Recognizing Thyroid Cancer: Symptoms and Variants
This article explores the key symptoms and types of thyroid cancer, emphasizing early detection. It covers signs like neck lumps, voice changes, and persistent cough, while describing the four main variants of the disease. Understanding these indicators can facilitate prompt treatment, which is crucial for better outcomes. With most thyroid growths being benign, awareness of early symptoms ensures timely medical intervention, improving prognosis and quality of life.
Sponsored

Each year, approximately 53,000 individuals are diagnosed with thyroid cancer worldwide. This disease originates in the thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ at the front of the neck that regulates hormones responsible for metabolism and other vital functions. This article highlights key early warning signs and the different types of thyroid cancer to help with prompt detection and treatment.
Initial Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
Early stages often show no obvious signs. However, certain symptoms warrant attention:
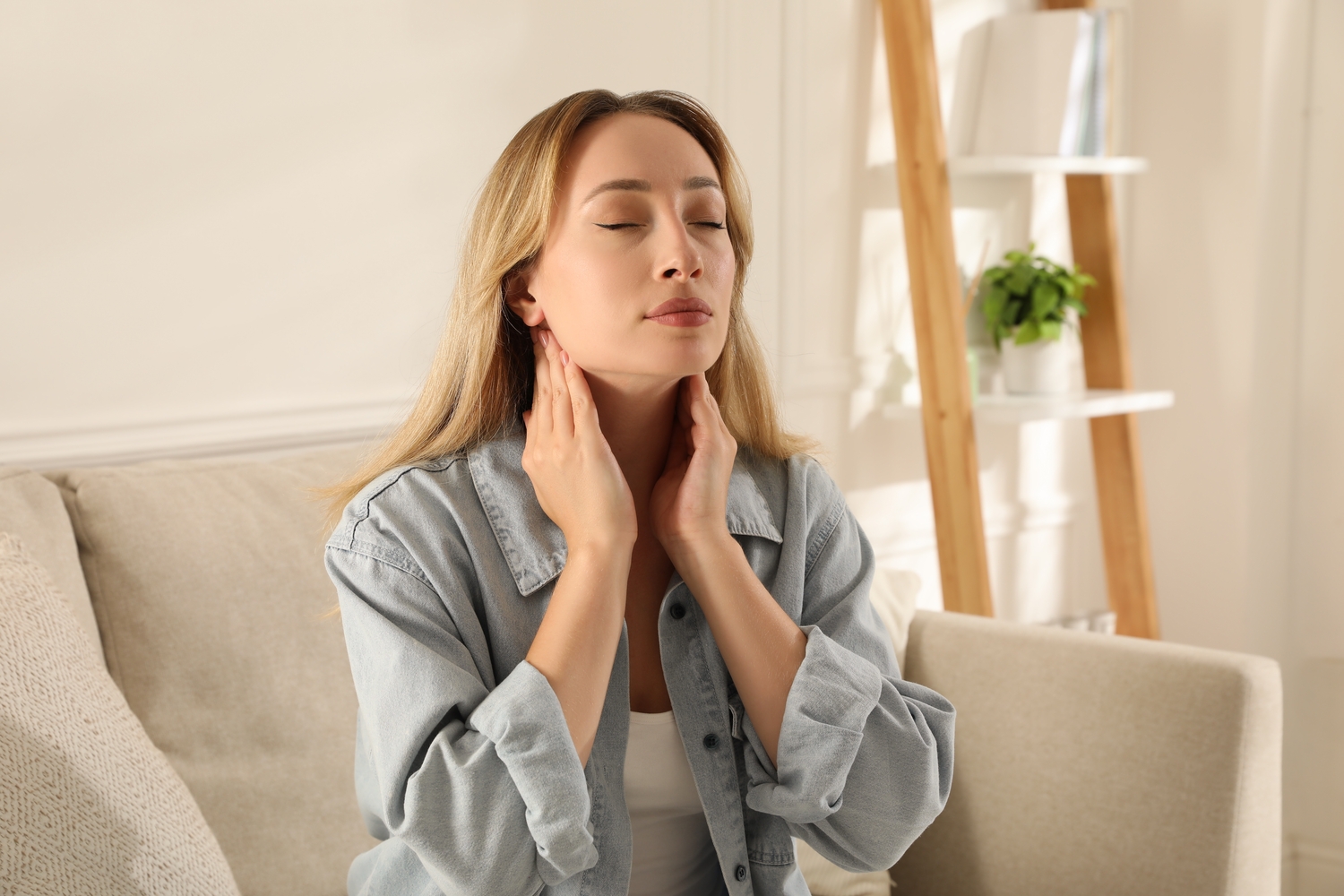
Neck Lump
A noticeable lump or swelling in the neck, especially near the Adam’s apple, may be felt. If this swelling is tender or painful, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Usually painless, such lumps are common early indicators.
Voice Alterations
Unexpected hoarseness or a husky voice that persists should be evaluated. Such changes typically develop gradually and can impair speech and breathing over time. The severity varies per individual.
Enlarged Lymph Nodes
Persistent swelling of neck lymph nodes can signal thyroid issues, as disease-related lymphatic enlargement occurs.
Chronic Cough
An ongoing cough without cold or allergy causes may suggest thyroid gland enlargement irritating the throat and airways.
Fatigue
Unexplained tiredness and weakness are common in many cancers due to immune and organ system impacts. If these symptoms persist despite a healthy routine, medical evaluation is advisable.
Other Notable Symptoms
Additional signs include:
Difficulty Breathing: Breathing difficulty or shortness of breath may result from gland inflammation or growth pressing on airways and lungs.
Swallowing Difficulties: Enlarged thyroid may exert pressure on the esophagus, causing dysphagia or choking sensations.
Neck Discomfort: Pain that starts at the neck base and radiates to ears or head can be an early warning, especially if persisting.
Thyroid Cancer Variants
The disease presents in four primary types, distinguished by aggressiveness and progression:
Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Representing around 80% of cases, this slow-growing type is highly treatable and rarely life-threatening, though it can spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Follicular Carcinoma: Making up about 10%, it can metastasize to lungs and bloodstream but is curable if diagnosed early.
Medullary Thyroid Cancer: About 4%, identifiable via calcitonin hormone levels in blood; often hereditary.
Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: The rarest (around 2%), fast-growing and challenging to treat, with high potential for spreading to other organs.
Hurthle Cell Cancer: An uncommon subtype of follicular carcinoma, accounting for roughly 3% of cases.
Despite over 90% of thyroid nodules being benign, recognizing early signs and consulting a doctor is crucial for timely diagnosis and management.