Understanding Atrial Fibrillation: Signs and Management
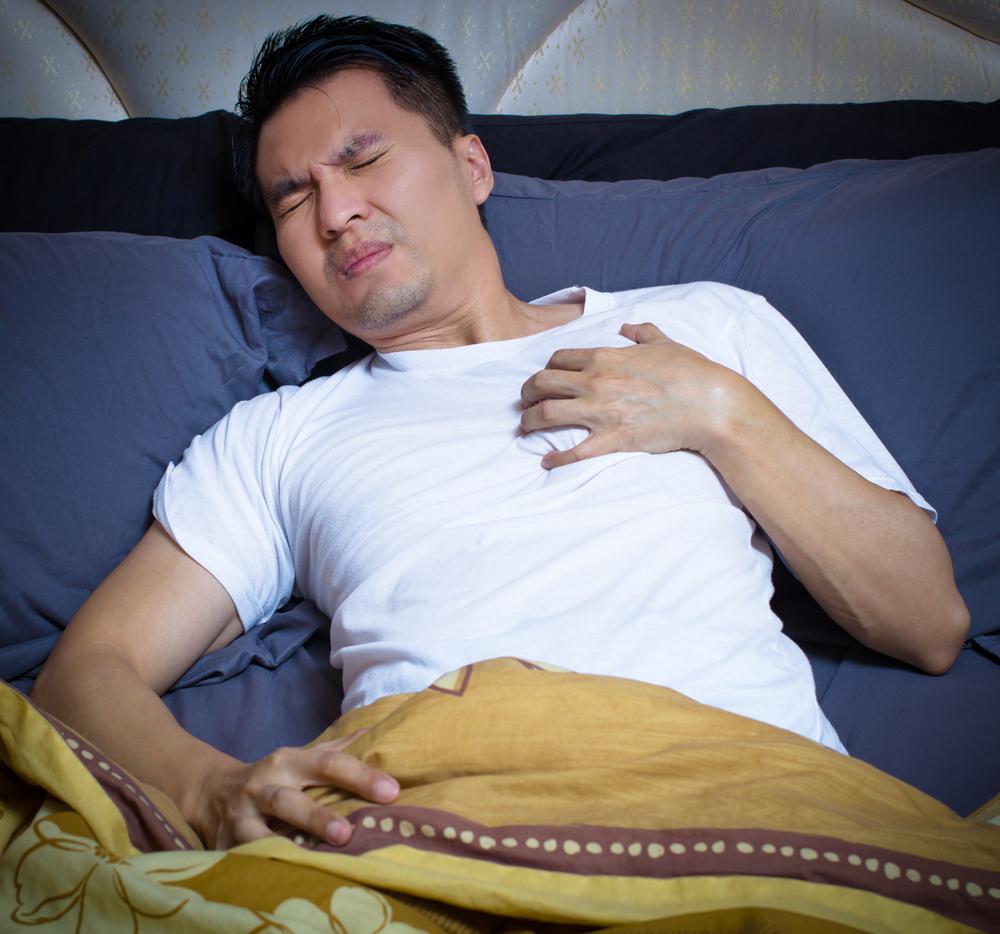
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) affects millions, especially seniors, causing irregular heartbeats and increased health risks. Symptoms vary from subtle to severe, including rapid heartbeat, fatigue, and chest discomfort. Management involves medications, minimally invasive procedures, and lifestyle changes to prevent complications like stroke. Recognizing early signs and addressing underlying causes are vital for effective treatment. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing heart-related conditions can significantly reduce AFib risks and improve quality of life.
Sponsored

Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a condition characterized by an irregular and rapid heartbeat. This disorder increases the risk of stroke, heart failure, and other cardiovascular issues. In AFib, the top chambers of the heart beat out of sync with the lower chambers, impacting blood flow. The irregular rhythm can cause blood to pool and form clots, which may lead to serious complications. Over 2 million individuals, primarily over 60, are affected by AFib.
Symptoms of AFib
Sometimes, symptoms are subtle, making it difficult to detect. Common signs include:
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Weakness and fatigue
Dizziness or lightheadedness
Exercise intolerance
Shortness of breath
Chest discomfort
Managing Atrial Fibrillation
Severe symptoms may require medical intervention, which includes medication, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery.
Medications: Blood thinners, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers help control heart rhythm and prevent blood clots. Patients should be aware of potential side effects.
Non-surgical approaches: Catheter ablation involves inserting a catheter into the heart to restore normal rhythm by targeting specific areas.
Surgical options: Surgical ablation involves open-heart surgery to scarring problematic tissue, helping regulate rhythm over time.
Treating underlying causes: Addressing other health issues, such as heart disease, contributes to restoring normal heart function.
Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise can reduce the risk and manage AFib effectively.
Risk factors include heart valve issues, previous heart surgeries, heart failure, and cardiomyopathy. A healthy lifestyle is essential for prevention and control.