Effective Strategies to Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Learn how to effectively manage diabetes by maintaining blood sugar levels within healthy ranges. This article covers normal blood sugar levels, target goals for diabetics, and practical tips for controlling blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol. Regular monitoring, stress management, and lifestyle adjustments are key to preventing complications and ensuring a better quality of life.
Sponsored

Diabetes is a long-term metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, stemming from insufficient insulin production or the body's inability to effectively use insulin. Insulin plays a vital role in controlling blood glucose. When insulin production or function is disrupted, blood sugar levels become abnormal. Globally, approximately 8.5% of adults are diagnosed with diabetes each year.
What constitutes normal blood sugar levels?
Keeping blood glucose within the normal range is crucial for managing diabetes effectively.
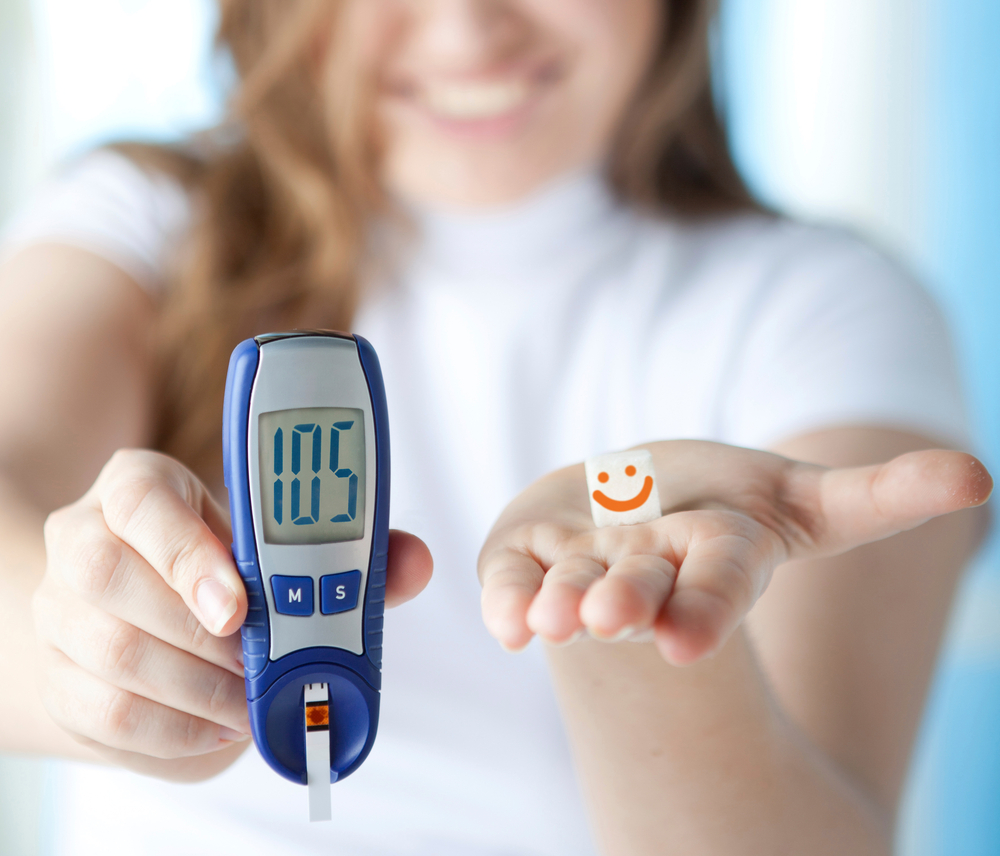
Understanding blood sugar levels and how to interpret their measurements is essential. Blood sugar, or glucose, refers to the sugar derived from food that circulates in the bloodstream. Normal levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl). Blood glucose fluctuates throughout the day, and charts display three key readings: fasting blood sugar, post-meal blood sugar, and HbA1c levels.
Fasting Blood Sugar: Measures glucose after overnight fasting, typically in the morning before eating. The normal fasting level is between 70 mg/dl and 100 mg/dl.
Post-Meal Blood Sugar: Measures glucose two hours after a meal. For individuals without diabetes, normal levels are below 140 mg/dl.
HbA1c Levels: Reflects average blood sugar over 2-3 months by measuring hemoglobin A1c. Normal HbA1c values range from 4% to 5.6%.
Blood Sugar Targets for People with Diabetes
For diabetics, target ranges differ to better manage the condition:
Fasting Blood Sugar: Should be between 80 mg/dl and 130 mg/dl.
Post-Meal Blood Sugar: Aim for below 180 mg/dl.
HbA1c: Keep under 7% to indicate good control.
Maintaining blood glucose near normal levels helps prevent complications affecting nerves, eyes, and kidneys. Strategies include:
Regular Monitoring: Checking blood sugar periodically helps adjust diet and activity, enhancing control.
Adapting to Life with Diabetes: Managing stress and anxiety is crucial, as they can trigger blood sugar spikes. Developing hobbies, exercising, and socializing support better management.
Controlling Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: Keeping blood pressure below 140/90 mmHg and lowering LDL cholesterol reduces cardiovascular risks linked to diabetes.
Blood sugar management emphasizes staying within target ranges, supporting overall health and reducing complications.