Effective Strategies for Managing Hypertension
Discover effective lifestyle changes to control hypertension naturally. Learn about diet, exercise, stress management, and avoiding harmful habits to maintain healthy blood pressure levels and reduce cardiovascular risks.
Sponsored
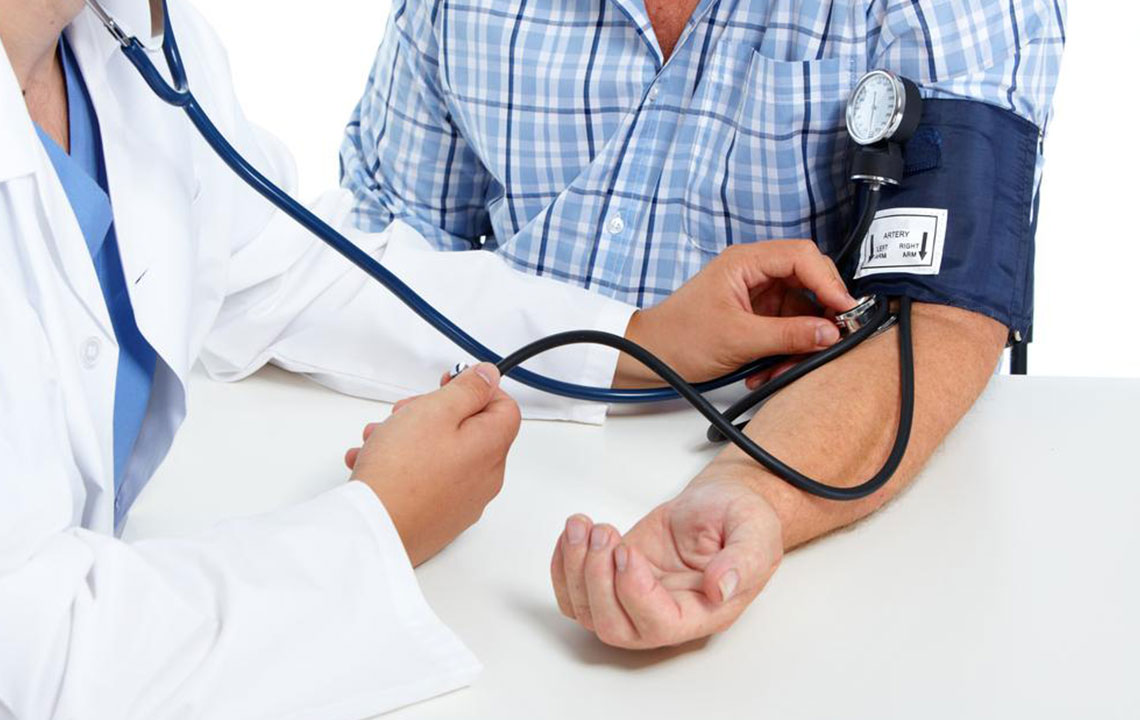
Hypertension, also called high blood pressure, happens when your arteries are under excessive strain. It’s diagnosed when blood pressure readings are consistently above 140/90 mm Hg.
Your blood pressure consists of two numbers: the systolic (the pressure during heartbeats) and diastolic (the pressure when the heart is resting). Elevated levels increase risks of cardiovascular complications.
If you have hypertension, consult your doctor. Besides medication, adopt these lifestyle changes to help lower blood pressure naturally!
Maintain a Healthy Weight and Stay Active
Excess weight strains the heart and raises blood pressure. Regular physical activity like walking, jogging, cycling, and simple aerobic exercises can help shed unwanted pounds and reduce hypertension risk.
Follow a Nutritious Diet
Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and herbs. The DASH diet is highly effective in managing high blood pressure. Focus on increasing potassium intake through natural foods and reducing sodium intake—avoid processed and salty foods, limiting salt to under 1500 mg daily.
Enhance Vitamin Intake
Vitamin C aids in eliminating excess sodium, so include citrus fruits and juices in your diet. Adequate vitamin D levels are also beneficial; consume fortified cereals and sunlight exposure to support good health.
Manage Stress Chronic stress elevates blood pressure. Engage in relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or hobbies that promote mental calmness to maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
Avoid Alcohol, Tobacco, and Excessive Caffeine
Reducing alcohol and quitting smoking can significantly impact blood pressure control. Limit caffeine consumption and monitor your readings regularly. Seek medical advice if you experience persistent hypertension symptoms.