The Impact of Diabetes on Overall Health
This article explores the wide-ranging complications of diabetes, including nerve damage, foot ulcers, and vascular issues. It emphasizes the importance of blood sugar management and proper foot care to prevent severe outcomes like infections and amputations. The piece also highlights lifestyle changes and medical practices essential for minimizing diabetes-related health risks and maintaining quality of life.
Sponsored

Understanding Diabetes and Its Complications
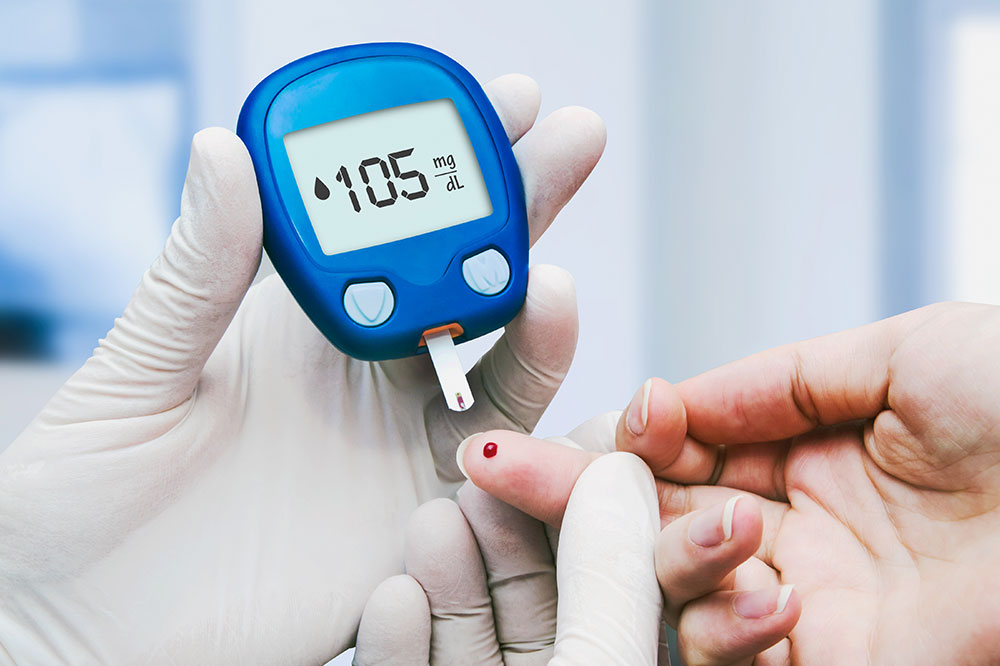
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by the body's inability to produce sufficient insulin or effectively use it, leading to high blood sugar levels. Type 1 diabetes primarily affects young individuals where the immune system destroys pancreatic beta cells. Type 2 diabetes, common among those over 50, involves insulin resistance or reduced insulin production. Persistent high glucose levels can damage vital organs including eyes, kidneys, heart, and skin. Managing blood sugar through lifestyle, medication, and regular check-ups is crucial to prevent severe health issues.
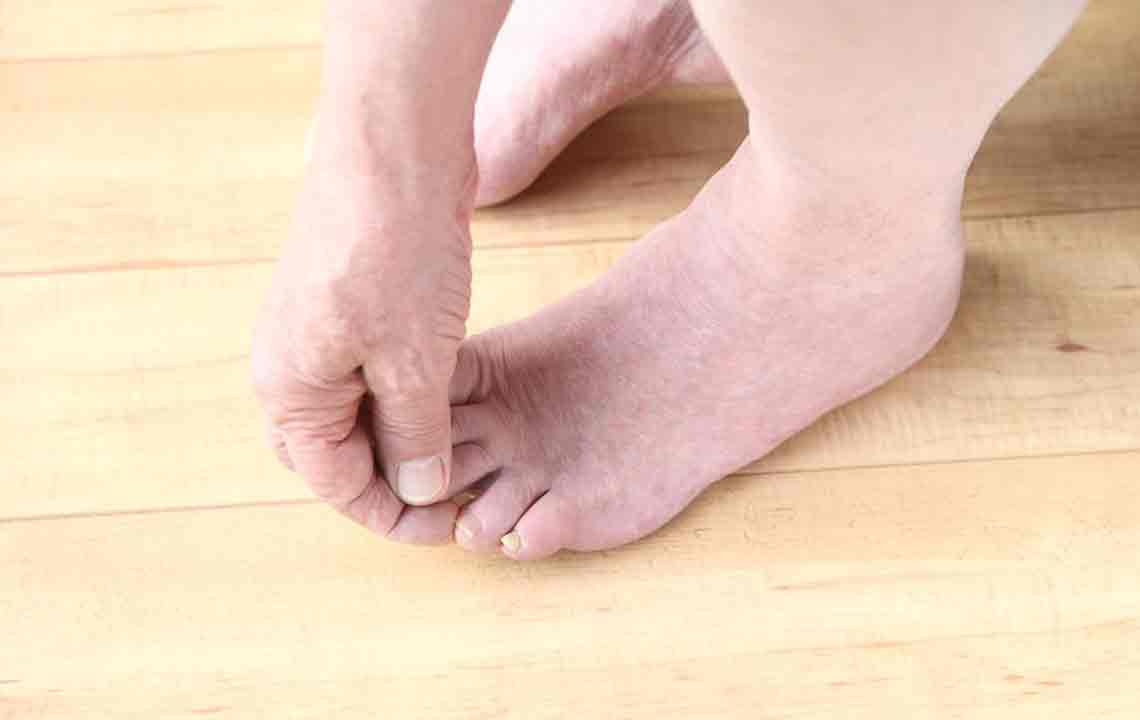
Diabetic foot problems are common consequences of poor circulation. Neuropathy can cause loss of sensation, making injuries unnoticed and increasing infection risks. Foot discoloration, dryness, cracking, and callus formation require regular care. Neglected ulcers, often on the sole or toes, can become severe, risking amputations if untreated. Proper foot hygiene, professional trimming, and wearing suitable footwear help prevent complications. Prompt treatment of ulcers and strict blood sugar control are essential for avoiding limb loss and maintaining mobility in diabetic patients.
Diabetic nerve damage can also lead to skin dryness and peeling, inviting infections. Applying moisturizers like petroleum jelly helps retain moisture, but should be avoided between toes to prevent fungal growth. Calluses develop from pressure areas, particularly in diabetics, and need professional management. Careful trimming, moisturizing, and pressure relief strategies can prevent ulcer formation. Regular foot inspections and immediate diabetes management are vital to avoid serious outcomes like gangrene or tissue loss.
Vascular health is often compromised in diabetics, with fat deposits and artery hardening causing peripheral vascular disease. This reduces blood flow, slowing healing and increasing infection risks. Symptoms include cold extremities, which should be warmed safely with socks and gloves rather than heating devices. Lifestyle modifications such as strict blood sugar regulation, exercise, and quitting smoking can significantly prevent these issues. Maintaining circulatory health is key to avoiding complications and promoting overall well-being.