Comprehensive Guide to Melanoma Detection and Diagnosis
Learn essential methods for early melanoma detection, including self-examination tips and various biopsy techniques used by healthcare professionals to diagnose the skin cancer effectively. Regular skin checks and prompt medical attention are vital for early intervention.
Sponsored

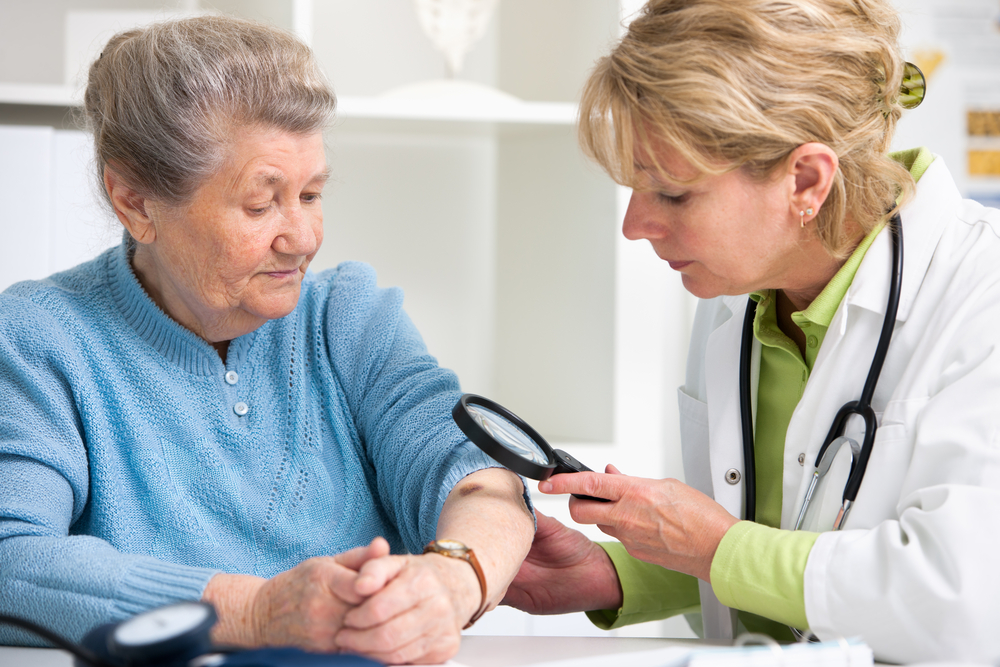
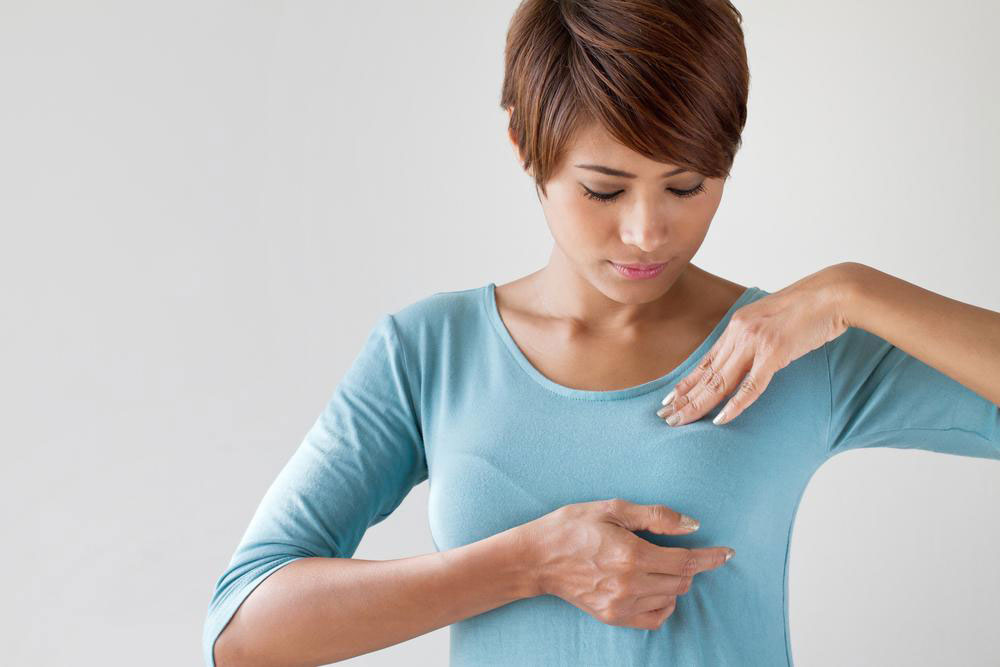
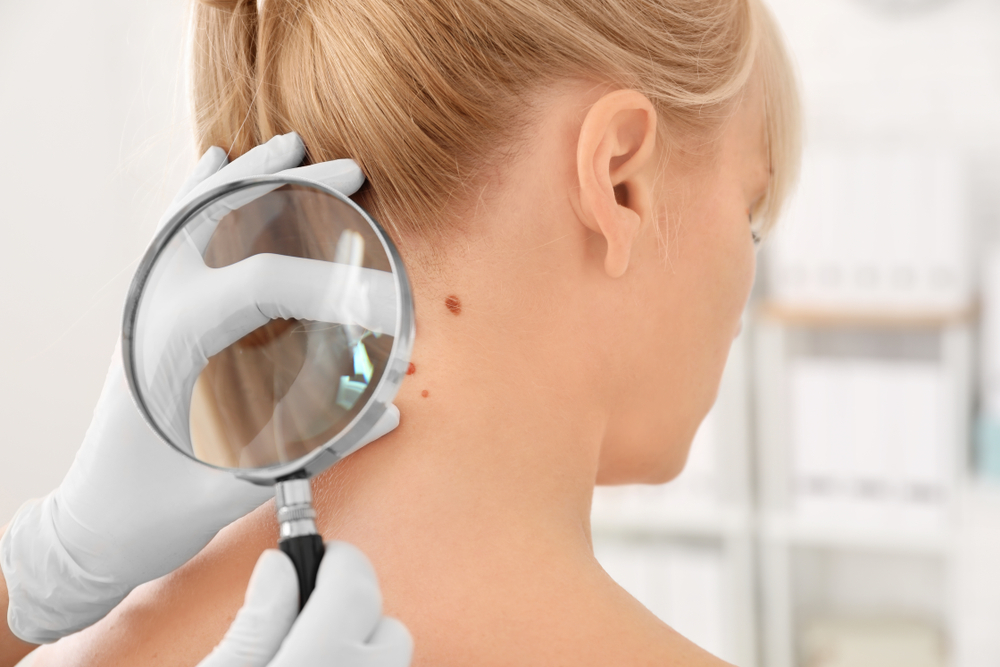
Early identification of melanoma significantly improves treatment outcomes. Regular self-examinations of your skin are crucial, especially if you're frequently exposed to sunlight or have many moles and freckles, particularly if you have fair skin. Watch for any changes such as elevation, flaking, shape alteration, or tenderness. An annual professional skin assessment is recommended for high-risk individuals.
Performing a thorough self-check involves inspecting common problem areas with a mirror:
Back
Shoulders
Neck
Chest and abdomen
Scalp
Face
Both front and back of arms
Groin area
Legs from front and back
Hands, feet, and toes, including under nails
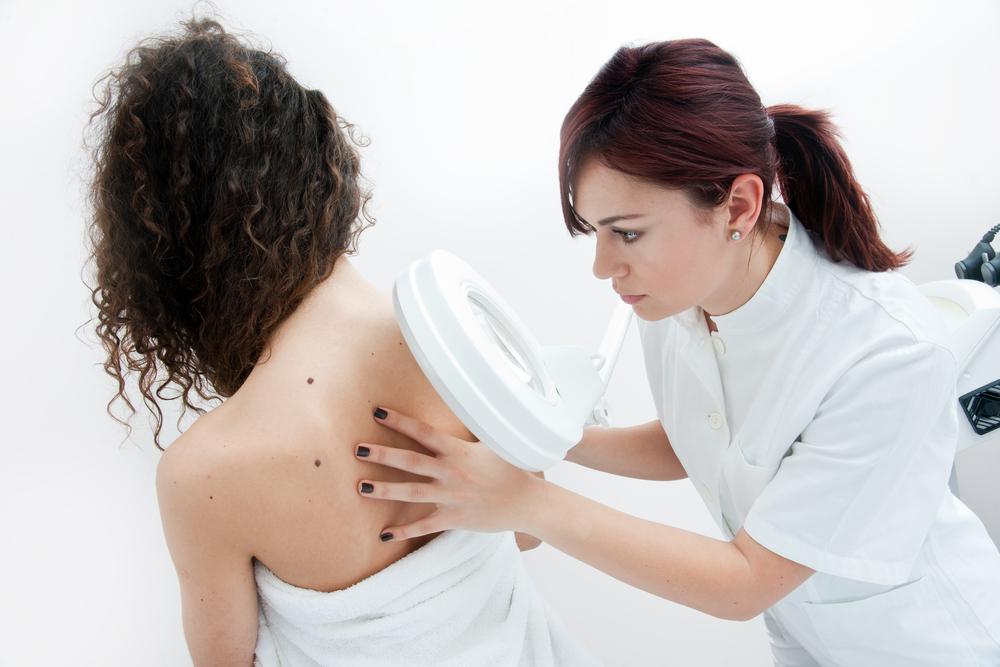
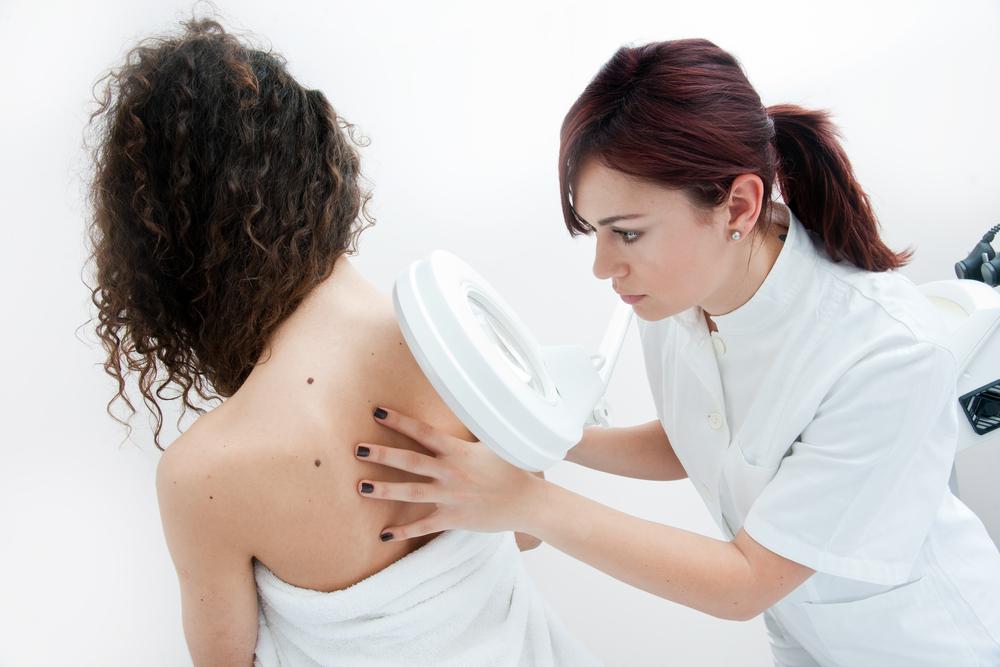
Biopsies for melanoma
If a dermatologist finds suspicious skin, they may recommend a biopsy. Types include:
Punch biopsy
Uses a circular blade to remove a small, round tissue sample for analysis.
Optical biopsy
Employs reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM), a non-invasive imaging technique, to examine skin layers without cutting.
Tangential (Shave) biopsy
Involves shaving off the top skin layer with a surgical blade; bleeding control may be necessary.
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)
Uses a thin needle guided by imaging to extract cells, often from deeper or suspicious lesions for evaluating cancer spread.
Incisional biopsy
Removes part of a larger suspicious lesion for testing.
Sentinel and Surgical biopsies
Used in advanced cases to assess spread to lymph nodes; involves dye injections and tissue removal for staging cancer.