Effective Strategies for Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis and Gout Foot Discomfort
Explore comprehensive treatment options for foot pain caused by rheumatoid arthritis and gout. Learn the differences between these conditions and discover effective strategies, including medications, lifestyle changes, and dietary adjustments, to manage symptoms and prevent joint damage. Consulting healthcare professionals is essential for tailored treatment plans that address both conditions and promote joint health.
Sponsored

Foot pain caused by rheumatoid arthritis and gout is common and often presents similar symptoms. Effective treatment combines medications with lifestyle adjustments. Without proper management, both conditions can lead to irreversible joint damage and impact vital organs like the kidneys and heart. Occasionally, individuals may suffer from both diseases simultaneously. Accurate and timely diagnosis is essential for selecting suitable treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis and gout-related foot pain.
Distinguishing Rheumatoid Arthritis from Gout
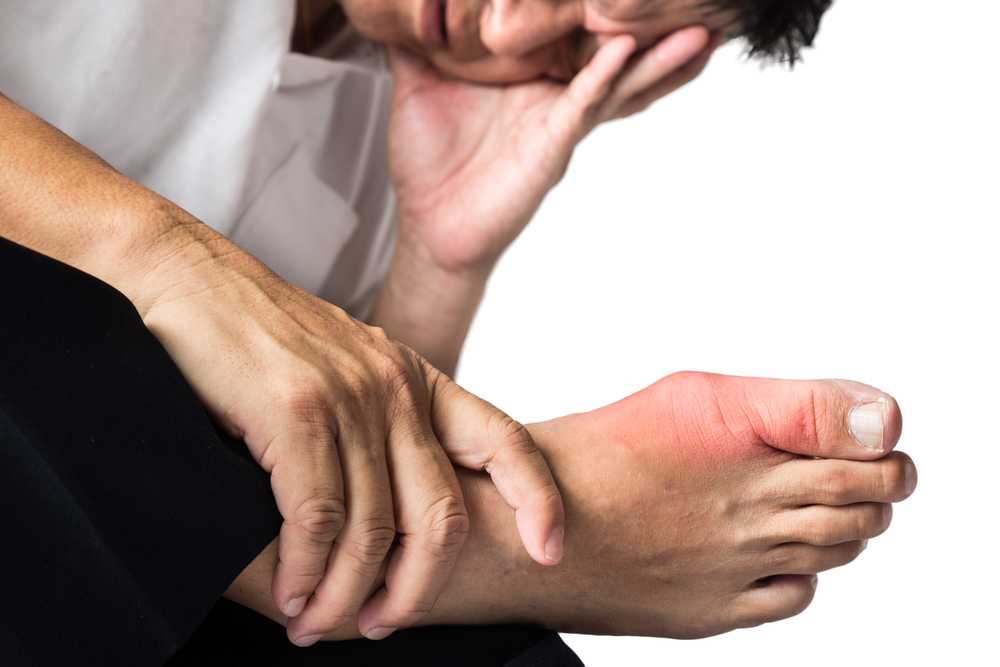
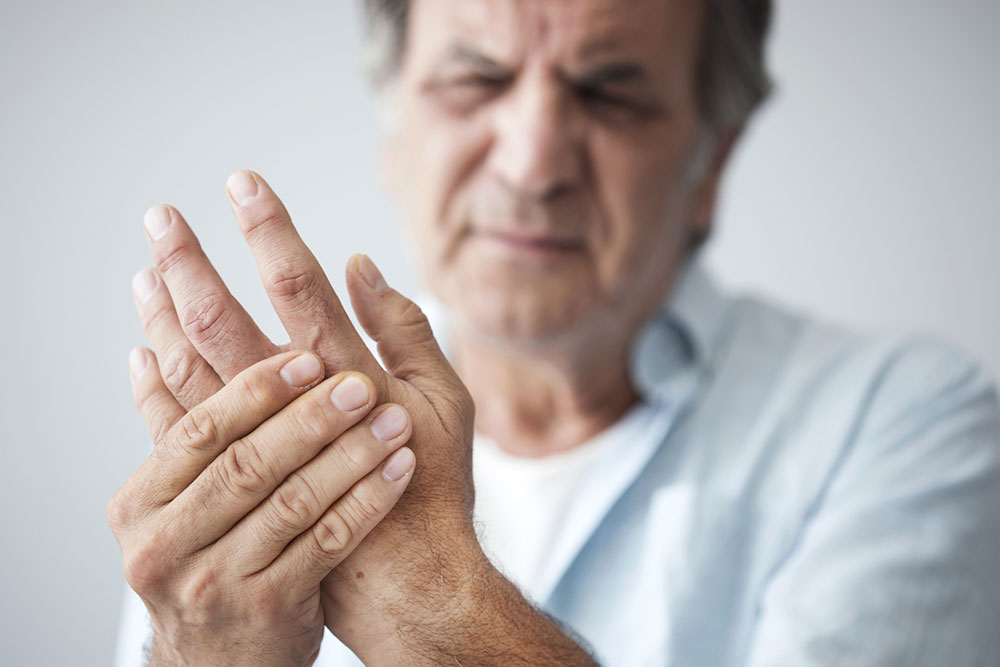
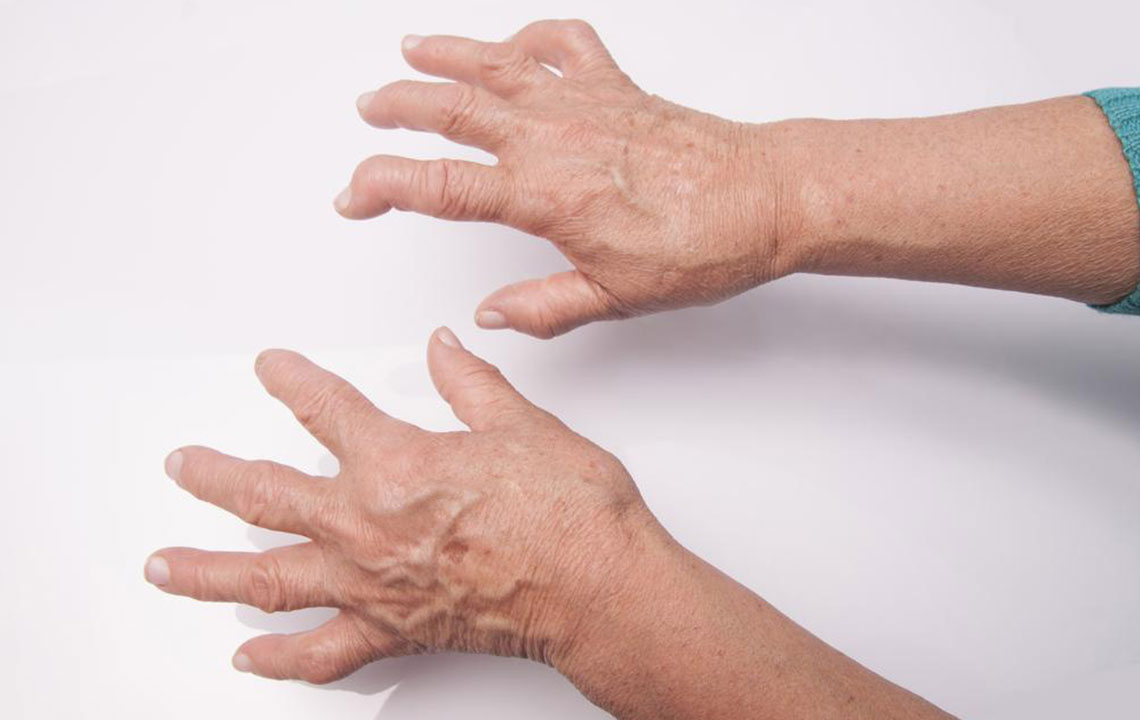
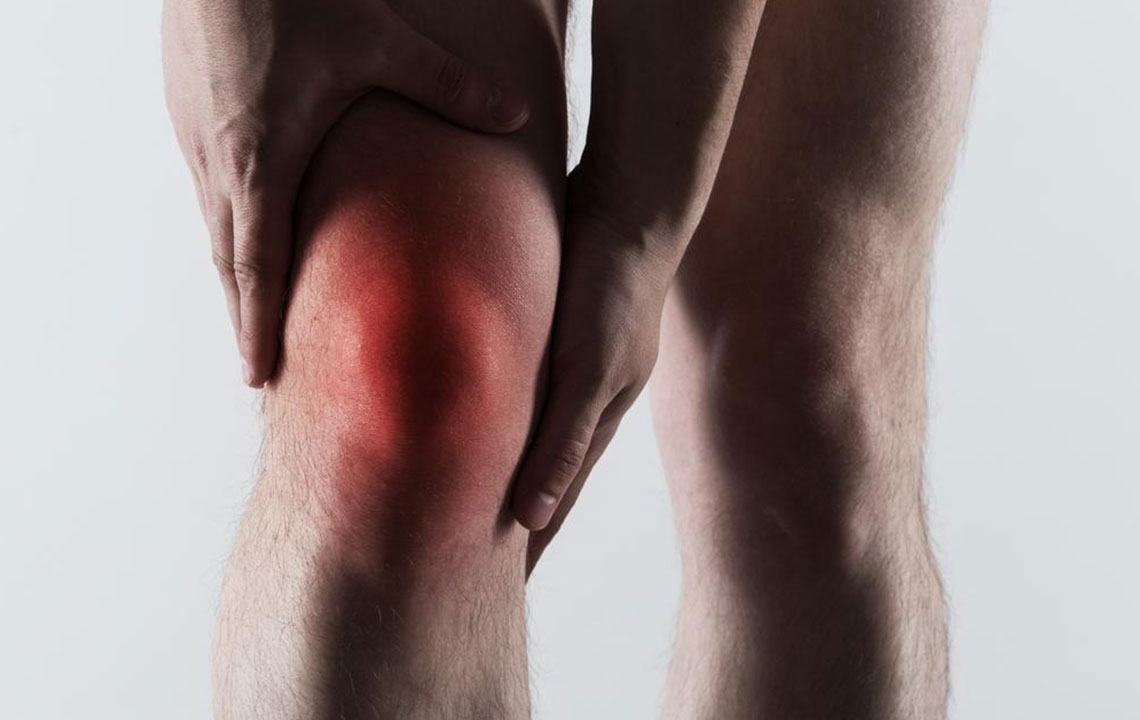
While both affect joints, they differ in symptoms. Rheumatoid arthritis causes joint stiffness and swelling, whereas gout impacts smaller joints, leading to redness and swelling. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that results in synovial fluid thickening, while gout stems from uric acid crystal deposits.
Additionally, rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of cardiovascular issues, whereas gout heightens the risk of kidney disease.
Approaches to Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis and Gout
Managing foot pain from rheumatoid arthritis and gout depends on symptom severity. Treatment options include medications, physical therapy, lifestyle and dietary modifications, and sometimes surgery.
Medications for rheumatoid arthritis include anti-inflammatory drugs and steroids, which slow disease progression, as well as pain relievers that help alleviate discomfort. Physical therapy can improve joint stiffness, and in severe cases, surgical joint replacement may be necessary. For gout, treatment involves pain medication, uric acid blockers, and drugs that aid in uric acid elimination. Dietary adjustments—reducing high-purine foods, sugary treats, and alcohol—along with maintaining a healthy weight, significantly relieve symptoms.
Consultation with a healthcare professional is crucial for individuals suffering from both conditions to determine the most effective treatment plan and prevent further damage.
Those with rheumatoid arthritis should monitor their diet, especially avoiding high-uric-acid foods, to reduce gout risk. Overall, maintaining a balanced diet and healthy weight plays a vital role in managing and preventing both conditions effectively.