Understanding Swollen Neck Lymph Nodes: Causes and Detection
This article explores the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis of swollen lymph nodes in the neck. It highlights common and rare reasons for swelling, when to seek medical help, and the diagnostic procedures used to determine the underlying cause. Understanding lymph node health is vital for early detection and effective treatment of underlying conditions, including infections and cancers.
Sponsored

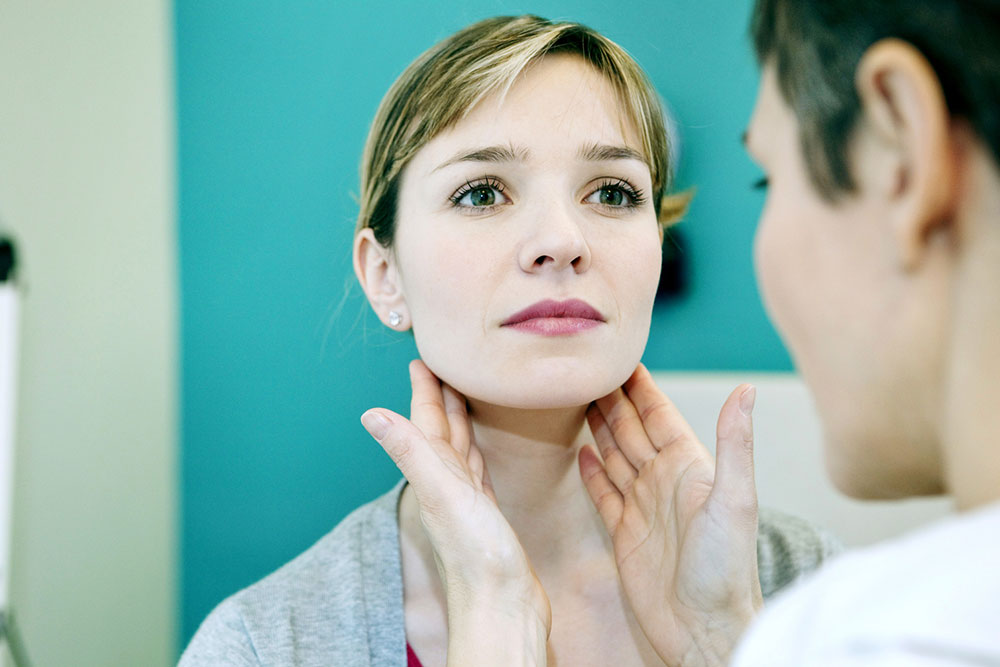
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck often indicate your body's response to infection or illness. Typically, these swellings diminish once the underlying issue resolves. Interestingly, these enlarged glands are actually lymph nodes, vital components of the lymphatic system that play a crucial role in maintaining overall health.
Here's essential information about swollen neck lymph nodes you should know.
Why do lymph nodes become enlarged?
These nodes are small, round, and bean-shaped, containing immune cells called lymphocytes that combat bacteria, viruses, and foreign invaders.
When these immune cells engage pathogens, the lymph nodes respond by swelling, a natural defense mechanism.
Common infections like colds or ear infections can lead to noticeable swelling of these glands.
Rare causes of lymph node swelling include:
Some uncommon reasons include:
Tuberculosis, which affects the lungs, can also cause neck lymph nodes to enlarge.
Autoimmune conditions like lupus may result in swollen lymph nodes.
Cancers such as lymphoma (a cancer of the lymphatic system) and leukemia (a blood cancer) can also be behind persistent swelling.
When should you consult a healthcare professional?
While most swollen glands resolve with infection treatment, seek medical attention if:
The swelling appears suddenly without gradual development.
The glands are excessively large or hard and immovable.
Swelling persists beyond five days in children or two to four weeks in adults.
The area around the swelling turns red or purple.
You experience symptoms like unexplained weight loss, swelling in other areas, or night sweats.
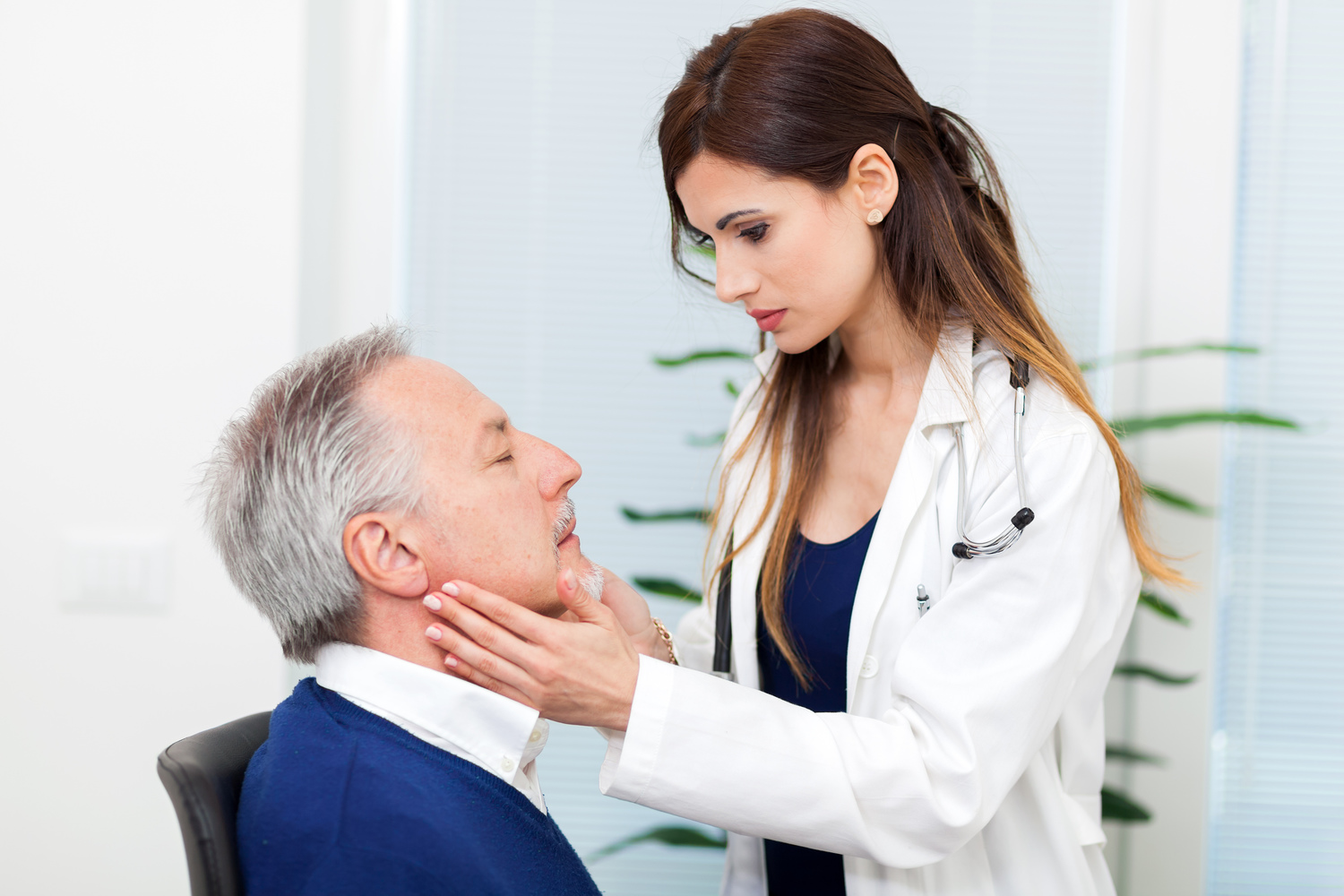
Diagnosis methods for swollen lymph nodes
Proper evaluation involves several tests:
PET scan — detects chemical activity and changes within the body, helping identify infections, cancers, or other conditions.
CT scan — provides detailed cross-sectional images of the body to assess the extent of swelling.
Biopsy — involves extracting a lymph node for microscopic examination to determine the cause.
Based on findings, treatment options can include antibiotics, radiation therapy, or surgical removal.