Understanding GIST: Treatment Options and Nutrition Strategies
This article explores effective treatment options for GIST, including surgery, targeted therapy, and supportive care. It emphasizes the importance of tailored nutrition strategies to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of tumor recurrence. Practical dietary tips include reducing sugar, fats, salt, and alcohol intake while ensuring balanced nutrition. Collaborating with healthcare professionals ensures personalized and effective management of GIST, promoting better health outcomes and quality of life.
Sponsored

Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) develop in digestive organs like the stomach and small intestine. Although this type of cancer can be serious, there are effective ways to treat and manage it. Patients benefit from various therapies combined with a proper diet and lifestyle adjustments. This article highlights key treatment approaches and nutritional tips to support GIST management.
Primary Treatment Approaches for GIST
Surgical Removal
Most GISTs are small and less aggressive, making surgery a primary treatment option. Research indicates that about 85% of tumors can be successfully excised.
Post-surgery, the tumor is examined microscopically to assess the risk of recurrence.
Targeted Medical Therapy
For larger or more aggressive tumors, targeted therapy may be recommended. This involves medications designed to specifically attack cancer cells within the gastrointestinal system.
Supportive Care
Supportive interventions help manage side effects and emotional well-being during treatment, complementing surgery and targeted drugs.
It’s important to note that GIST can return within two years after removal, emphasizing the importance of vigilant follow-up.
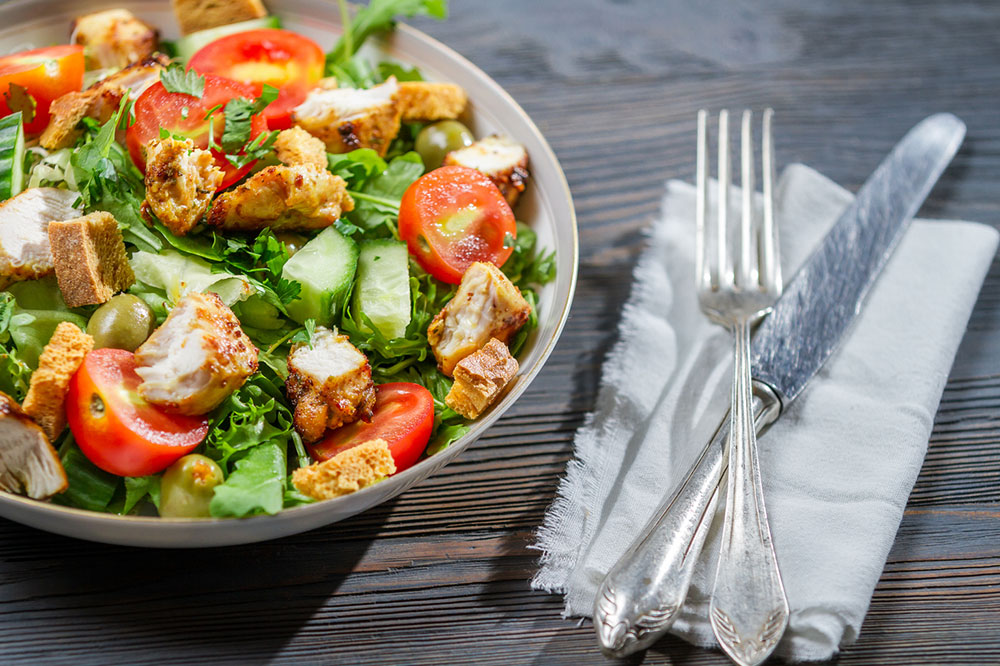
However, adopting the right dietary habits can lower the risk of recurrence. Managing GIST also involves proper nutrition to ease symptoms like pain, nausea, fatigue, and digestive issues. Consider these dietary tips:
Consume adequate vitamins and minerals for overall health.
Avoid foods high in sugar to prevent symptom aggravation.
Reduce daily calorie intake by 20-30% to support weight management.
Limit or avoid hydrogenated and animal fats, which are hard to digest and may cause discomfort.
Cut down on salt intake to support overall health.
Limit alcohol consumption to aid recovery and reduce complication risks.
Working with a nutritionist can help develop a personalized diet plan. Additionally, consulting a healthcare provider about measures to prevent tumor recurrence is advisable following tumor removal.