Understanding Tree Allergies: Symptoms and Relief Strategies
This article provides a comprehensive overview of tree allergy symptoms, identifying common allergenic trees and offering practical management tips. It emphasizes how to reduce pollen exposure and alleviate allergic reactions through lifestyle adjustments, medication, and environmental control, helping allergy sufferers navigate peak seasons more comfortably.
Sponsored
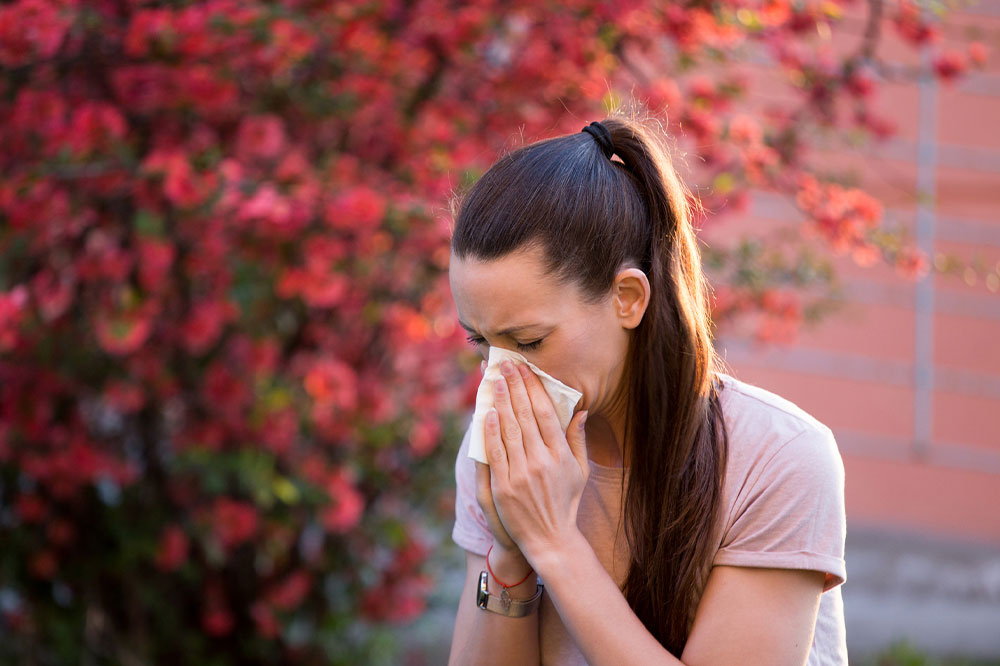

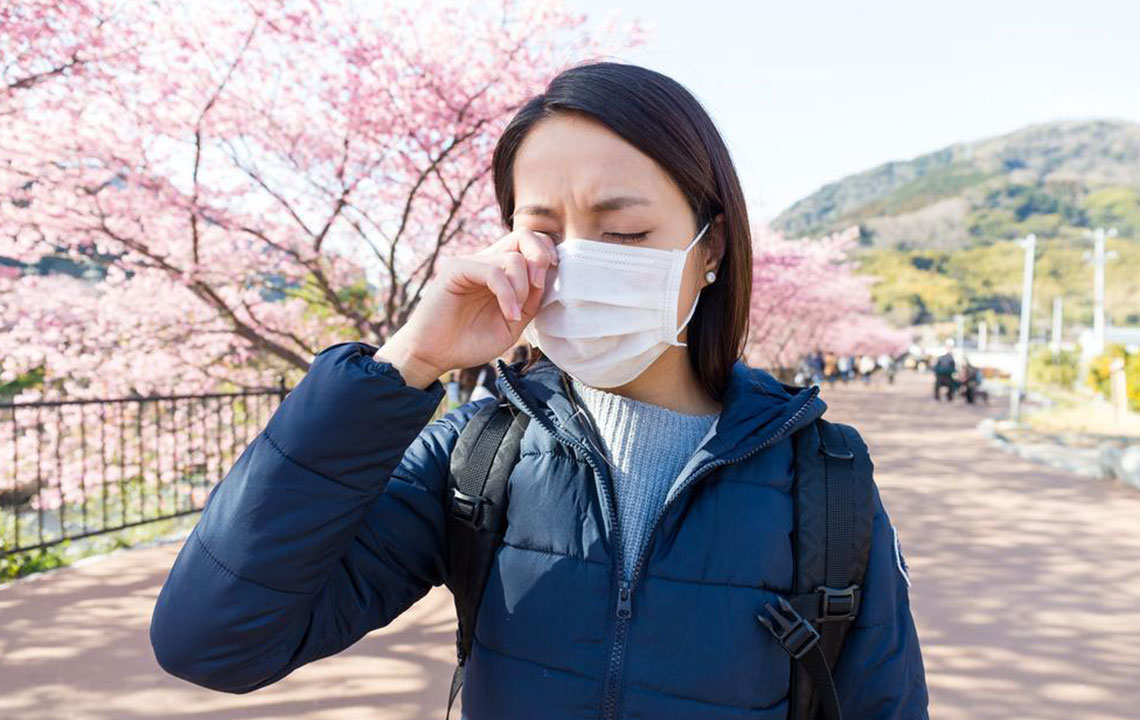
Tree pollen becomes airborne primarily in spring, causing many individuals to suffer from respiratory irritation, sneezing, and inflammation. These symptoms are often linked to tree pollen allergies, which may also occur intermittently throughout the year when certain trees release pollen during late winter or summer. Notable trees that can trigger allergic responses include birch, oak, cedar, maple, and willow. Recognizing signs of tree allergy and knowing how to manage exposure can significantly improve comfort during pollen seasons.
Trees Known to Trigger Allergic Reactions
Many tree species, such as birch, hickory, elm, oak, beech, ash, sycamore, cottonwood, willow, alder, juniper, cypress, ragweed, maple, walnut, olive, pine, acacia, and cedar, are associated with pollen allergies. In particular regions like central Texas, cedar pollen causes "cedar fever," which peaks from November to January, leading to allergy-like symptoms during winter.
Common Symptoms of Tree Allergies
Individuals allergic to tree pollen often experience symptoms shortly after pollen are airborne, typically within an hour. These signs tend to persist throughout the day and can intensify at certain times. Typical symptoms include a runny nose, nasal congestion, postnasal drip, frequent sneezing, itchy nose, mouth, eyes, and ears, along with red, watery, or swollen eyes. Irritability, fatigue, and disrupted sleep are also common, especially during peak pollen periods.
For those with asthma, symptoms can worsen, resulting in coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, and chest tightness. Additionally, pollen exposure may trigger oral allergy syndrome, causing mouth itching and swelling after eating certain foods.
Effective Strategies to Manage Tree Allergy Symptoms
Complete avoidance of pollen is challenging due to outdoor exposure and indoor plants. However, various measures can help control symptoms. Consulting a healthcare professional for appropriate medications is recommended. Minimize outdoor activities between 5 am and 10 am when pollen counts are highest. Keep windows closed during travel and at night to prevent pollen entry. Avoid outdoor laundry drying during high pollen seasons and shower immediately after outdoor exposure to wash away allergens. Staying indoors on windy days or when pollen levels are elevated also reduces symptom severity.