Effective Strategies to Manage Viral Infection Symptoms
Learn how to effectively manage and treat symptoms of viral infections through proper diagnosis, vaccination, and antiviral therapies. Early medical attention is vital for recovery, especially in children. Preventive vaccines play a key role in protecting against various viruses, significantly reducing illness severity.
Sponsored
Approaches to Alleviate Symptoms of Viral Diseases
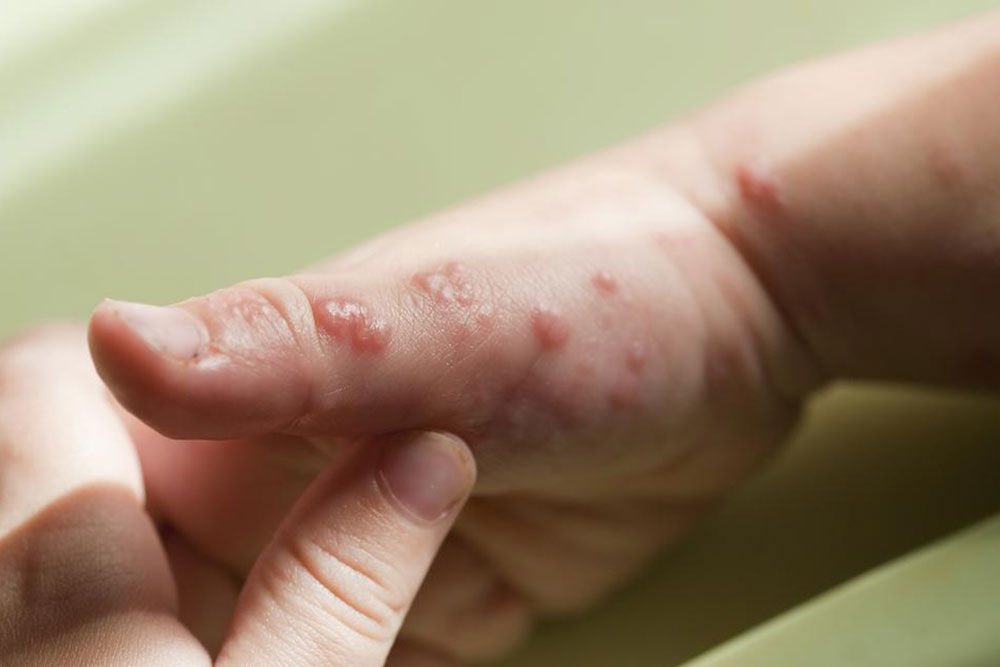
Viral illnesses result from various viruses present in our environment, which can spread easily through different modes depending on the specific virus. Respiratory viruses infect via airborne particles, while foodborne viruses are transmitted through contaminated foods and beverages. Certain viruses can also spread through intimate contact, such as kissing or sexual activity, entering the body through saliva.
Typical signs of viral infections include fever, fatigue, muscle pain, skin rashes, coughing, vomiting, sneezing, diarrhea, nasal discharge, chills, and headaches.
More serious symptoms may involve personality changes, neck stiffness, excessive drowsiness, urinary and bowel issues, dehydration, seizures, back pain, confusion, and limb paralysis.
Identifying a viral infection can be challenging due to overlapping symptoms, so seeking prompt medical advice is essential, especially for children. Proper diagnosis is crucial before initiating treatment.
Diagnostic procedures include:
A blood examination to detect specific viruses, antibodies, or antigens responsible for the infection.
Laboratory tests, such as blood or bodily fluid cultures, to isolate and identify the viral strain.
For skin-related viral infections, samples from the affected area are analyzed. A spinal tap test can assess cerebrospinal fluid to diagnose neurological involvement. To precisely trace the virus, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques amplify viral genetic material, aiding in accurate identification.
Treatment options for viral infections include:
Vaccination remains the most effective preventive measure, helping to build immunity against specific viruses—and hence, prevention is better than cure. Keeping up with recommended immunizations helps safeguard health.
Antiviral medications are also used to manage symptoms, though they are generally less effective than vaccines. These drugs work by inhibiting virus replication within the body, helping to control symptoms and reduce severity. For lasting protection, vaccines are preferred.






