Understanding H. Pylori Infection: Symptoms, Tests, and Treatment Options
This article explains H. pylori infection, including its symptoms, diagnostic methods, and effective treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of medical consultation and adherence to prescribed therapies to eliminate the bacteria and prevent serious health issues like ulcers and gastric cancer.
Sponsored

Understanding H. Pylori Infection: Symptoms, Diagnostic Methods, and Treatment Strategies
H. pylori, or Helicobacter pylori, is a bacteria that infects the human digestive system, often remaining unnoticed for years. Over time, it can cause stomach ulcers and, in some cases, lead to stomach cancer. Discovered in 1982, H. pylori is primarily contracted through contaminated food, water, or utensils, especially in regions lacking sanitation. Symptoms include persistent stomach pain, bloating, nausea, and weight loss. Diagnosis involves blood tests, breath tests, endoscopy, or X-rays. Treatment typically includes antibiotics and medications to reduce stomach acid to eliminate the bacteria and promote healing.
Persistent stomach pain and burning sensation
Bloating, nausea, and unexplained weight loss
Signs of ulcers such as dark stools, dizziness, and vomiting blood
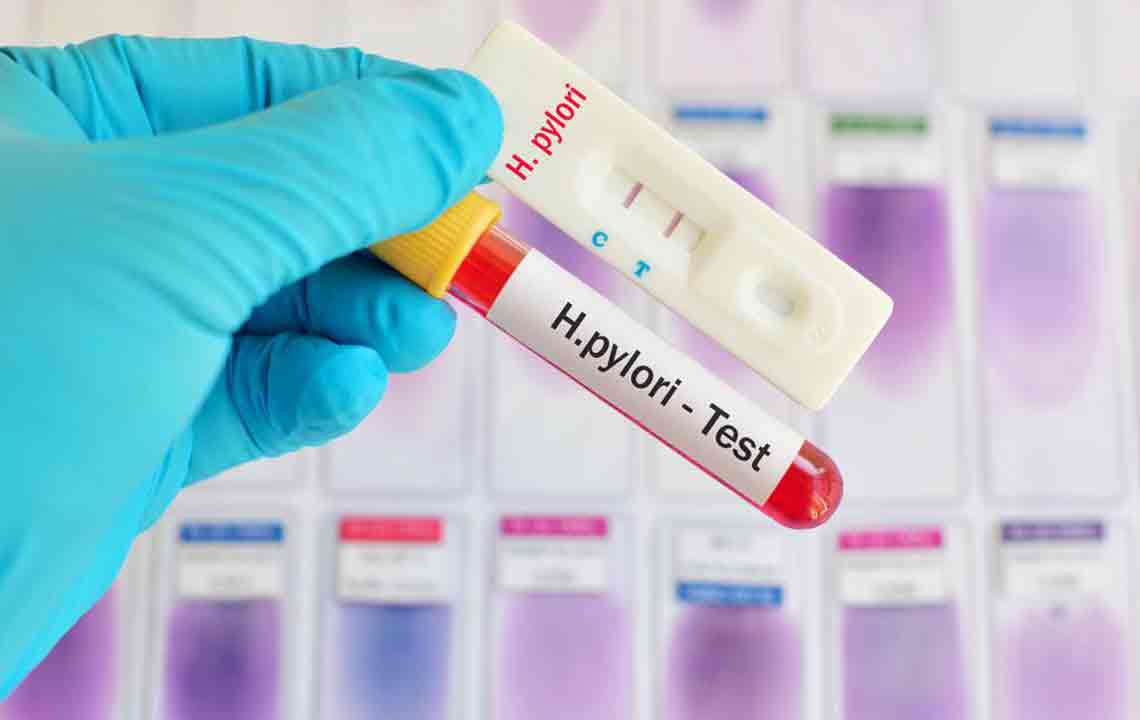
Diagnosis via breath tests, endoscopy, and stool tests
Treatment with antibiotics and acid reducers for 1-2 weeks
Proper medical guidance is essential to effectively treat H. pylori infection. Following prescribed medications helps prevent resistance and ensures complete eradication of the bacteria. Post-treatment testing confirms successful recovery and reduces the risk of complications.