Understanding Sjogren’s Syndrome: Causes and Signs
Sjogren’s syndrome is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by dry eyes, dry mouth, and gland swelling. Though its exact cause is unknown, infections may trigger the disorder. Managing symptoms with proper treatment can help improve quality of life for affected individuals. Awareness of symptoms and early diagnosis are key to effective management of this lifelong condition.
Sponsored
Advances in medicine have fueled hopes of curing even the most challenging illnesses. Recognizing the root causes of diseases is crucial for developing effective treatments. While many conditions still lack clear explanations, managing long-term illnesses is possible through various strategies. Sjogren’s syndrome is one such chronic disorder requiring patients to learn to live with it.
What is Sjogren’s Syndrome?
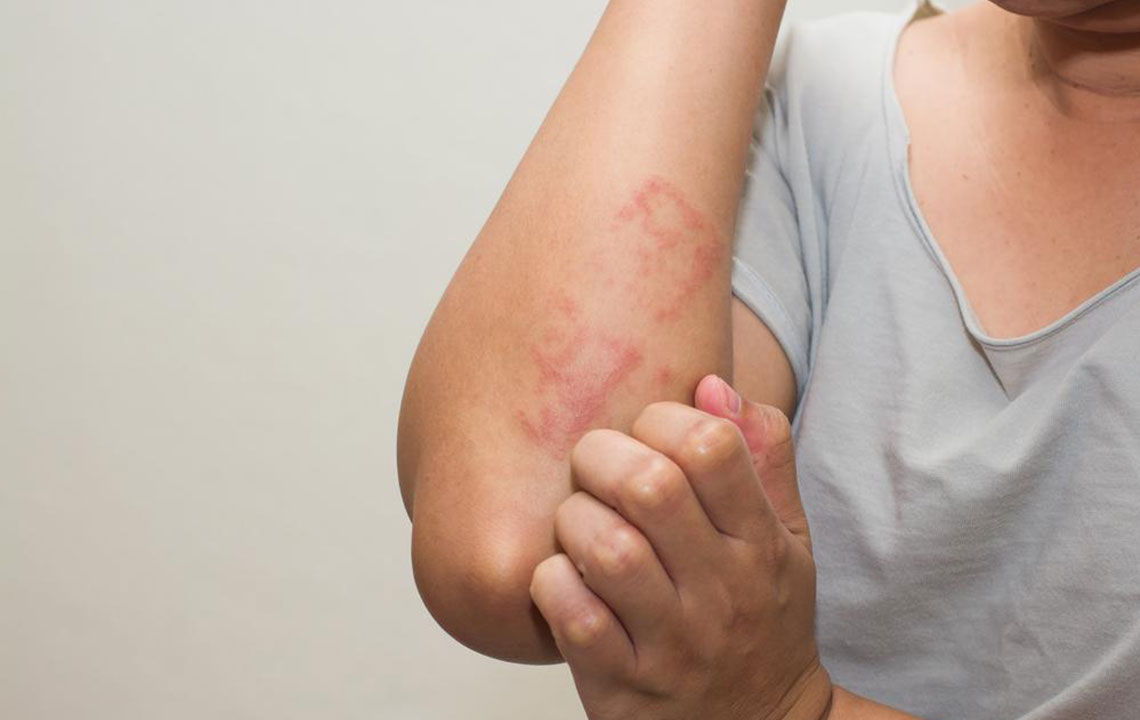
Sjogren’s syndrome is an autoimmune condition where the immune system malfunctions and starts attacking the body's healthy tissues instead of harmful pathogens. It’s a lifelong condition, and while a complete cure remains elusive, patients can adopt measures to manage symptoms effectively. Often, Sjogren’s occurs alongside other autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
What causes Sjogren’s Syndrome?
Although the exact cause remains unknown, environmental triggers such as infections with certain bacteria or viruses may initiate this immune response.
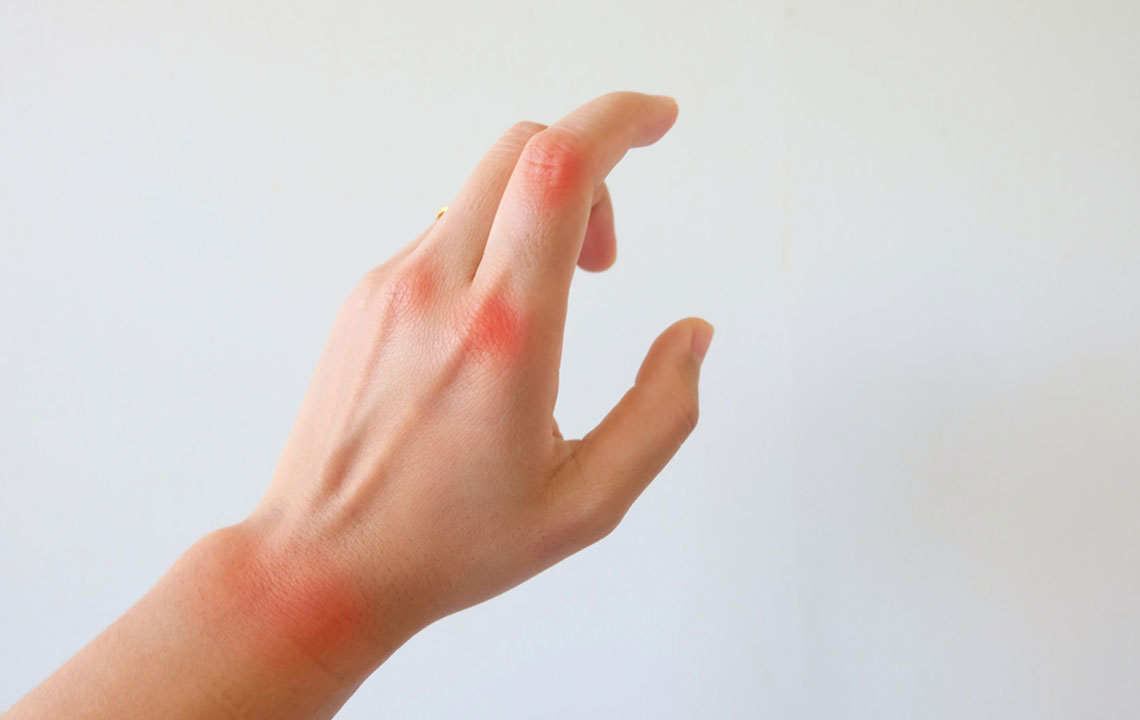
This disorder hampers immune regulation, leading white blood cells to target healthy glands, particularly those responsible for saliva and tears. Symptoms intensify without proper treatment, though the cause is still under investigation.
What are the common symptoms?
One primary symptom is dry mouth due to decreased saliva production, causing discomfort, difficulty chewing or swallowing, and increased risk of oral infections like thrush.
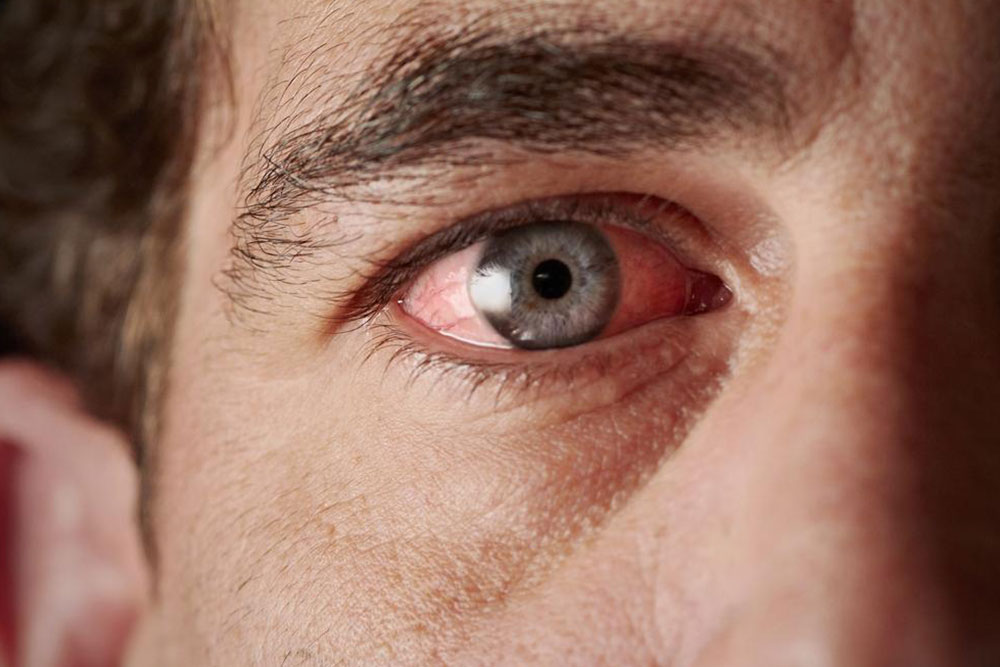
Dry eyes are also typical, resulting in burning, itching, and potential vision issues if untreated. Eye drops and medications help manage these symptoms.
Sjogren’s can affect other areas like the throat, skin, lips, and nose, and cause swelling in facial or neck glands due to immune activity.