Recognizing the Top 6 Indicators of Leaky Gut Syndrome
Leaky gut syndrome presents with various signs such as skin issues, thyroid problems, food sensitivities, digestive troubles, mental health challenges, and nutrient deficiencies. Recognizing these symptoms early and seeking medical advice can help manage the condition effectively and improve overall health.
Sponsored
Understanding the Six Key Signs of Leaky Gut
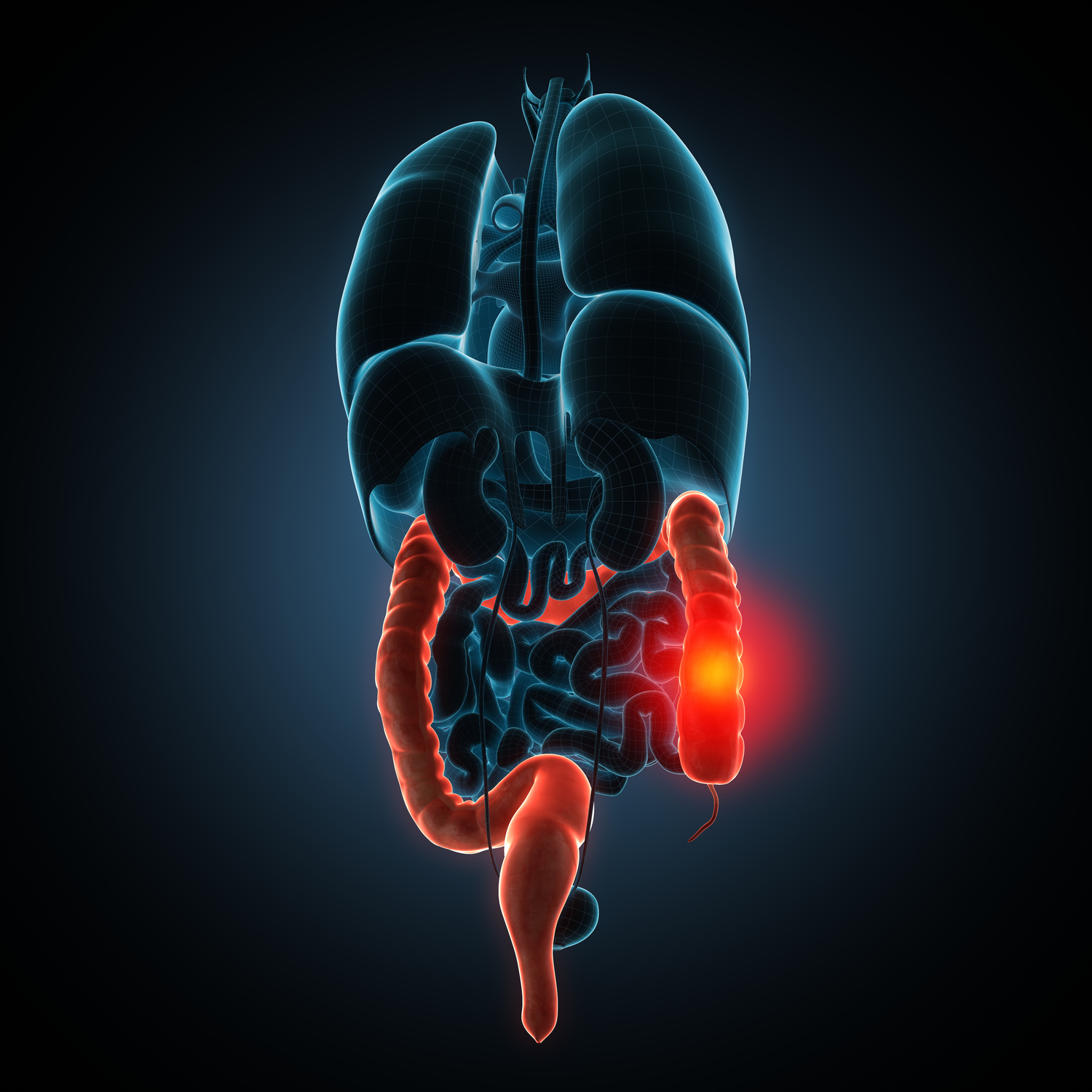
Leaky gut syndrome is an increasingly acknowledged health issue that has gained attention in recent years. It occurs when the tight junctions in the intestinal lining become compromised, allowing toxins and microbes to enter the bloodstream. This can lead to systemic toxicity and contribute to various health problems, including skin conditions, digestive issues, fatigue, and more.
Common signs that may suggest leaky gut include:
Skin inflammation – Skin conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis often reflect internal gut health. The connection between gut wellness and skin appearance is well-established, indicating that internal imbalances can manifest externally.
Thyroid issues – Conditions such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis are common in those with leaky gut, often resulting in fatigue, weight gain, and mood disturbances.
Food sensitivities – Increased intestinal permeability can cause reactivity to foods like gluten and dairy, along with cravings for sugary and carbohydrate-rich foods.
Digestive disruptions – Inflammation in the gut may lead to irritable bowel syndrome, characterized by constipation, diarrhea, and bloating due to compromised bowel motility.
Mental health effects – Neurocognitive symptoms, including depression, mood swings, and anxiety, can be linked to leaky gut through chemical imbalances in the brain.
Nutritional deficiencies – Impaired nutrient absorption and enzyme production often result in deficits of essential vitamins and minerals.
If these symptoms appear collectively or frequently, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.