Understanding Advanced Melanoma: Risks, Treatments, and Management Tips
This article explores advanced melanoma, highlighting risk factors, treatment options, ongoing research, and self-care tips. It emphasizes the importance of early detection, discusses emerging therapies, and offers supportive strategies for patients managing metastatic melanoma, aiming to improve outcomes and quality of life.
Sponsored

Advanced melanoma – an overview of risks, treatment options, and self-care strategies
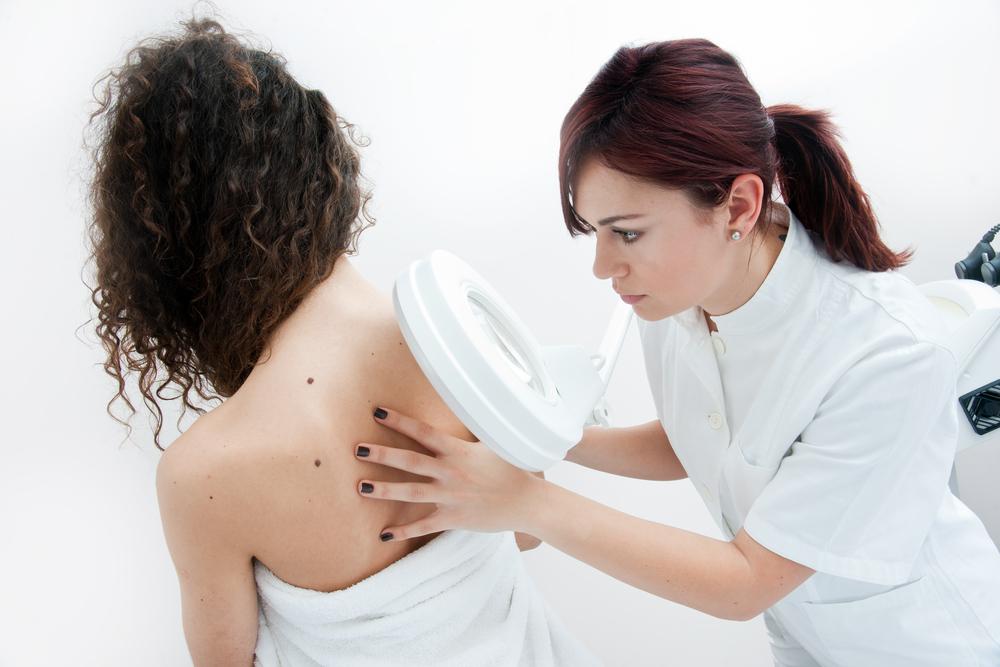
When melanoma spreads beyond the skin to other organs, it is termed advanced or metastatic melanoma. Common sites include the liver, lungs, brain, lymph nodes, and subcutaneous tissues. Symptoms may include swollen lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, liver swelling, headaches, firm lumps under the skin, bone pain, persistent cough, and appetite loss. Once reaching an advanced stage, treatment becomes more challenging. Prompt medical consultation is vital if any skin changes or symptoms appear.
What factors increase the likelihood of developing melanoma?
Excessive unprotected sun exposure primarily causes melanoma, but certain factors can heighten the risk, including:
Indoor tanning devices and lamps
Having numerous moles on the skin
Fair skin, freckles, light-colored eyes, and blond or red hair
A family history of melanoma
Genetic mutations
Inherited conditions like Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Werner syndrome, xeroderma pigmentosum, retinoblastoma, and hereditary breast or ovarian cancers
Age over 40
Compromised immune system
Current treatment options for advanced melanoma
Presently, treatment approaches include:
Surgical removal of tumors and affected lymph nodes
Chemotherapy
Targeted therapies
Immunotherapy
Radiation therapy
The choice of therapies depends on the disease’s progression severity, often combining multiple methods for optimal results. Emerging therapies and ongoing research for advanced melanoma
Medical researchers are actively exploring new treatments through clinical trials. These experimental options may include advanced diagnostic tools, novel drugs, and vaccines, though their safety and effectiveness are still being evaluated. Potential breakthroughs involve:
• Reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM)
• Immune checkpoint inhibitors
• Melanoma vaccines
• Drugs targeting BRAF gene mutations
Self-care tips for managing advanced melanoma
Facing metastatic melanoma can be physically and emotionally demanding. To support well-being, patients and loved ones can adopt these strategies:
Support systems and communication – Feeling frustrated or anxious is normal. Seeking support from family, friends, support groups, or mental health professionals can make a significant difference. Resources like the American Cancer Society and American Melanoma Foundation provide valuable support networks.
Nutrition – Treatments may cause fatigue. A balanced diet with lean proteins, whole grains, healthy fats, fruits, and vegetables can boost energy levels. Staying hydrated is equally important.
Physical activity and rest – Gentle exercises like yoga, walks, or light jogging can alleviate stress and improve mood. Adequate sleep is crucial; relaxing activities such as listening to music or journaling can enhance sleep quality.
Regular skin checks are key. Noticing changes in moles’ appearance warrants prompt medical consultation for early detection. Early-stage melanoma can be successfully treated, improving survival odds and quality of life. When metastasized, therapy effectiveness may vary, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis.