Understanding Psoriasis: Types, Causes, and Effective Therapies
This article provides an overview of psoriasis, highlighting its main types, causes, and treatment strategies. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and individualized care to manage this chronic condition effectively. Learn about the common locations, symptoms, and available therapies to better understand and control psoriasis.
Sponsored

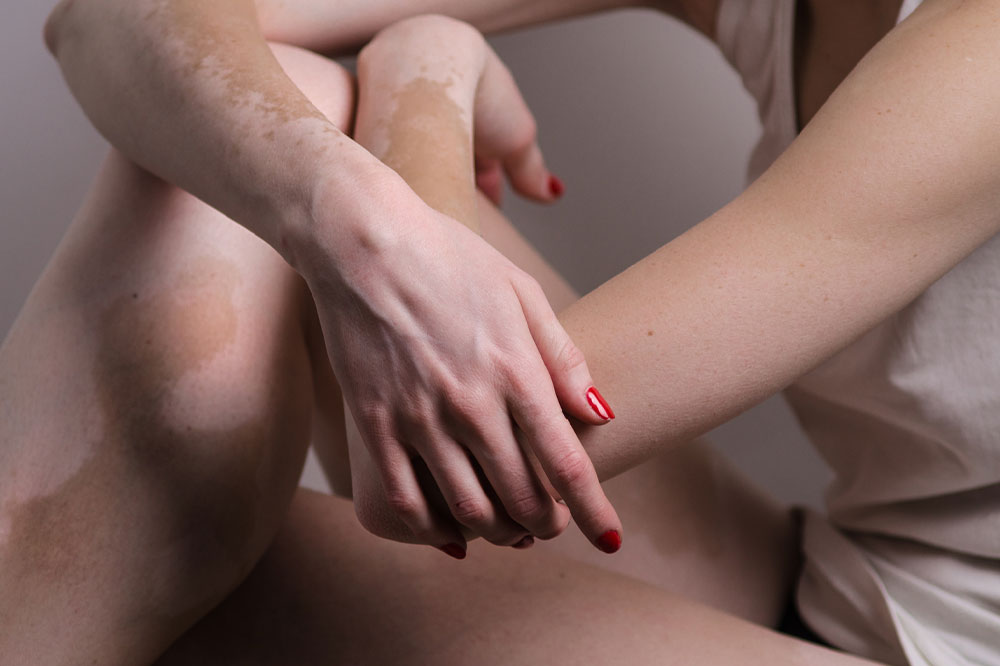
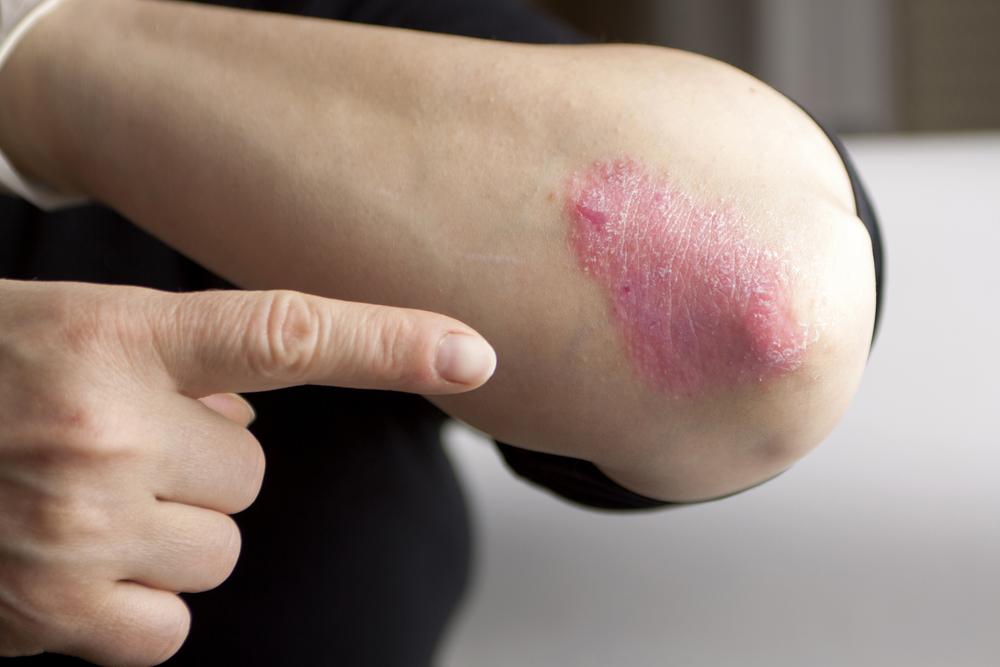
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disorder characterized by rapid skin cell growth, leading to red, scaly, and inflamed patches on the surface. In severe cases, the skin may crack and bleed. Most commonly affecting joints like elbows and knees, psoriasis can also appear on hands, feet, scalp, face, and genitals.
Types of Psoriasis
The main forms include plaque, guttate, pustular, inverse, and erythrodermic psoriasis.
Plaque psoriasis
The most prevalent type, manifesting as red, inflamed patches covered with silvery scales, typically on elbows, knees, and scalp.
Guttate psoriasis
Common among children, characterized by small pink spots on the torso, arms, and legs, often less raised than plaque type.
Pustular psoriasis
Seen mainly in adults, featuring white pus-filled blisters and inflamed skin on hands and feet.
Inverse psoriasis
Bright red, shiny areas of skin developing under arms, breasts, groin, or genitals.
Erythrodermic psoriasis
An extensive form covering large body areas, giving a sunburned appearance, and less common.
Causes of Psoriasis
Genetics play a crucial role, with family history increasing susceptibility. A weakened immune system and triggers like stress, skin injuries, infections, and certain medications also contribute.
Treatment Options
Mild cases often improve with topical creams, lotions, or sprays, and sometimes injections. Severe cases may require UV therapy, systemic treatments, tablets, or injections. Although not curable, proper skin care and medical management can control psoriasis effectively.