Effective Blood Sugar Monitoring for Diabetes Management
This article emphasizes the importance of blood sugar charts in managing diabetes effectively. It covers how these charts help monitor glucose levels, interpret readings, and guide lifestyle and treatment adjustments. Regular use of blood sugar charts can prevent complications, aid in early diagnosis, and support sustainable diabetes management for both diabetics and those at risk.
Sponsored
Maintain Optimal Blood Sugar Levels with Monitoring Charts
Diabetes is a chronic condition marked by elevated blood glucose due to inadequate insulin production or utilization. It is often dubbed a silent threat, especially when combined with high blood pressure, increasing the risk of severe health issues.
Approximately 37% of the world's population suffers from diabetes, a number rising due to obesity and unhealthy lifestyles.
Understanding Diabetes
There are two main types: Type 1, where insulin dependence is total, and Type 2, which is more prevalent and involves insufficient insulin or insulin resistance.
Additionally, juvenile and gestational diabetes are increasingly common. Proper medication and lifestyle adaptations can effectively control these conditions.
Diabetes can lead to blindness, strokes, and slow-healing infections, sometimes resulting in limb amputations. Regular blood sugar monitoring using dedicated charts is crucial for managing these risks.
Sugar level charts track the amount of glucose in your blood, helping you stay informed about your health status.
What Is a Blood Sugar Chart?
This tool records your blood glucose levels over time, including dates, fasting, and post-meal readings. It also displays target ranges, enabling you to compare your levels against normal benchmarks.
Typical fasting blood sugar should be between 70-130 mg/dl, while post-meal levels should stay below 180 mg/dl. Exceeding these ranges suggests possible diabetes, requiring consultation with a healthcare professional. Extremely low levels below 50 mg/dl can cause hypoglycemia, posing serious health risks. Monitoring helps maintain blood sugar within safe limits.
You can download and print blood sugar charts to track your levels regularly. Comparing your readings helps determine if medication adjustments are necessary.
How to Use a Blood Sugar Chart
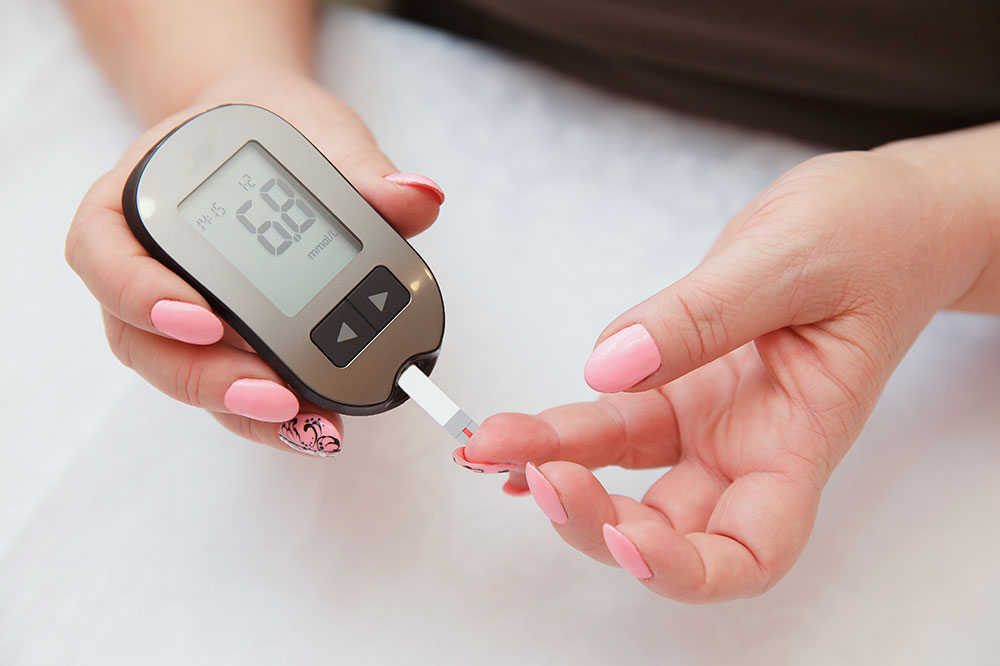
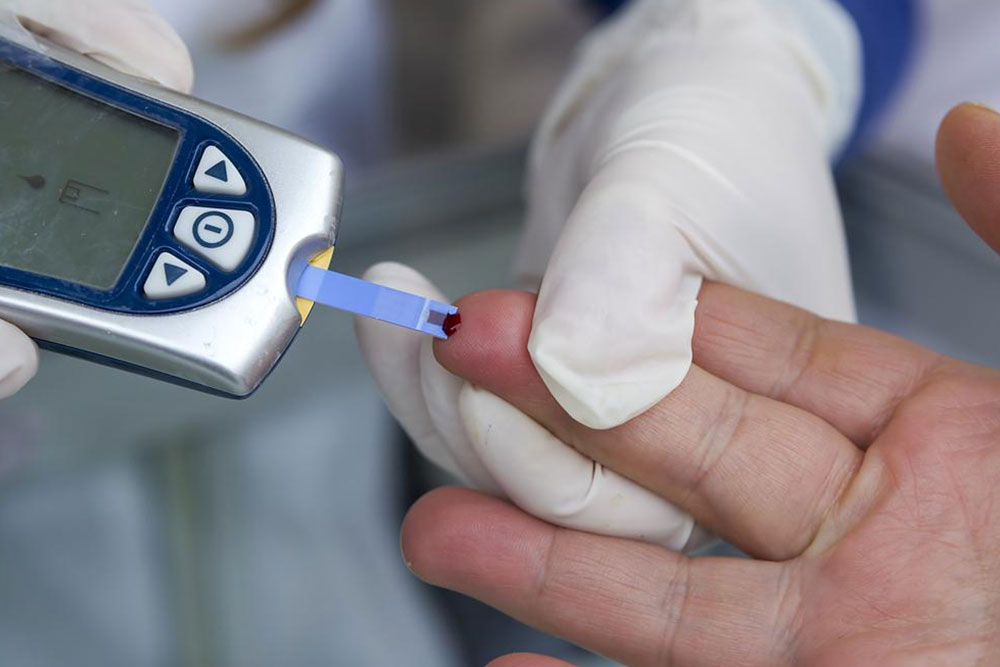
Using portable blood glucose meters with test strips, you can check your levels at home by pricking your finger and applying a blood drop to the strip. The device displays your glucose level, which you can compare to normal ranges.
Regular testing before and after meals helps you identify spikes and understand their causes. Consistent monitoring supports better diabetes management.
The Benefits of Blood Sugar Charts
Frequent testing at clinics is costly and time-consuming. Having a personal blood sugar monitor and a chart simplifies daily tracking. These charts interpret mg/dl readings, providing crucial insights. For example, a post-meal level of 220 mg/dl indicates a potential concern like ketoacidosis.
Self-monitoring guides insulin dosing and lifestyle changes. Maintaining a blood sugar log assists doctors in tailoring treatments and observing trends. It also helps non-diabetics assess their risks, enabling early intervention to prevent diabetes onset.
In summary, blood sugar charts are vital tools for effective diabetes control, enabling timely medical responses, better lifestyle choices, and reduced complication risks.