramps
Proper treatment, including a specific diet and medications, helps recover faster. Avoiding certain foods can ease symptoms and prevent complications.
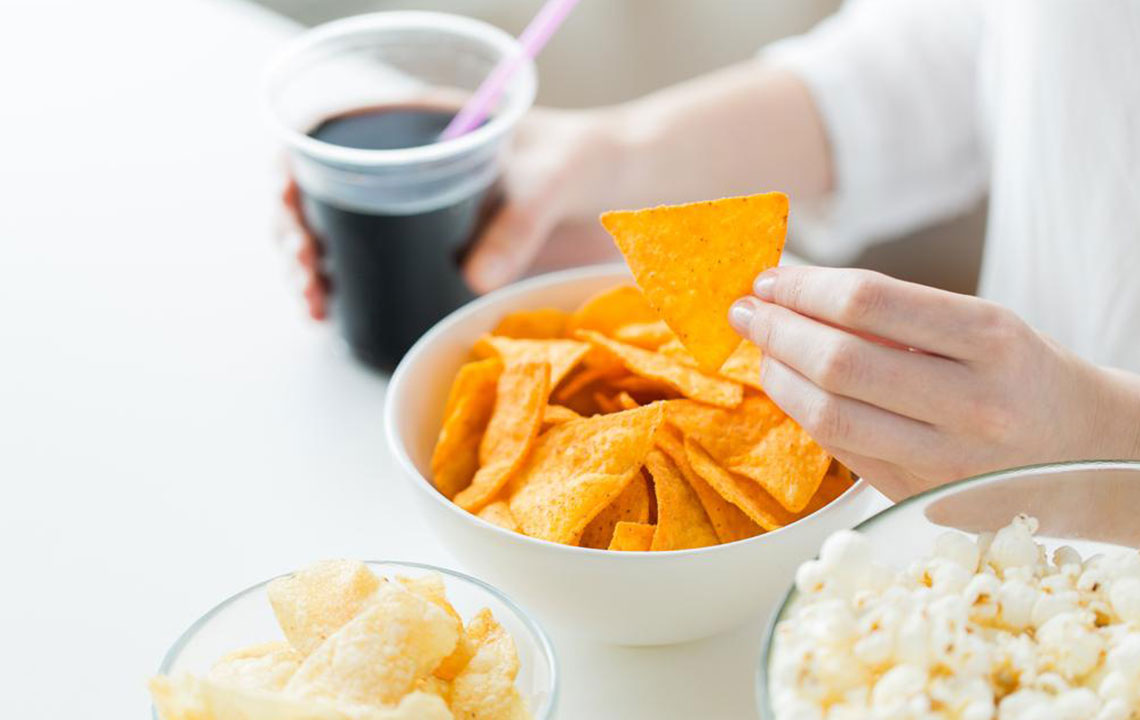
Foods to Avoid During Diarrhea
Fried and greasy foods: These can irritate the digestive tract and worsen symptoms.
Dairy products: Milk, cheese, butter, and ice cream can aggravate diarrhea, especially in lactose-intolerant individuals.
Alcohol and caffeinated drinks: Beverages like coffee and soda promote dehydration and should be avoided.
Artificial sweeteners: Substitutes like sorbitol and other sugarless products may have laxative effects.
Gas-promoting vegetables: Cabbage, beans, cauliflower, and broccoli can increase bloating and discomfort.
Unhygienically stored foods: Avoid raw or improperly stored foods such as unrefrigerated meat and fish to prevent infection.
Foods to Incorporate into Your Diet
Clear broths: Chicken or vegetable broth helps replenish lost electrolytes and soothes the digestive system.
Bananas: Rich in potassium and gentle on the stomach, bananas assist in electrolyte replacement and stool regulation.
Mashed potatoes: Plain and starchy, they are easy to digest and help stabilize the gastrointestinal tract.
Oatmeal: Consumed plain, oatmeal provides soluble fiber that promotes regularity, especially when combined with bananas.
Lean proteins: Steamed or baked chicken provides essential nutrients and is easy to digest without added fats or spices.