Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies
Rheumatoid arthritis is a lifelong autoimmune disorder causing joint inflammation, pain, and mobility issues. Early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, lifestyle adjustments, medications, and occasionally surgery are vital for managing symptoms effectively. Regular checkups and honest communication with healthcare providers enhance treatment success and improve quality of life.
Sponsored
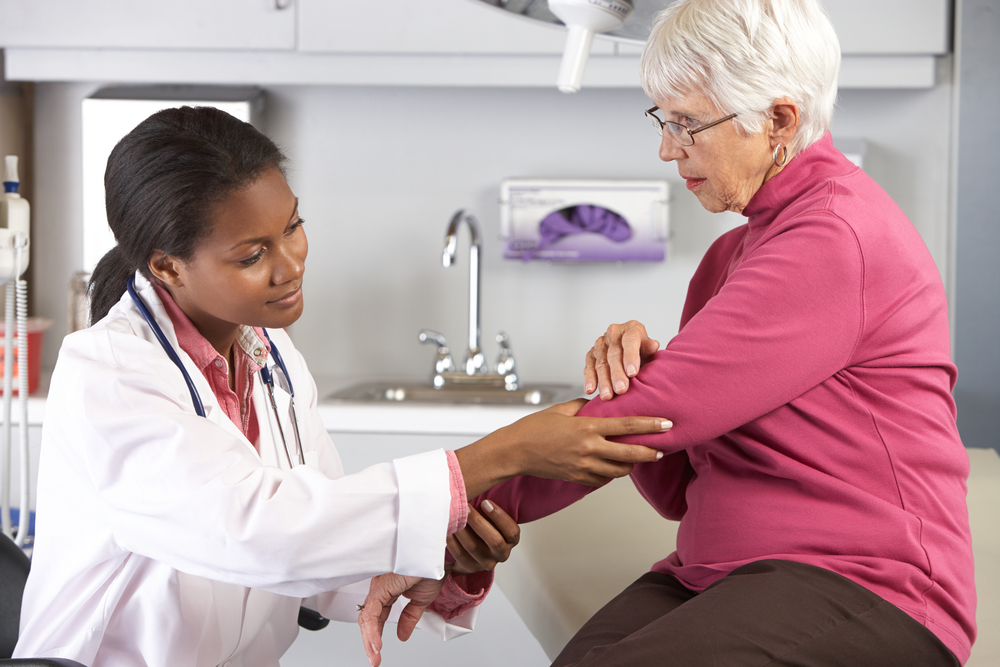
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing swelling, pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. The condition arises from an autoimmune response where the immune system mistakenly attacks the joint linings instead of protecting the body. Early consultation with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans. The disease varies in severity and presentation, often persisting for life. Proper management involves medication, lifestyle adjustments, and sometimes surgery to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Diagnosing RA
Symptoms differ among individuals, ranging from mild discomfort to severe joint damage. Recognizing these signs early allows for timely treatment. Diagnosis involves a combination of physical examinations, blood tests, and imaging techniques to confirm RA and assess its progression.
As a lifelong condition for many, RA's symptoms may fluctuate, with periods of flare-ups and remission. To determine the best treatment plan, healthcare providers consider individual health status and the severity of symptoms. Effective management relies heavily on open communication with your doctor, detailed record-keeping of symptoms, and regular health checkups.
Lifestyle changes can significantly improve symptoms. Finding a balance between rest and activity helps reduce joint pain and fatigue. Using supportive devices like splints can protect joints, while stress reduction techniques can improve emotional well-being. A nutritious diet rich in proteins and calcium supports joint health. Medications such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and DMARDs remain key to symptom control. Biologic agents like infliximab and adalimumab target specific immune responses to reduce inflammation. In severe cases, surgical options like joint replacement offer pain relief and restored mobility. Consulting your doctor is essential before considering any treatment to ensure it suits your condition and health profile.