Understanding Herpes Zoster: Symptoms, Risks, and Prevention
Herpes Zoster, or shingles, affects millions and can cause painful rashes and serious health issues. Recognizing early symptoms, especially via rash images, is vital for prompt treatment. Vaccination and immune support are key preventive measures. The article details the causes, symptoms, risks, and prevention strategies for shingles, emphasizing early detection and medical intervention to avoid complications.
Sponsored

Herpes Zoster – A Comprehensive Overview
Herpes Zoster, commonly known as shingles, is a prevalent condition affecting millions worldwide. Characterized by a painful skin rash, shingles can last for weeks and sometimes lead to serious complications. The severity of symptoms varies depending on individual immunity, age, and health conditions. Recognizing the signs early is essential for effective management and reducing complications.
Shingles results from reactivation of the Varicella-zoster virus, the same virus responsible for chickenpox. After initial infection, the virus remains dormant in nerve tissues and can be triggered by stress, weakened immunity, or illness.
The virus doesn't cause chickenpox again after the initial infection but can reactivate later in life.
Factors like stress, aging, and diseases can activate the dormant virus, leading to shingles outbreaks.
Weaker immune defenses, stress, and other health issues are common triggers for shingles.
Once triggered, the virus causes the characteristic skin rash and nerve pain.
Is herpes zoster a serious health concern?
If untreated, shingles can lead to complications like postherpetic neuralgia, vision problems, and even stroke in some cases.
Older adults are at heightened risk of severe symptoms, including nerve damage and skin infections.
The condition may also contribute to cardiovascular issues by promoting arterial plaque buildup.
Stress not only triggers shingles but can also worsen symptoms by elevating blood pressure.
While it mainly affects adults over 50, children with weakened immunity are also susceptible.
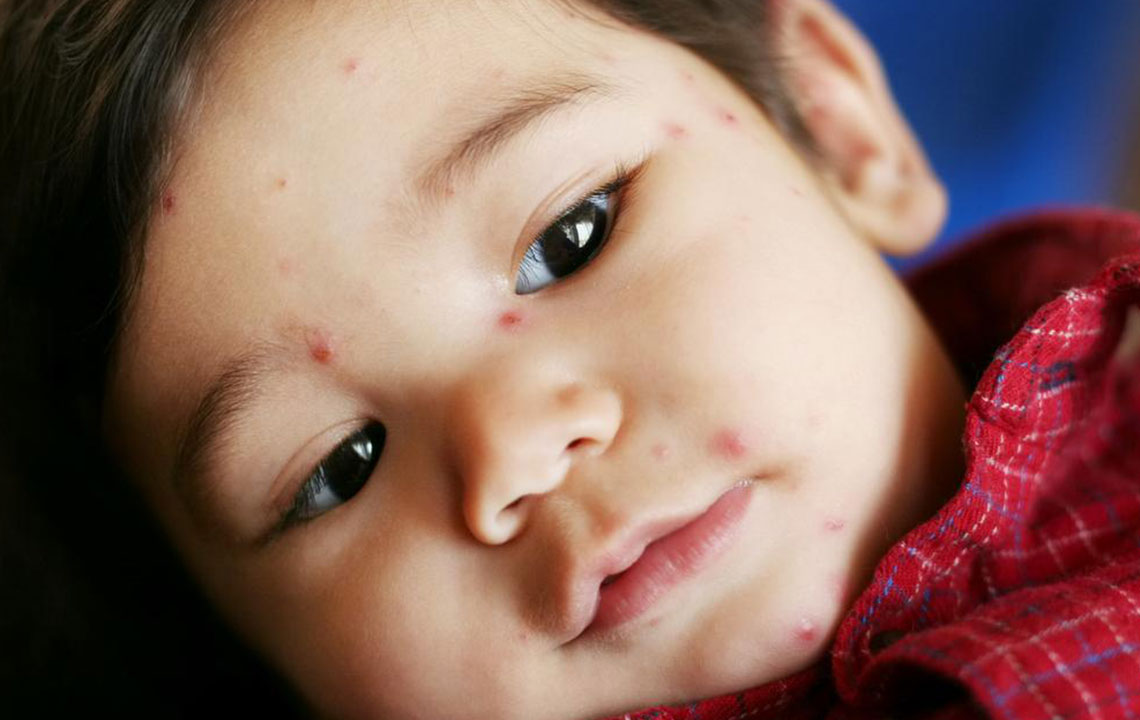
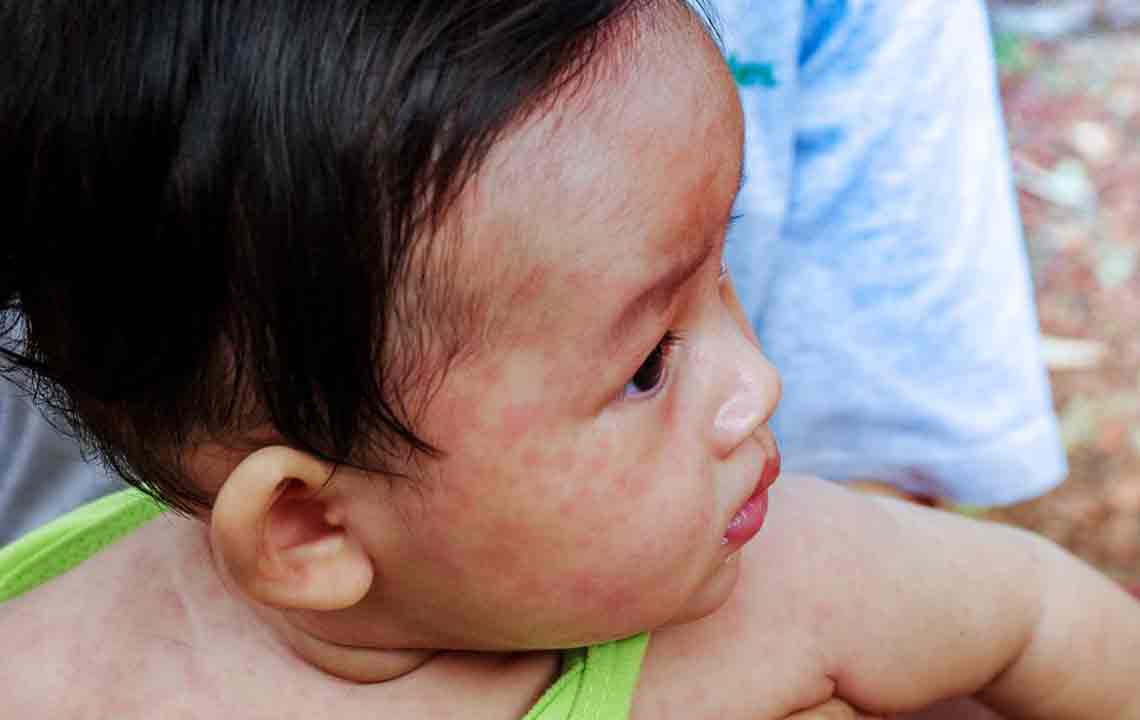
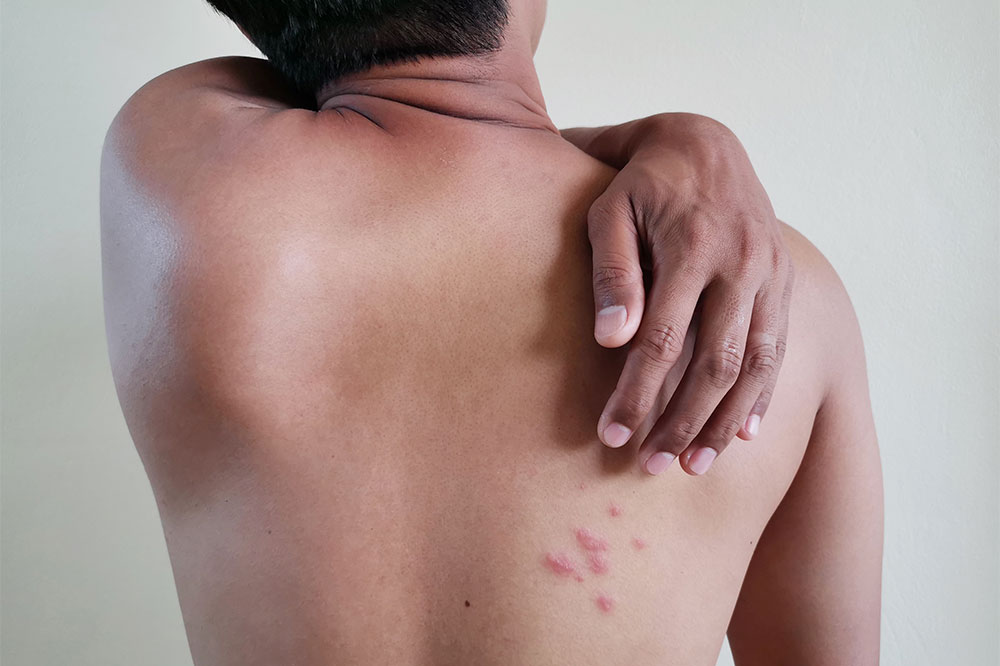
Recognizing shingles: Visual cues and rash identification
Symptoms are often subtle initially; headaches and fever may precede rash appearance.
As the rash develops, individuals might experience light sensitivity, weakness, and dizziness.
Shingles rash appears as distinctive blisters on one side of the body, typically on the torso, which can be confirmed by online rash reference images.
Itching, mild touch sensitivity, burning sensations, numbness, and tingling are common early signs.
More severe symptoms include intense burning pain and skin discomfort around the blisters.
Can visual cues help determine severity via rash images?
Reviewing shingles rash photos can assist in assessing the condition’s progression and severity.
Many online resources provide free images illustrating different stages for comparison.
Prompt medical consultation is essential once shingles is suspected.
Is there a cure for herpes zoster?
Currently, there is no definitive cure, but antiviral medications effectively reduce symptoms and duration if administered early.
Vaccinations can lower incidence, especially in adults over 50, and help prevent recurrence.
Timely vaccination is highly recommended for at-risk populations to minimize outbreaks.
Preventive strategies for herpes zoster
The CDC estimates nearly a third of individuals will develop shingles, primarily those who previously had chickenpox.
Strengthening the immune system through healthy lifestyle choices is key to prevention.
Vaccination offers significant protection and reduces pain and discomfort from outbreaks.
Individuals who have already had chickenpox are not contagious but can still develop shingles.