Recognizing the Top 10 Indicators of Heart Attacks
This article highlights the top 10 critical symptoms of a heart attack, including chest pain, arm pain, dizziness, and sleep apnea signs. Recognizing these early can be life-saving. Immediate medical attention is essential if symptoms appear, especially in at-risk individuals or those with a history of heart disease.
Sponsored
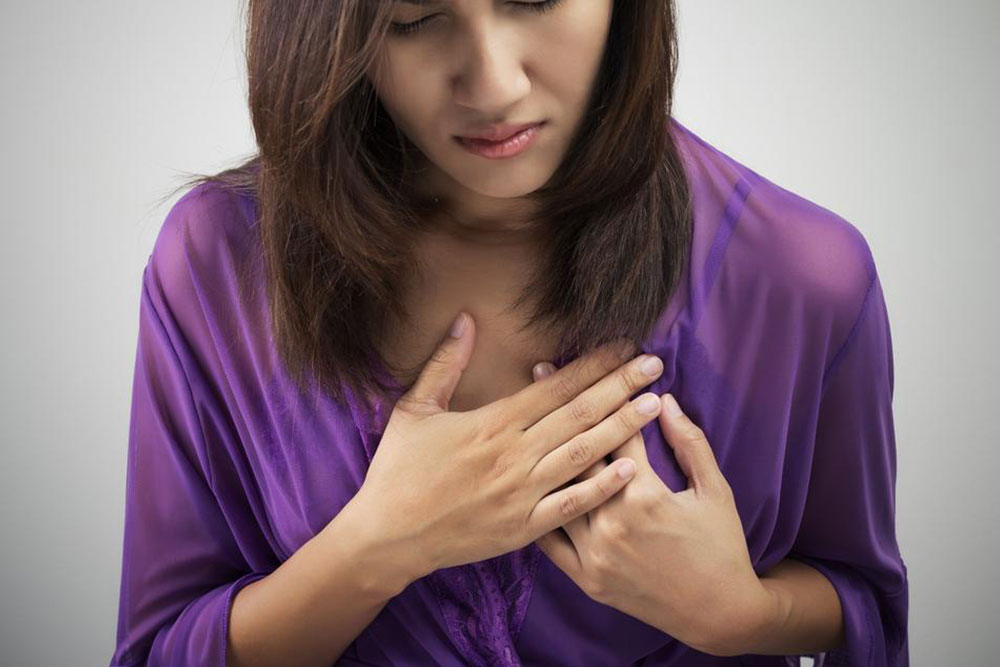

Heart attacks pose a significant health risk and can strike unexpectedly. Being aware of the key symptoms can save lives. Here are the top 10 signs indicating a heart attack:
Chest discomfort
The heart resides on the left side of the chest; persistent discomfort or pain lasting more than a few minutes should prompt immediate medical attention. Contact emergency services without delay.
Nausea, indigestion, or stomach pain
These symptoms are common during a heart attack, especially in women, and may be accompanied by vomiting. Recognizing these early is crucial.
Pain radiating to the arm or neck
Pain that starts in the chest and spreads to the arm indicates potential artery blockage and signals an imminent heart attack.
Dizziness or lightheadedness
If you experience sudden dizziness, it could be due to reduced heart function and warrants immediate medical evaluation.
Unusual fatigue
Feeling extremely tired after routine activities might be an early warning sign of heart trouble.
Persistent cough
A cough persisting beyond a week may indicate cardiac issues, particularly if you have a history of heart disease.
Excessive sweating
Unexpected cold sweats without clear cause could be associated with a heart attack and require immediate medical attention.
Swollen limbs
Swelling in the legs, feet, or ankles suggests impaired blood circulation caused by inefficient heart pumping.
Irregular heartbeat
Repeated episodes of abnormal heartbeat patterns should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Loud snoring or choking during sleep
Heavy snoring or breathing interruptions might indicate sleep apnea, which adds stress and strain on your heart, increasing risk.