Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis and Healthcare Providers Involved in Treatment
This article explains rheumatoid arthritis, its causes, symptoms, complications, and the various healthcare professionals involved in diagnosis and treatment. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and knowing when to consult specialists like rheumatologists, orthopedic surgeons, physiotherapists, and occupational therapists for optimal management of this autoimmune condition.
Sponsored
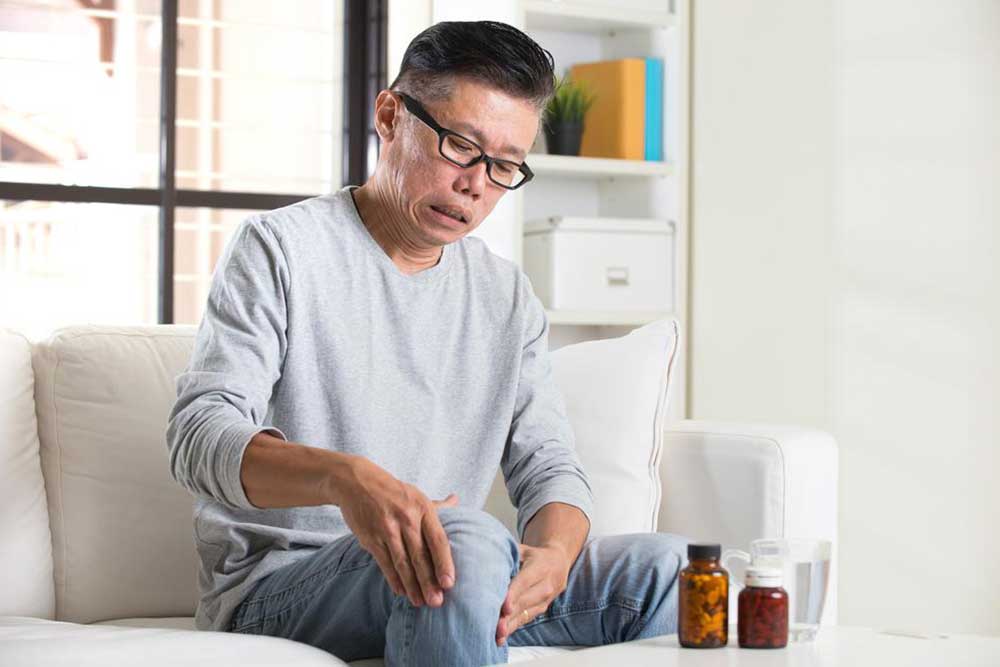
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes joint inflammation, potentially affecting multiple body parts beyond just the joints. This condition arises when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. The exact cause remains uncertain, but factors like infections from bacteria, fungi, or viruses, along with genetic predisposition and lifestyle habits such as smoking, are believed to influence its development.
Complications include damage to internal organs, eye dryness, vision problems, and lung inflammation, which can result in breathing issues. A major concern is the increased risk of cardiovascular events. Symptoms fluctuate; during inactive phases, signs may diminish, making diagnosis challenging. Common symptoms include stiffness, fatigue, and loss of appetite, which vary among individuals and children. Diagnosis involves multiple tests assessing joint inflammation and swelling.
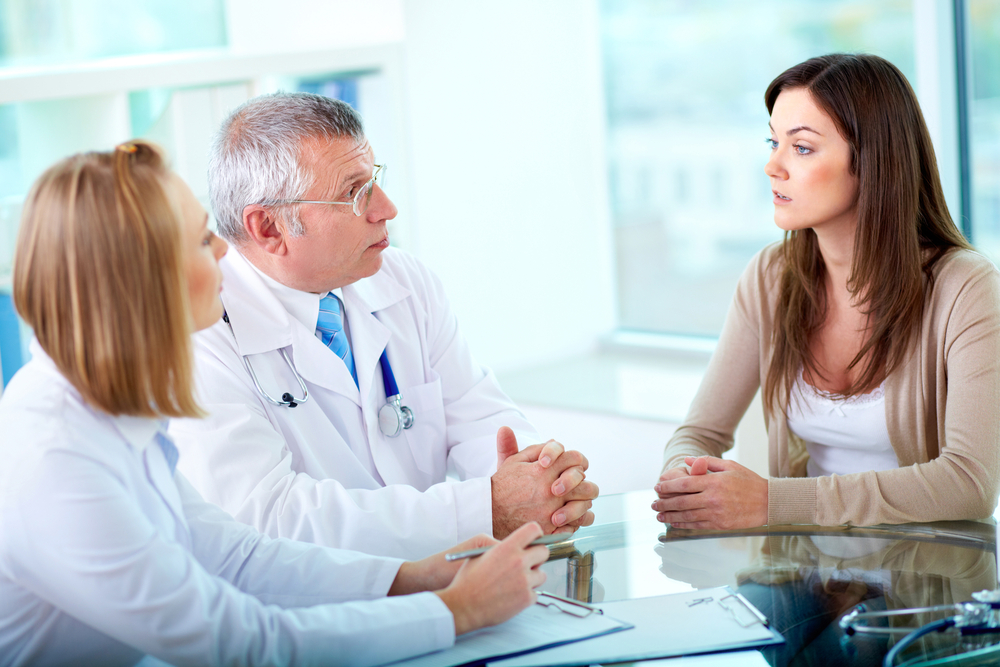
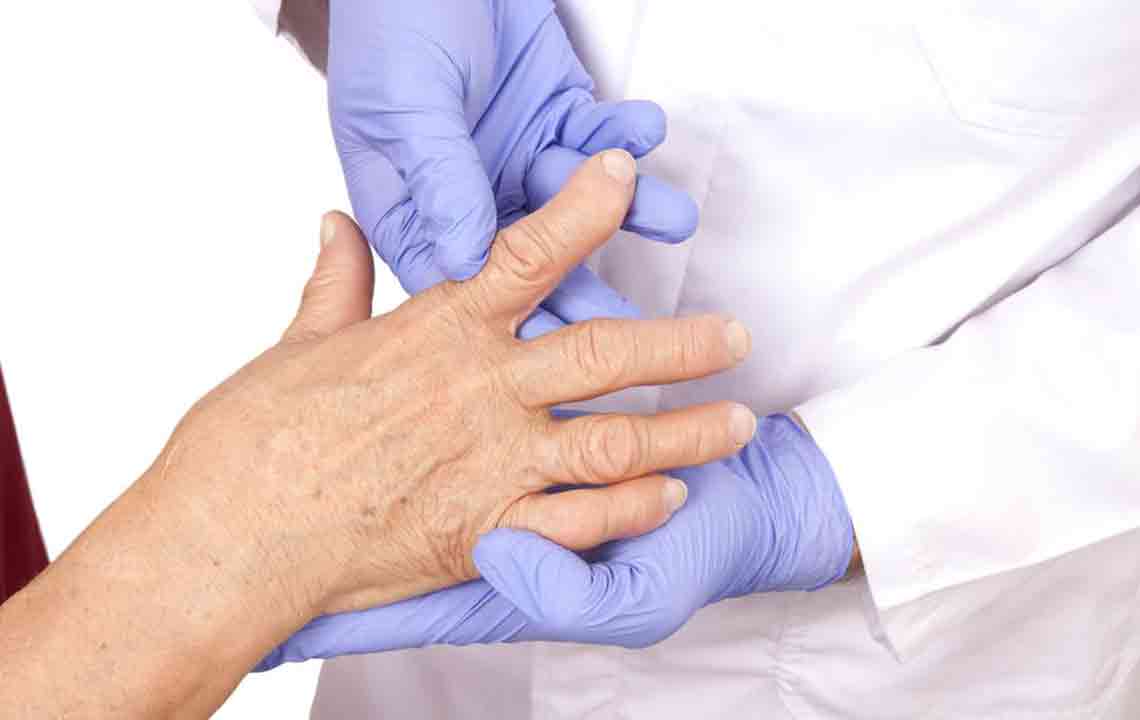
Choosing the right healthcare provider is crucial. A family doctor is typically the first point of contact, capable of initial assessment and referring patients to specialists. Orthopedic surgeons focus on joint and bone surgeries when needed. Rheumatologists are specialized in managing autoimmune joint diseases and tailoring treatment plans. Physiotherapists help improve joint mobility and reduce pain through targeted exercises. Occupational therapists assist patients in performing daily activities comfortably despite mobility challenges. Providing comprehensive symptom details aids in accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.