Effective Strategies for Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Discover effective methods to manage type 2 diabetes through proper diet, regular exercise, medication, and blood sugar monitoring. Learn about low glycemic foods, consulting health professionals, and insulin therapy options to maintain optimal health and prevent complications.
Sponsored

Type 2 diabetes has become a prevalent health concern worldwide, often described as a lifestyle-related condition. Without proper management, it can pose serious health risks. Controlling blood sugar involves maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, taking prescribed medications or insulin when necessary, and consistently monitoring blood glucose levels. These approaches help stabilize blood sugar and prevent or delay complications associated with diabetes.
What does a healthy diet involve?
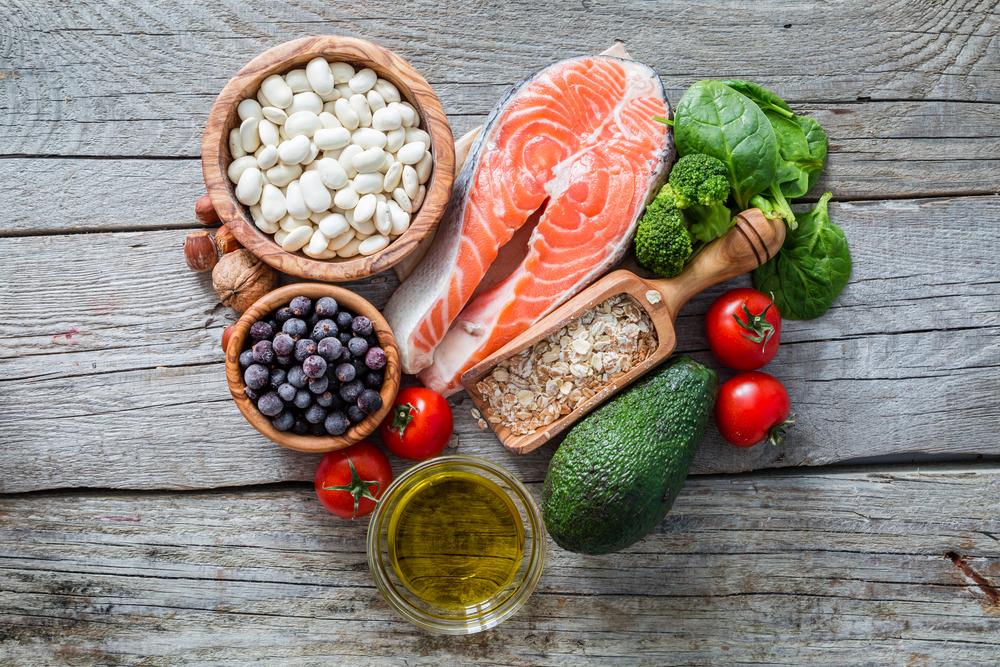
Contrary to the misconception that diabetics must follow restrictive diets, healthy eating focuses on nutrient-rich foods. Incorporate plenty of fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while reducing intake of red meats, dairy, sweets, and refined carbs to better manage blood glucose.
Opt for low glycemic index foods
Foods with a low glycemic index slow down blood sugar spikes, aiding in better control. These foods are typically high in fiber, which helps maintain steady blood sugar levels. Choosing such options can make a significant difference in diabetes management.
Consult a dietitian
An expert dietitian can develop personalized meal plans, guiding carbohydrate intake to optimize blood sugar control. They help you understand portion sizes and meal timing to keep your glucose levels stable.
Engage in regular physical activity
Incorporating aerobic exercises like walking, swimming, or dancing into your routine is essential. Aim for at least 30 minutes of activity, five days a week. Combining resistance training or yoga twice a week can enhance blood sugar regulation and overall health.
Overview of diabetes medications
Though lifestyle changes suffice for some, others may need medications or insulin therapy. Metformin, the most common drug, enhances insulin sensitivity and lowers liver glucose production. Sulfonylureas stimulate insulin secretion, while Meglitinides encourage the pancreas accordingly. Thiazolidinediones increase tissue sensitivity to insulin, and DPP-4 inhibitors assist in moderate glucose reduction. GLP-1 receptor agonists like Exenatide and Liraglutide slow digestion to lower blood sugar. SGLT2 inhibitors help prevent kidneys from reabsorbing sugar, promoting excretion.
Insulin therapy options
Insulin injections are highly effective for certain individuals, especially when other measures are insufficient. Injected via fine needles or insulin pens, this therapy helps maintain blood glucose levels. Regular monitoring of blood sugar is crucial to adapt insulin doses and ensure balanced control, reducing the risk of fluctuations and complications.