Managing Diverticulitis with Proper Diet and Lifestyle Tips
This article offers comprehensive guidance on managing diverticulitis through diet and lifestyle adjustments. It covers symptoms, diagnosis, initial treatment with clear liquids, and gradual reintroduction of low-fiber foods. Practical tips include hydration, high-fiber foods, stress reduction, and avoiding processed foods, fried items, and alcohol. Following these recommendations can support recovery, prevent flare-ups, and promote overall digestive health during diverticulitis management.
Sponsored

Guidelines for Diet and Lifestyle in Diverticulitis Management
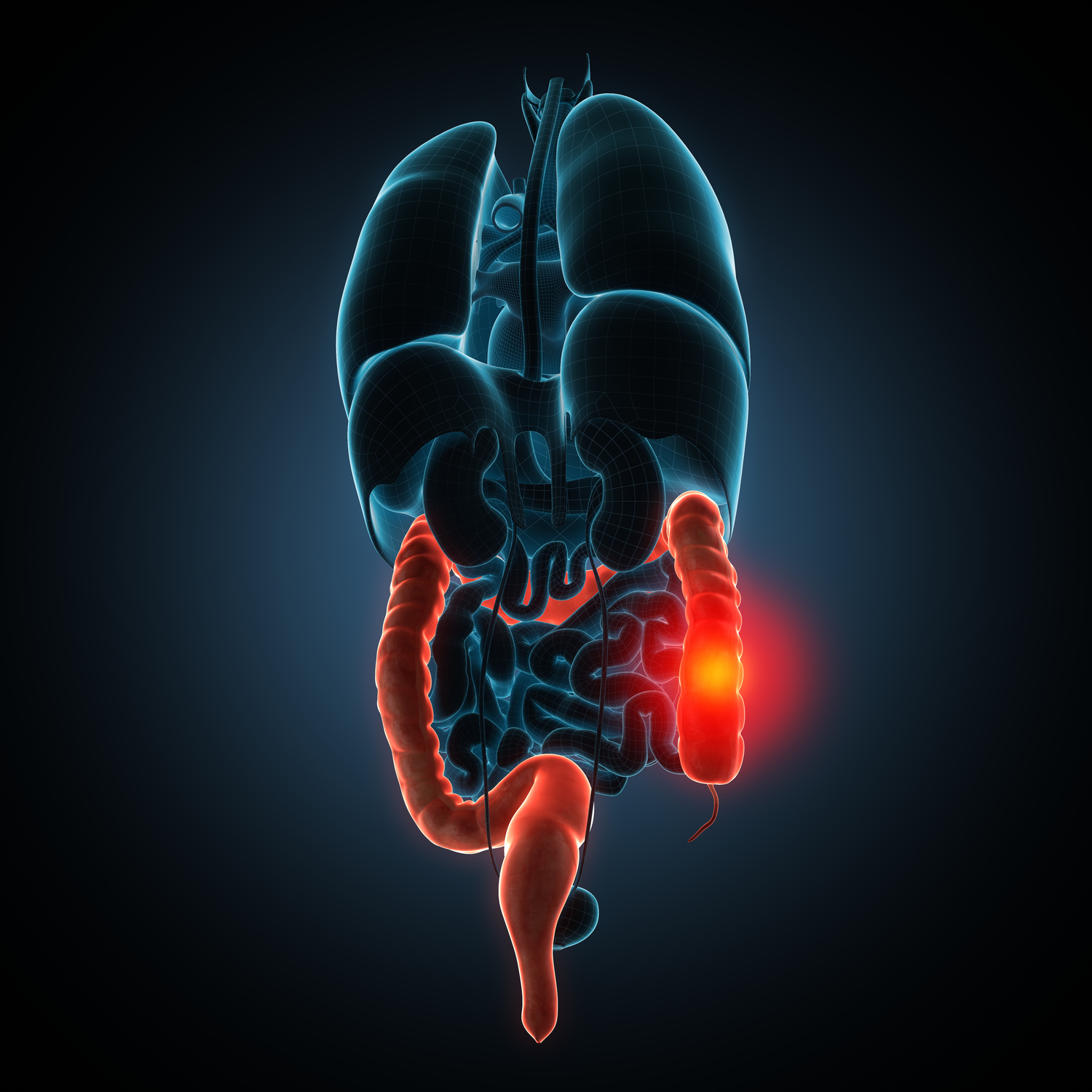
Diverticula are small pouches that develop in the lining of the large intestine, commonly seen after age 40. While often asymptomatic, these pouches can become inflamed or infected, resulting in diverticulitis. Managing early-stage diverticulitis involves dietary adjustments and lifestyle changes to promote recovery and prevent complications.
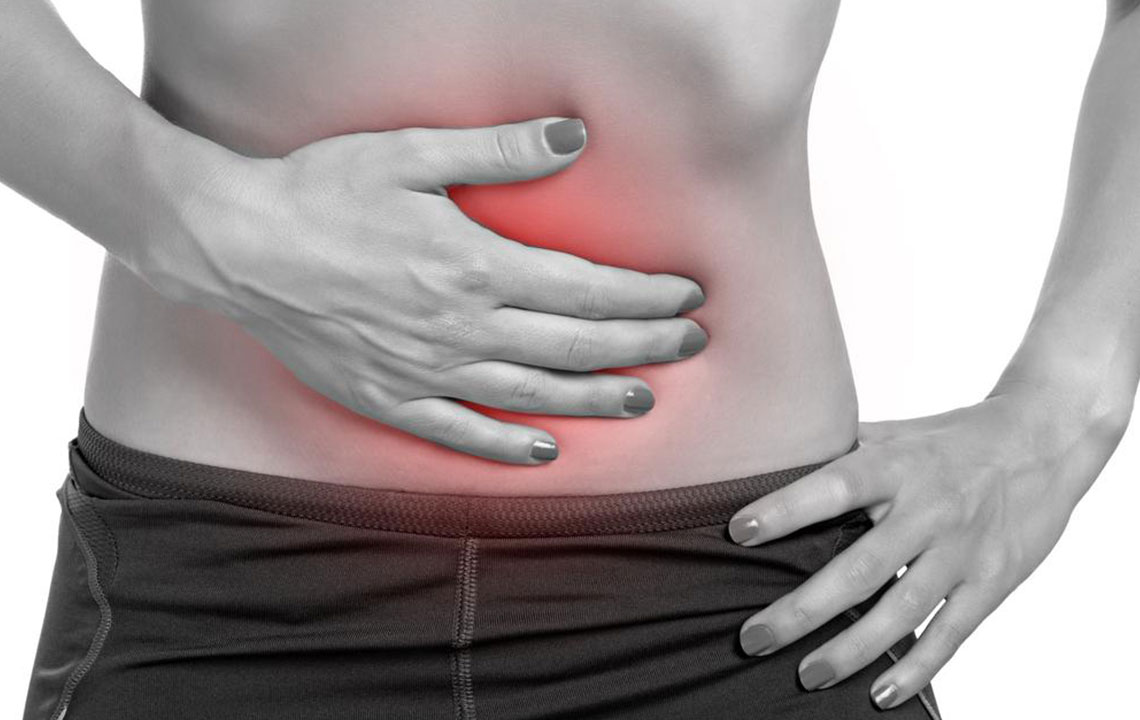
Signs of diverticulitis
Despite diverticula presence, only 10-25% develop diverticulitis
Lower abdominal discomfort and tenderness
Bleeding and changes in stool color
Fever and urinary pain
Severe nausea, cramps, diarrhea, and vomiting
Diagnosis Steps
If diverticula are known, symptoms such as above confirm diverticulitis.
Diagnostic tests such as colonoscopy, barium enema, or sigmoidoscopy may be performed.
Initial treatment involves a clear liquid diet, including broth, ice chips, and pulp-free fruit juices like apple juice.
Ice pops without fruit and gelatin are suitable, along with water, tea or coffee without cream, and herbal teas.
As recovery progresses, low-fiber foods such as skinless fruits, eggs, poultry, canned vegetables, white bread, yogurt, and cooked grains are introduced gradually.
Start with small quantities to allow your digestive system to adjust after initial clear liquids.
Recommended Dietary Practices for Diverticulitis Recovery
Consume at least 10 glasses of water daily to stay well-hydrated.
Opt for low-fat, high-fiber foods including whole grains, vegetables, and fruits whenever possible.
Use healthy oils like olive or flaxseed in moderation.
Begin each meal with a glass of warm water and lemon juice.
Consider antioxidant supplements and herbal remedies to support liver health.
Eat smaller, more frequent meals to support digestion and toxin elimination.
Incorporate relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing to reduce stress.
Foods to Avoid During Diverticulitis Recovery
Steer clear of processed and junk foods.
Limit coffee and avoid excessive green tea consumption.
Quit smoking and avoid alcohol during recovery.
Avoid hard-to-digest foods like heavy dairy, high-sugar items, and sugary substitutes.
Limit saturated fats and reduce meat intake.
Eliminate fried foods completely from your diet.