Essential Insights into Symptoms and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Discover comprehensive information on rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, risk factors, early signs, and management strategies. Early detection is vital for controlling inflammation, reducing pain, and maintaining joint health. This article provides insights into how RA impacts various organs and outlines effective treatment options including lifestyle changes, medication, and natural remedies. Understanding these symptoms empowers individuals to seek timely medical help and adopt preventive measures for better health outcomes.
Sponsored
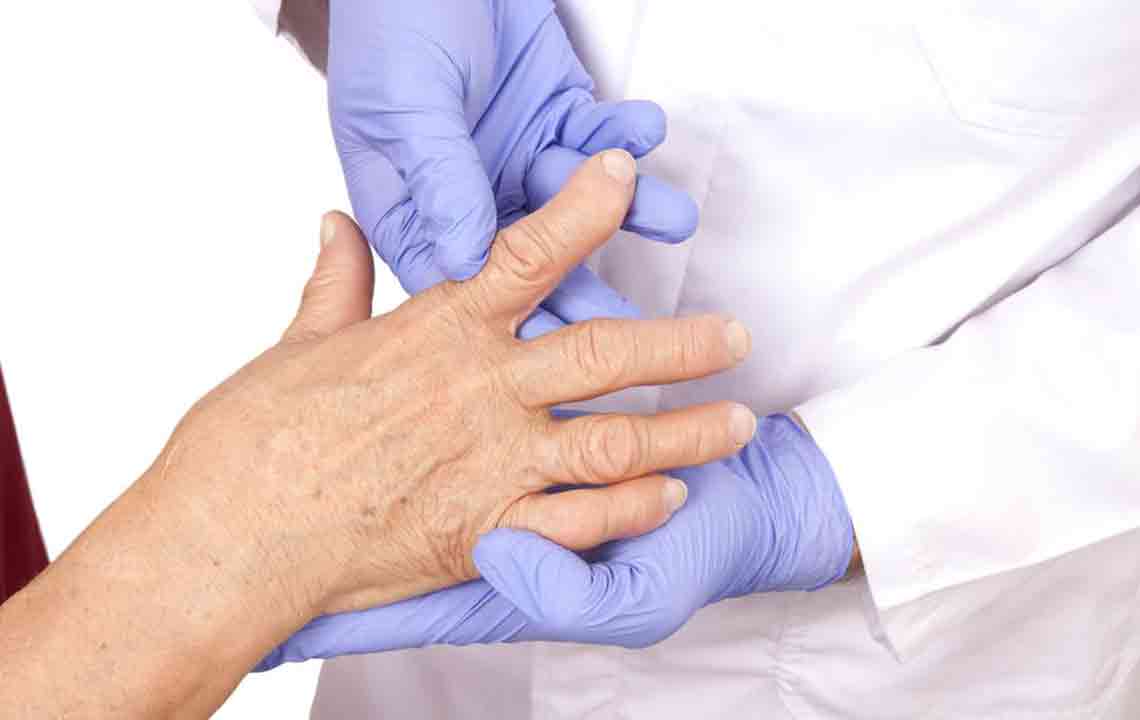
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common autoimmune disorder impacting many individuals worldwide. Often confused with general joint pain, RA specifically involves long-lasting inflammation of the joints. The term 'rheumatoid' originates from 'rheumatism,' encompassing various conditions causing persistent discomfort in muscles and joints.
How does rheumatoid arthritis differ from articular rheumatism?
RA presents as continuous joint pain and swelling, unlike articular rheumatism, which results from structural changes in the joint due to bone growth or tissue shrinkage, affecting joint integrity.
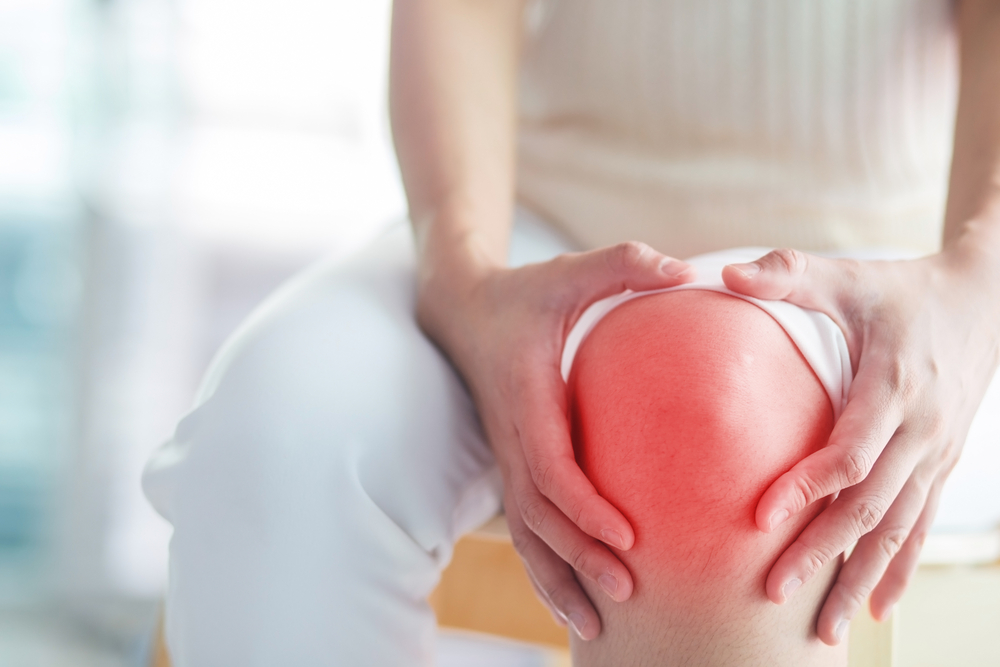
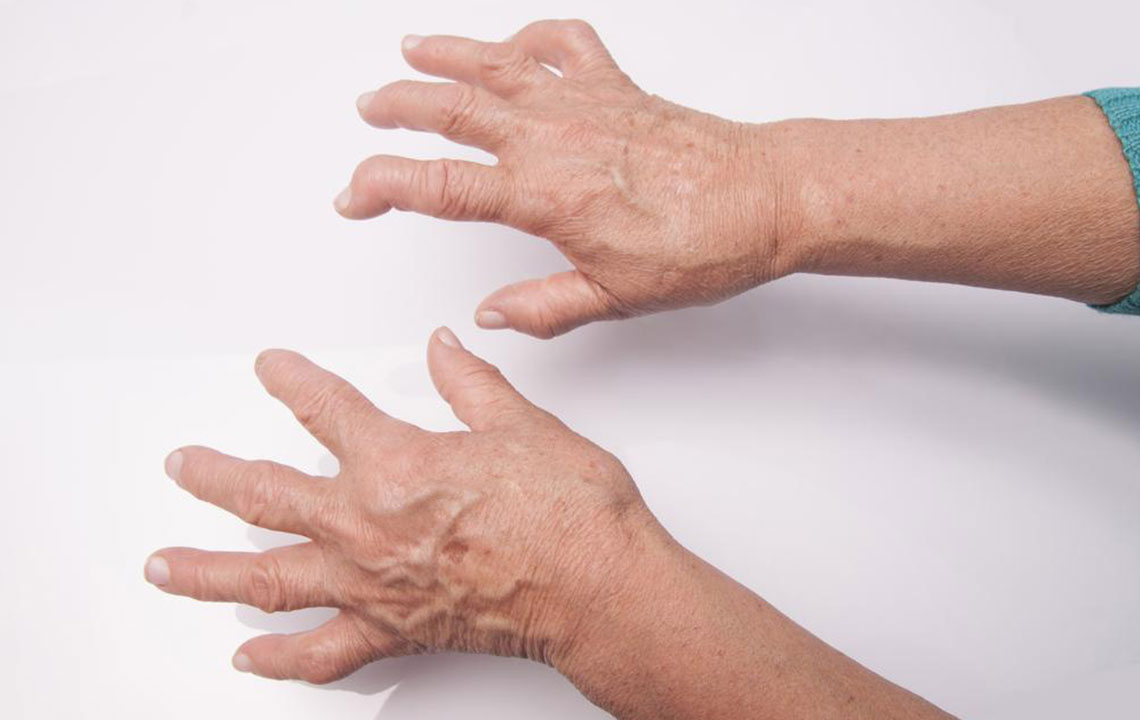
Typically, the soft tissues around joints diminish, leading to tenderness, pain, swelling, and stiffness. Symptoms may also appear in knees, wrists, elbows, hands, feet, and neck, and stiffness often occurs after periods of inactivity or in the morning, gradually subsiding over time.
Who is most at risk for RA?
RA is generally diagnosed in adults aged 30 and above, with higher prevalence among women aged 30 to 60. Men can develop RA too, but women are more commonly affected. The disease targets the inner lining of joints, which can progress to impair movement or cause partial paralysis if untreated. Early detection and management are crucial.
Rheumatoid arthritis mainly causes joint swelling and pain. Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention through medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. Rest, cold or hot compresses, anti-inflammatory diets, and gentle massages can help alleviate symptoms and promote long-term stability. Consistency is key to effective management.
Initial signs of rheumatoid arthritis
Although swelling or redness may not initially be apparent, early symptoms usually include persistent joint pain and tenderness. Common early signs are:
Joint tenderness, stiffness, or swelling lasting over five weeks
Persistent fatigue and low energy levels
Morning stiffness lasting for at least half an hour
Multiple joint pain, especially in small joints like wrists, fingers, and toes
General fatigue, decreased appetite, and mild fever alongside joint discomfort
Effects on other body systems
RA symptoms can fluctuate, with flare-ups increasing inflammation and symptoms over days or months. Severe inflammation may affect organs, including:
Eyes—leading to dryness, redness, pain, and vision issues
Mouth—causing dryness, irritation, or infections
Skin—appearance of rheumatoid nodules or lumps
Lungs—inflammation causing breathlessness
Blood vessels—leading to swelling and potential organ damage
Blood counts—possibly resulting in anemia
Additional rheumatoid arthritis indicators
Symptoms vary among individuals, and diagnosing RA early is challenging without specific tests. Tracking symptoms like weight changes, appetite, swelling, and numbness can aid doctors in early detection. Staying vigilant allows for better management and reduced severity over time.
Lack of appetite
Unexpected weight loss
Fluid accumulation around ankles or knees
Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
Being aware of these signs helps in adopting preventive steps that can lessen pain and improve quality of life.