Essential Guide to Ozempic for Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Explore the essential information about Ozempic®, a medication for type 2 diabetes management. Learn about dosage, administration tips, precautions, and how to use it safely for better blood sugar control. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance on effective treatment with Ozempic®.
Sponsored
Understanding Ozempic: A Key Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes
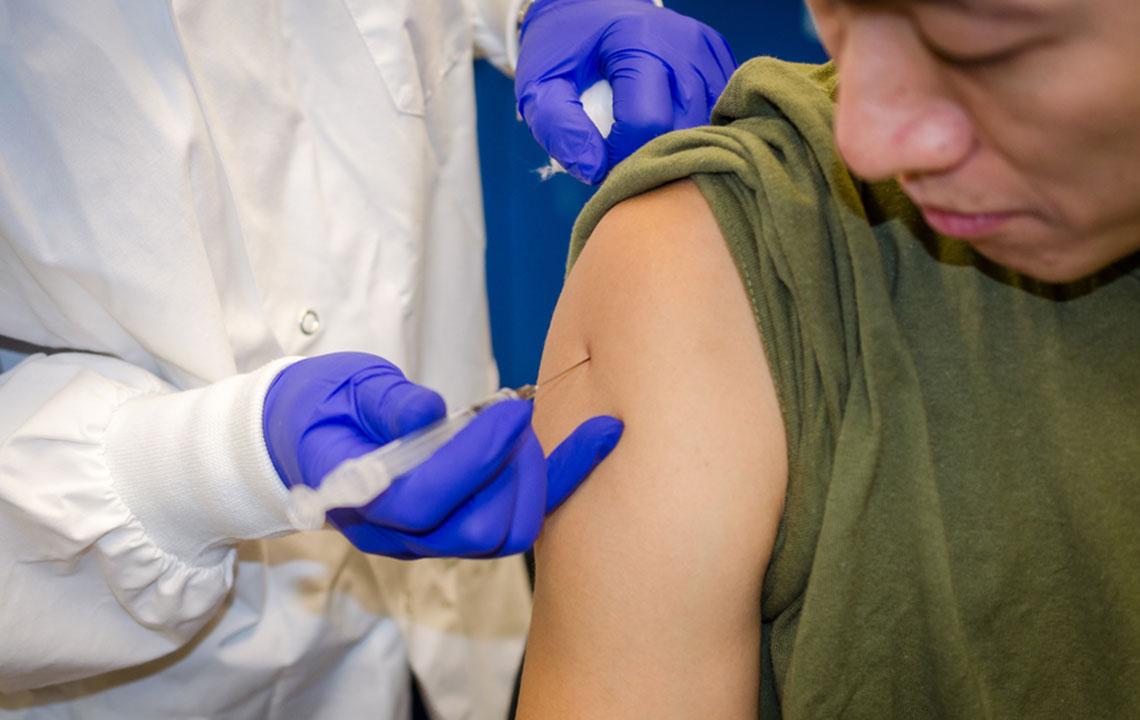
If traditional medications do not effectively control blood sugar, healthcare providers may recommend Ozempic® injections. This medication belongs to the GLP-1 receptor agonist class, which helps regulate blood glucose and boost insulin production. Ozempic® (semaglutide) is designed for subcutaneous use, with easy-to-use, disposable pens suitable for single patients. Following proper dosing and administration guidelines is crucial for safety and effectiveness.
Learn about the recommended Ozempic® dosing for type 2 diabetes and how to use it correctly.
Ozempic® Dosage for Managing Type 2 Diabetes
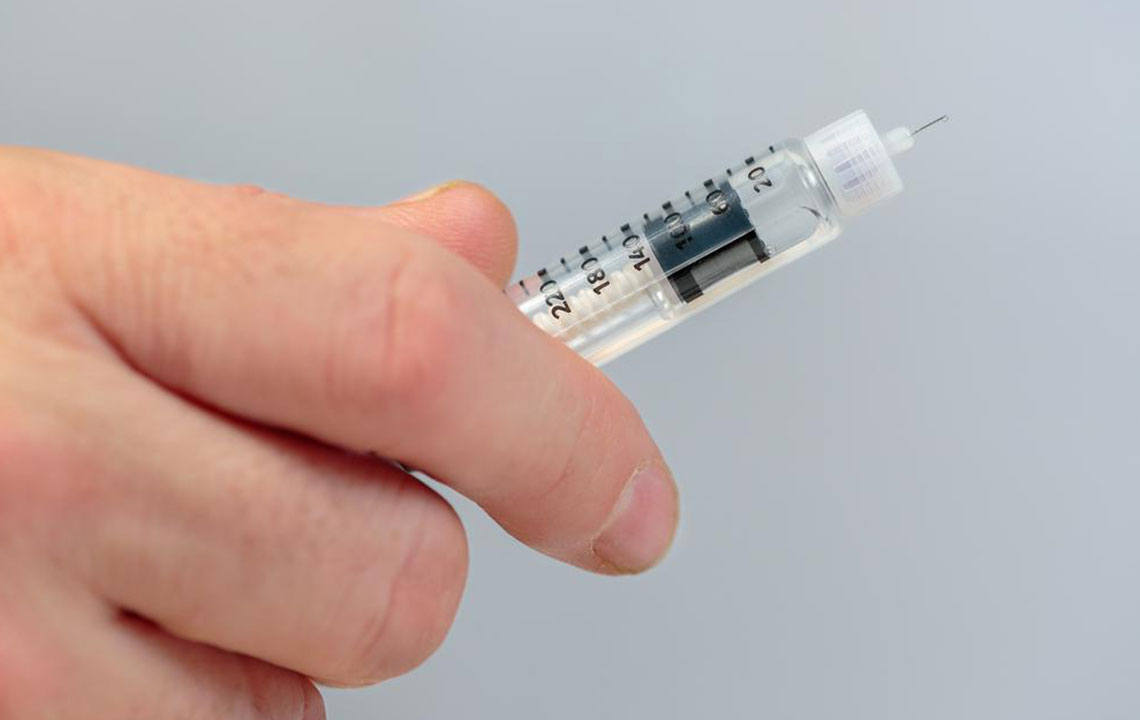
Initially, patients usually start with 0.25 mg injected subcutaneously once weekly for four weeks to initiate treatment. This dose primarily prepares the body for subsequent therapy.
After the initial period, the dose may be increased to 0.5 mg weekly for improved blood sugar control.
If blood glucose levels do not improve with 0.5 mg weekly, healthcare providers might escalate the dose to 1 mg per week, which is generally the maximum prescribed dose.
Administration should be consistent, ideally on the same day each week, with flexibility regarding timing—either with or without meals.
Changing injection days is possible, provided there is at least a 48-hour gap between doses.
If a dose is missed within five days, it can be taken later; beyond five days, skip the missed dose and resume the next scheduled injection.
Never share the Ozempic® pen or reuse needles to avoid infection risks.
Precautions Before Starting Ozempic®
Discuss any pancreatic or kidney issues with your doctor.
Inform your healthcare provider if you have diabetic retinopathy.
Women who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning pregnancy should consult their doctor—Ozempic® should be discontinued at least two months before conception.
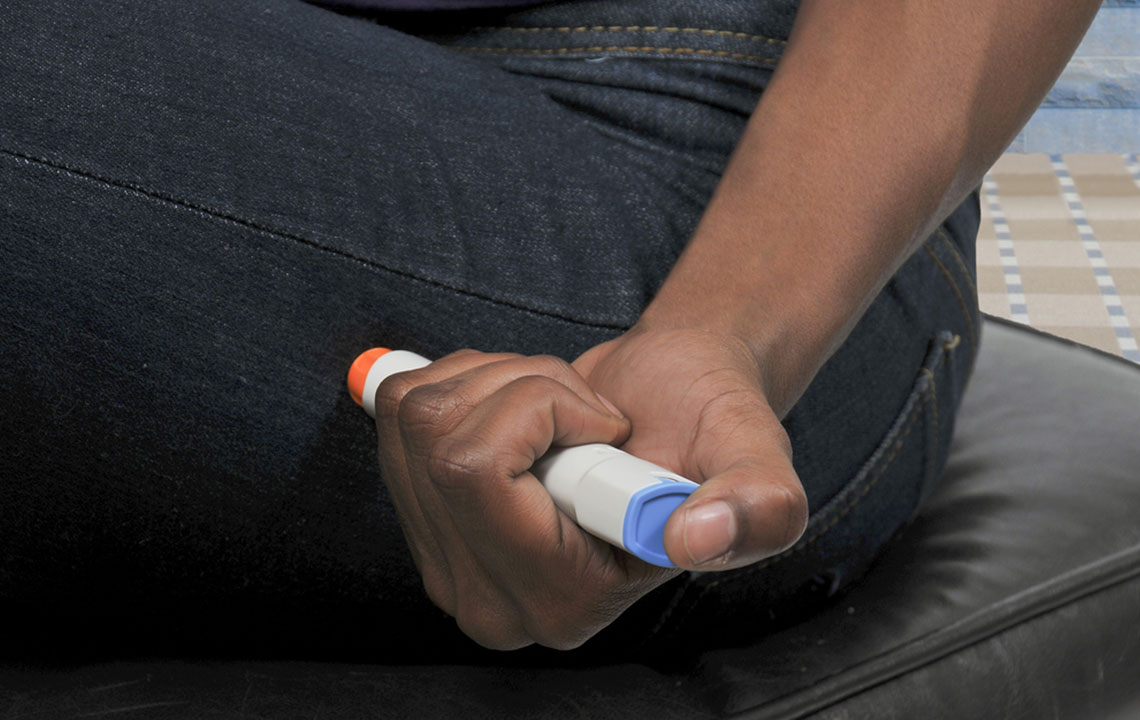
Proper Injection Technique
Inject Ozempic® into the abdomen, upper arm, or thigh, rotating sites weekly to prevent tissue irritation.
Check the medication before use; it should be clear and colorless without particles. Discard if contaminated.
While using other injections like insulin, ensure they are administered separately and spaced adequately, even if in the same area.
Note that Ozempic® is designed for type 2 diabetes management and is not a substitute for insulin, nor is it suitable for type 1 diabetes. When used as prescribed, combined with diet and exercise, it effectively improves blood sugar control. Always consult your doctor if unsure about proper usage or dosage to ensure safe and effective treatment.