Understanding and Managing Type 2 Diabetes
This article provides a comprehensive overview of type 2 diabetes, focusing on its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies. Emphasizing lifestyle modifications, medical treatments, and preventive measures, it aims to educate readers on controlling this widespread health condition and avoiding complications through early intervention and healthy habits.
Sponsored

Overview of Type 2 Diabetes: Management and Prevention Strategies
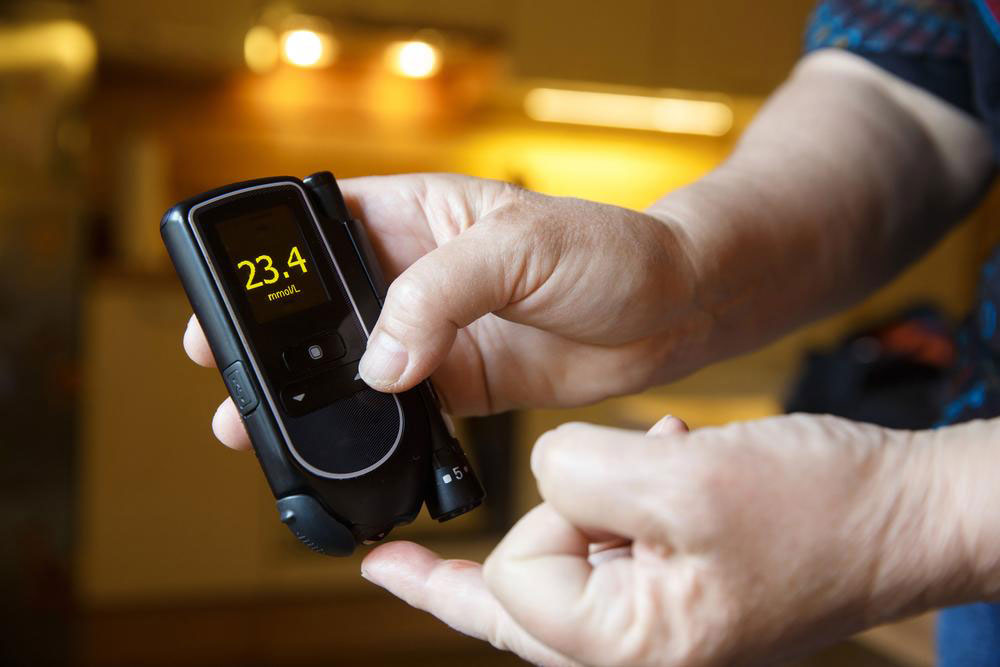
Type 2 diabetes, a metabolic condition also known as adult-onset diabetes, is characterized by elevated blood glucose levels over time. It occurs when the body either fails to produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to insulin's effects.
Insulin, produced by the pancreas, is essential for sugar and fat metabolism. Disruptions in insulin secretion or action lead to this disorder.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes:
Insufficient insulin production
Insulin resistance
Genetic predisposition
Types of Diabetes:
Type 1: Autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells
Type 2: Resistance to insulin and reduced production
Gestational: High blood sugar during pregnancy
Type 2 is most prevalent, accounting for about 90% of cases. It's linked to lifestyle factors like poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity, as well as genetic factors.
Symptoms include fatigue, blurred vision, frequent urination, dry mouth, increased thirst and hunger, and slow wound healing. It can also cause skin infections and frequent yeast infections.
Prevention emphasizes a healthy lifestyle: maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, monitoring weight, and avoiding tobacco. Medical options like Metformin can aid in prevention but are less effective than lifestyle modifications.
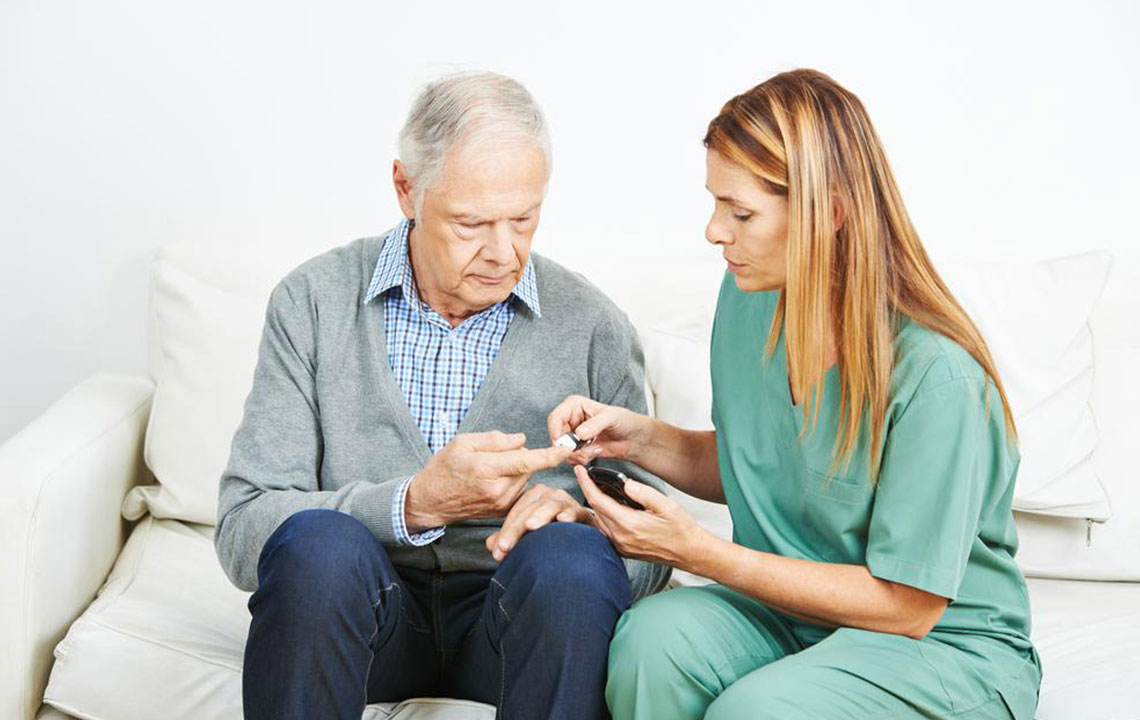
Treatment involves a combination of a nutritious diet, physical activity, blood sugar monitoring, and medications. Insulin therapy is now commonly used, especially for controlling blood glucose levels effectively. Early management is crucial to prevent complications.