Comprehensive Guide to Inflammatory Joint Disease
This comprehensive guide covers all aspects of inflammatory arthritis, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and lifestyle tips. Understanding this autoimmune condition can help manage symptoms, prevent progression, and improve quality of life through medical treatment and healthy habits.
Sponsored
Your Complete Overview of Inflammatory Arthritis
Arthritis is a long-term condition characterized by joint pain and swelling, affecting over a million individuals nationwide. It includes two primary types: inflammatory and non-inflammatory. Inflammatory arthritis is less common but critical to understand due to its distinctive causes, symptoms, and treatments. This article explores inflammatory arthritis, its causes, signs, diagnosis, treatment options, and lifestyle adjustments to manage the condition effectively.
What is Inflammatory Arthritis?
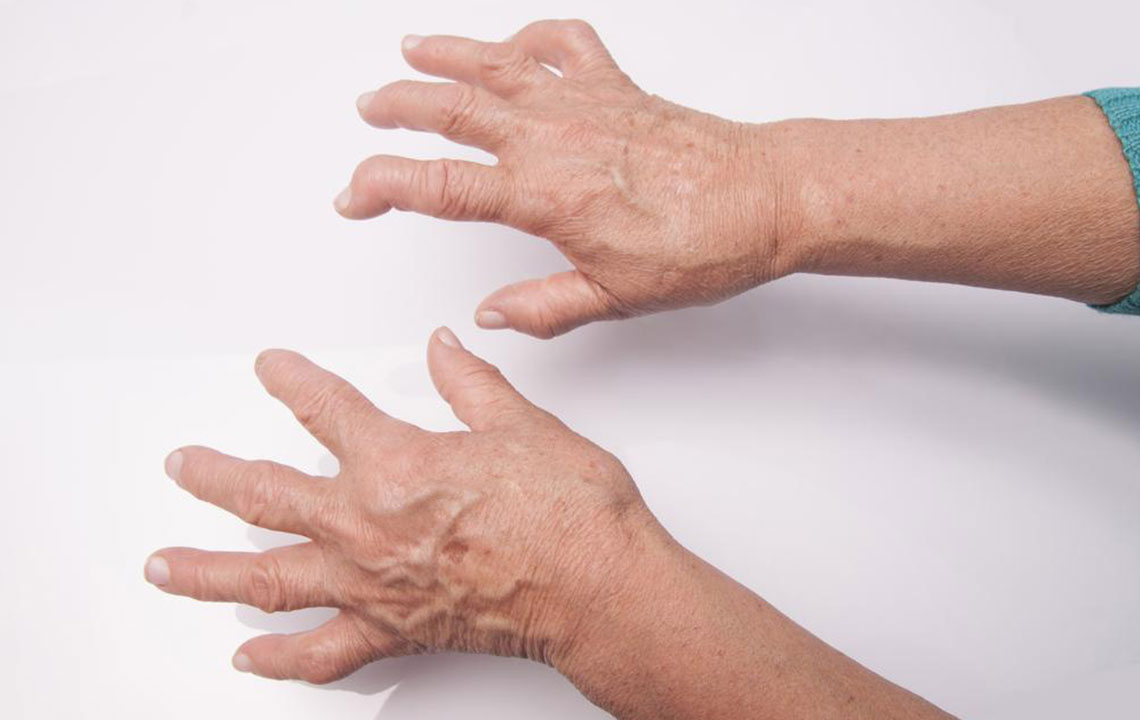
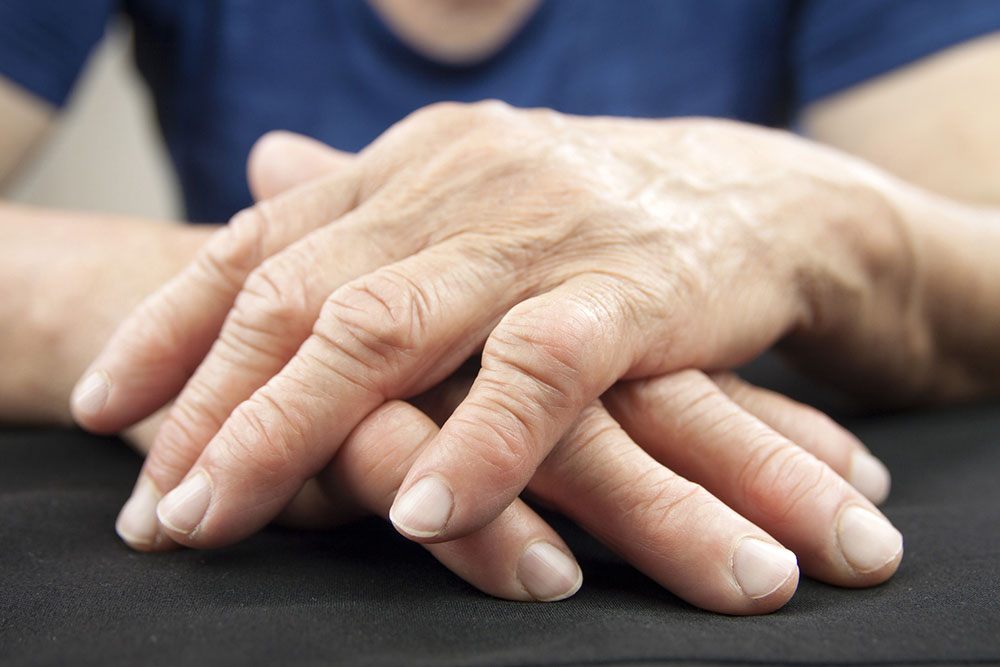
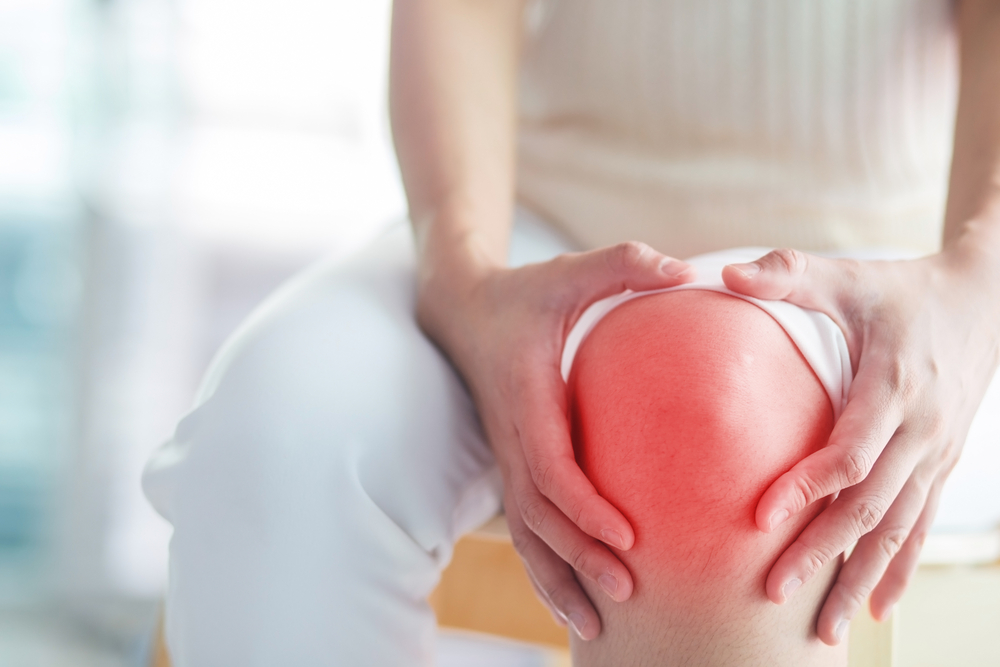
An autoimmune disease, inflammatory arthritis encompasses conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and others. It results in inflammation of joints and nearby tissues. Women are more susceptible, though the exact reasons remain unclear. Commonly affected areas include the wrists, knees, elbows, ankles, feet, and hands.
Types of Inflammatory Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Ankylosing spondylitis
Gouty arthritis
Causes of Inflammatory Arthritis
The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues, leading to inflammation. Contributing factors include:
Genetic predisposition
Infections
Chronic stress
Tobacco use
Gender (more common in women)
Obesity
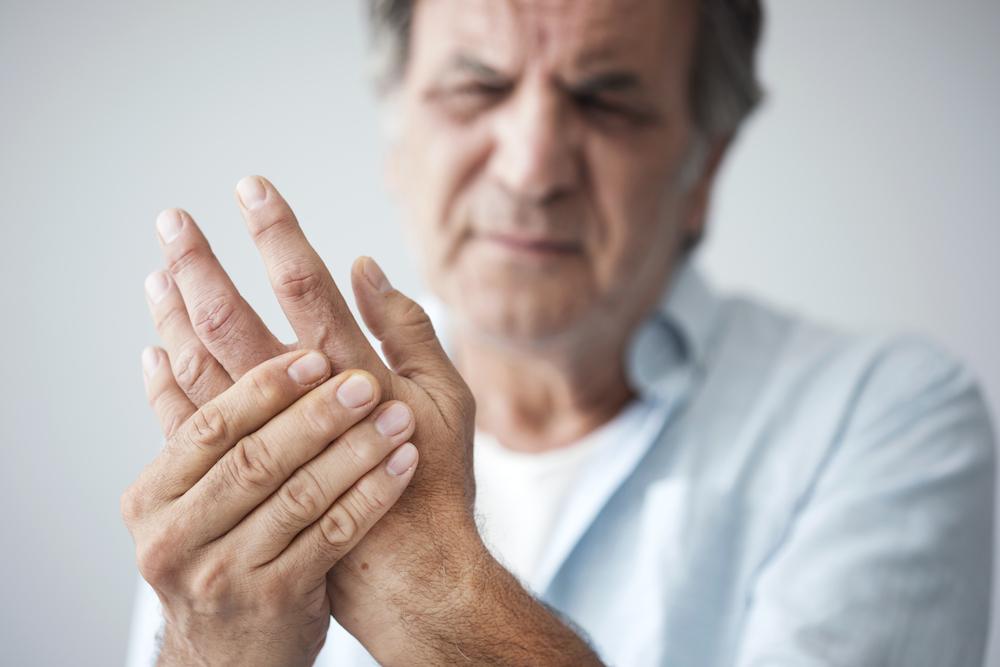
Recognizing Symptoms of Inflammatory Arthritis
Symptoms include:
Swelling around affected joints
Extended joint stiffness
Persistent fatigue
Some forms may also cause skin rashes, hair loss, eye inflammation, fever, and other systemic issues.
Diagnosis Methods for Inflammatory Arthritis
Medical professionals utilize various tests for accurate diagnosis, such as:
Blood analysis
MRI scans
X-rays
Synovial fluid examination
Urinalysis
CT scans
Ultrasound imaging
Medical Approaches to Managing Symptoms
While there’s no cure, treatments aim to reduce pain, control inflammation, and prevent joint damage. Common medications include:
NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, ketoprofen) for pain and inflammation relief
Corticosteroids for rapid swelling reduction
DMARDs (Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs) to slow disease progression
In severe cases with joint damage, surgical options such as joint replacement may be considered, involving replacing damaged joints with artificial components.
Dietary Strategies to Combat Inflammation
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods can help manage symptoms. Recommended foods include:
Fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel
Cheries and berries
Whole grains
Extra virgin olive oil
Green tea
Cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and spinach
Soy-based products
Avocados
Vitamin C-rich fruits like kiwis, oranges, and strawberries
Garlic and turmeric supplements
Lifestyle Modifications to Ease Symptoms
To support joint health, consider:
Quitting smoking
Limiting alcohol intake or abstaining
Ensuring adequate sleep
Engaging in low-impact daily exercises such as swimming or walking