Early Intervention Strategies for Scleroderma Symptoms
This article explores early signs of scleroderma and effective management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and treatment to prevent organ damage. Key interventions include medication, physiotherapy, and protective measures. Recognizing initial symptoms like skin hardening, numbness, and acid reflux can help individuals seek timely medical assistance. The article provides insights into treatments that can control symptoms and improve quality of life. Proper management plays a crucial role in preventing disease progression and safeguarding internal organs from irreversible damage.
Sponsored

Managing Initial Signs of Scleroderma
Scleroderma is a persistent autoimmune condition that primarily affects the skin, leading to hardening and thickening. Early detection and treatment are crucial for managing its progression.
The main challenge with scleroderma lies in its autoimmune nature, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's tissues by overproducing proteins, resulting in skin fibrosis and organ involvement.
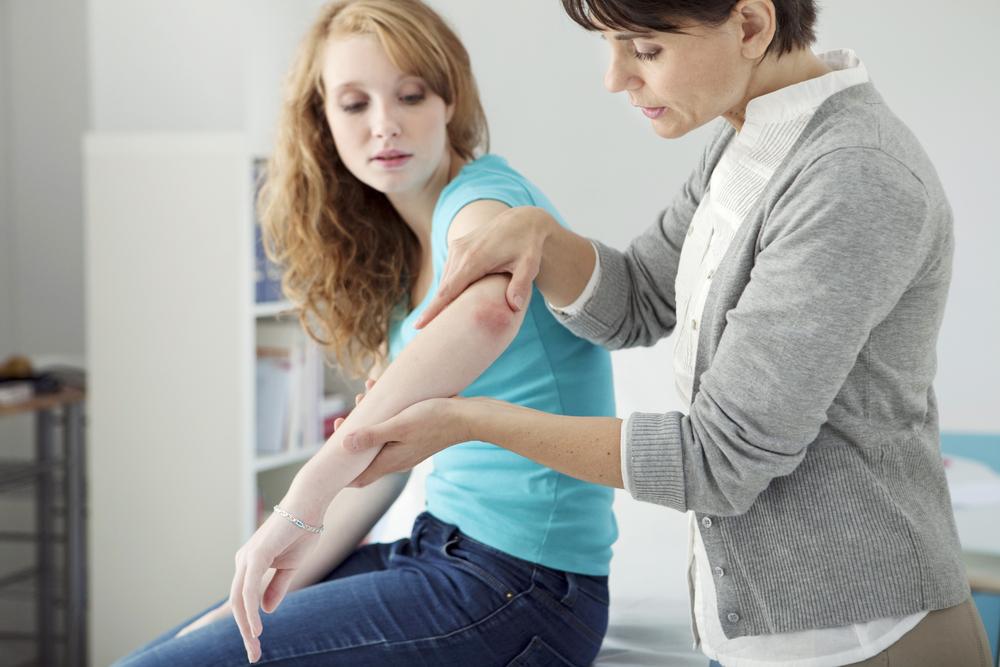
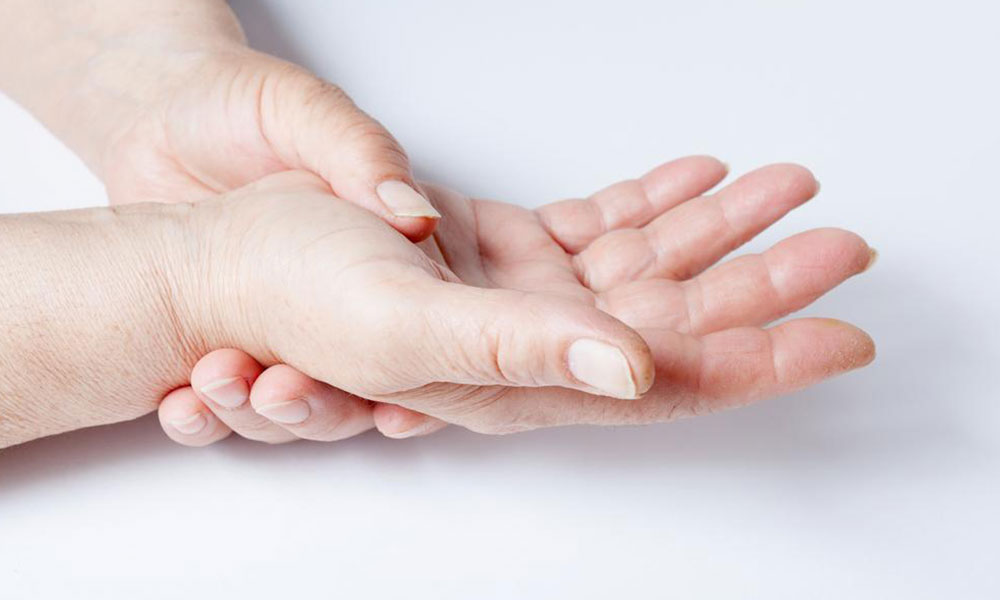
This image shows one of the common early signs: skin tightening.
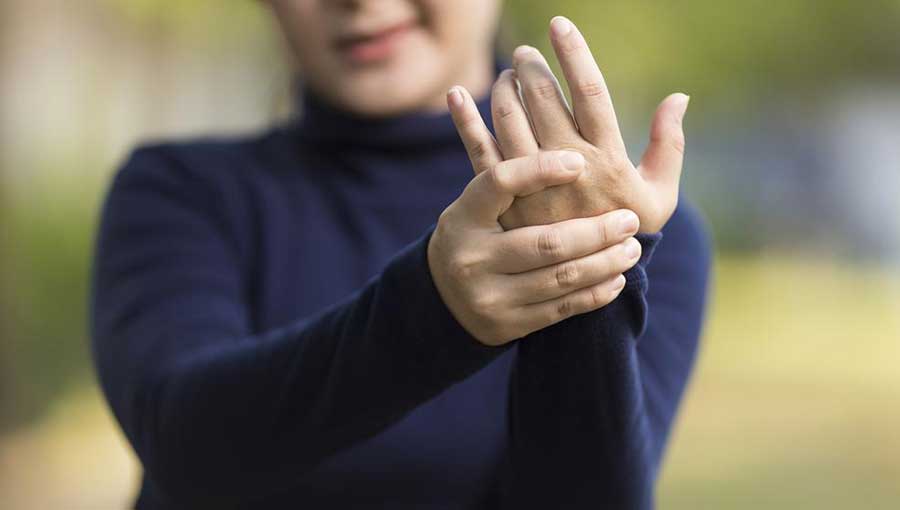
Individuals often notice patches of hardened skin that can be oval-shaped, linear, or extensive across the trunk and limbs. Finger numbness triggered by cold or emotional stress also indicates early stages.
Additionally, acid reflux can damage the esophagus, impairing nutrient absorption due to impaired intestinal movement, a common issue in scleroderma patients.
Treatment options for early scleroderma symptoms
In some cases, initial symptoms may resolve spontaneously within three to five years. However, if left untreated, they can worsen internal organ functions.
Several interventions can help manage symptoms, including medication, therapy, and surgery:
Vasodilation therapy
Medications can help relax blood vessels, preventing further damage to organs like the lungs and kidneys, and alleviating Raynaud's phenomenon.
Immune suppression
Prescription drugs can suppress immune activity, controlling disease progression as done in transplant cases.
Addressing gastrointestinal issues
Drugs like omeprazole can ease acid reflux caused by esophageal fibrosis, improving nutrient intake.
Infection prevention
Protecting fingertips with antibiotics during cold weather and vaccination against influenza and pneumonia can safeguard lungs and extremities affected by scleroderma.
Physiotherapy
Rehabilitative therapies enhance strength, reduce pain, and help maintain daily functional independence.
If early signs of scleroderma appear, consulting a healthcare professional promptly is essential for diagnosis and tailored treatment.