Understanding and Managing Enlarged Neck Lymph Nodes
This article explains the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for swollen lymph nodes in the neck. It highlights the importance of proper medical evaluation to determine whether the swelling results from infections, immune conditions, or rare cancer cases. Treatment varies based on the underlying issue, including antibiotics, immune management, or cancer therapies. Early consultation with a healthcare professional is essential to ensure appropriate care and recovery.
Sponsored
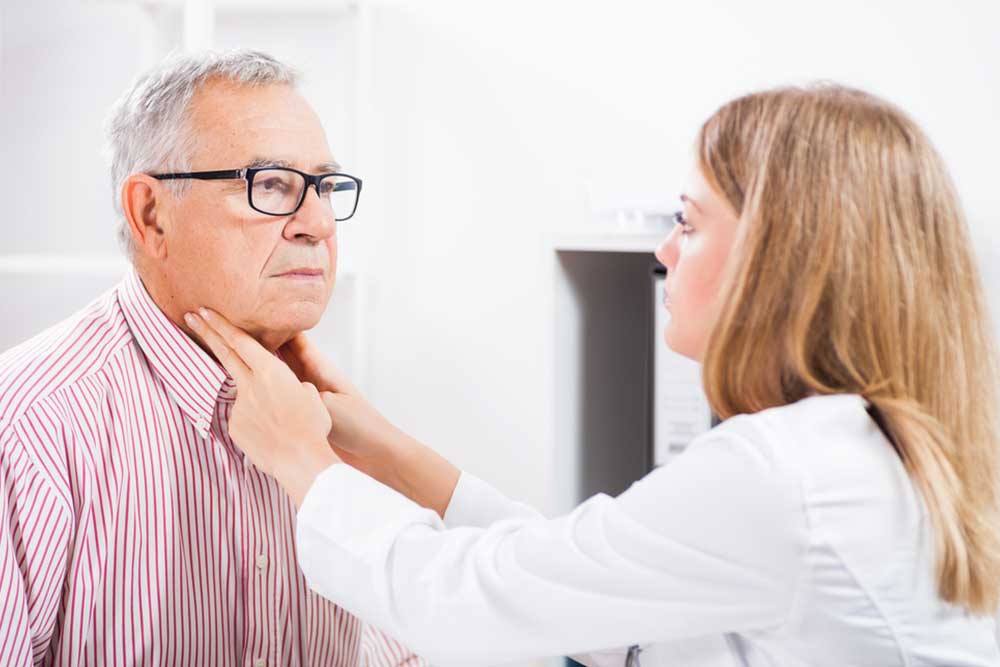
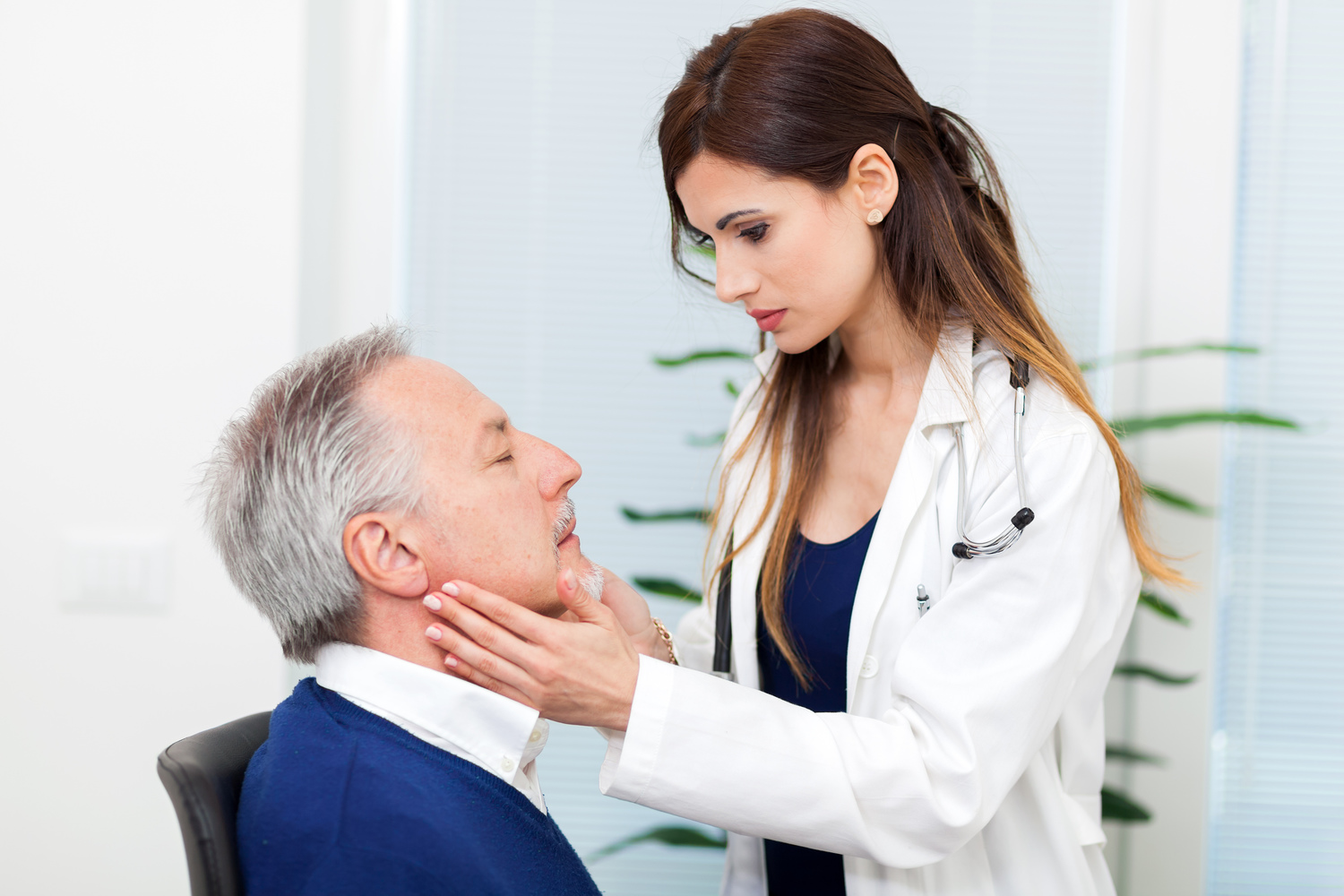
Lymph node swelling in the neck often results from infections caused by viruses or bacteria. This condition, known as lymphadenitis, can also be linked to rare cases of cancer. Lymph nodes play a vital role in your immune defense by filtering out harmful pathogens and preventing their spread throughout the body. Besides the neck, swollen lymph nodes can appear under the chin, in the groin, or under the arms.
Here's how to identify and treat swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
Diagnosis
Physicians will inquire about the onset of swelling and any accompanying symptoms. They may perform several tests, including:
Physical examination—Assessing tenderness, size, texture, and warmth of the swollen nodes
Blood tests—to identify infection or other underlying issues
Imaging scans—to locate the source of inflammation or infection
Lymph node biopsy—Extracting tissue for detailed analysis
Treatment
Approaches depend heavily on the root cause of the swelling.
For bacterial infections or illnesses, antibiotics are prescribed. When an immune disorder is involved, treatment targets managing that condition. For cases linked to cancer, options include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Sometimes, swollen glands resolve naturally or with simple remedies like warm compresses. Regardless, consulting a healthcare provider promptly is crucial, as compromised immunity can affect the body's ability to fight infections.






