Understanding Rotavirus: Symptoms, Transmission, and Prevention
Rotavirus is a contagious virus causing gastrointestinal inflammation, leading to symptoms like fever, vomiting, and diarrhea in children. Transmission occurs through fecal-oral contact, with surfaces and hands playing a key role. Preventative measures, including vaccination and proper hygiene, are essential to reduce infection risk and protect young children from severe dehydration and complications.
Sponsored
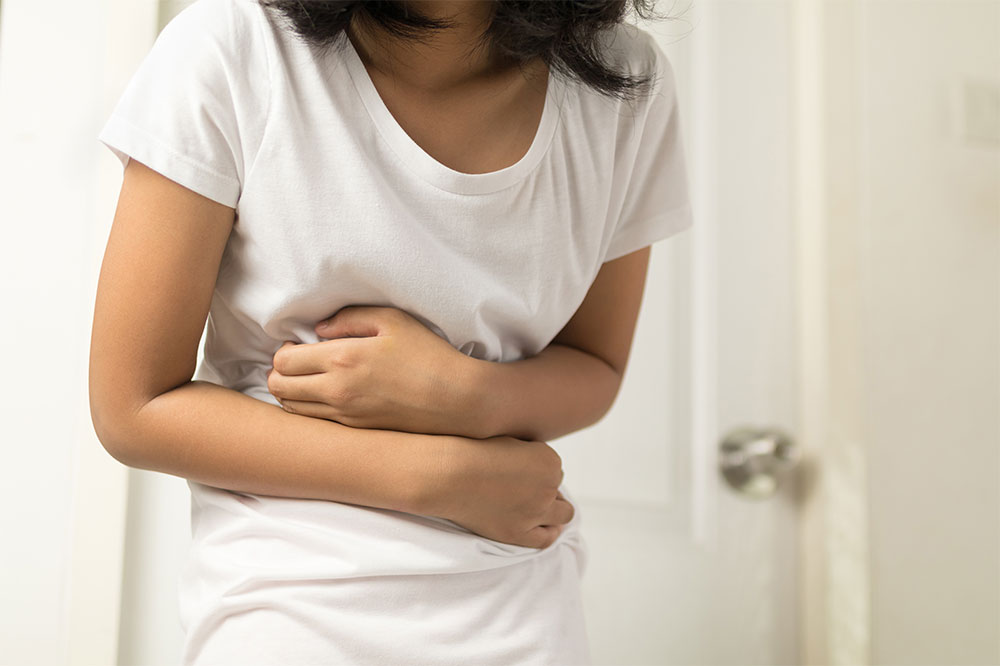

Rotavirus is a highly contagious virus responsible for causing inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. It is a leading cause of diarrhea among children worldwide. While there is no definitive cure, supportive treatments can help alleviate symptoms. Recognizing the signs of rotavirus infection promptly is essential for timely management.
This article explores the symptoms, transmission pathways, and effective prevention strategies for rotavirus.
Symptoms
The onset of symptoms typically occurs about two days after initial exposure, with manifestations lasting up to a week.
Fever and Vomiting
High fever and vomiting are common within the first three days. These symptoms often diminish by the fourth day.
Dehydration Risk
Infants and young children may develop severe dehydration, indicated by irritability, decreased urine output, lethargy, and refusal to drink fluids. Immediate medical attention is advised if these signs appear.
Watery Diarrhea
Following initial symptoms, watery diarrhea may persist for up to seven days, often accompanied by abdominal discomfort.
Stomach Pain
Stomach cramps commonly occur with diarrhea but tend to resolve within a few days.
Causes of Rotavirus
The virus primarily spreads through fecal-oral contact. Infected stool can contain the virus for up to two days before symptoms show. Poor hygiene, including not washing hands after bathroom visits or diaper changes, facilitates transmission. Surfaces contaminated with the virus can harbor it for months. Even vaccinated individuals can contract the virus, making preventive measures vital.
Prevention Strategies
Practicing thorough hand hygiene after bathroom use is crucial. Vaccination with RotaTeq and Rotarix is highly effective, especially when administered during childhood. These vaccines significantly reduce the risk of severe illness and complications.