Understanding Chest Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
This comprehensive guide explains the various causes of chest pain, including heart, lung, and musculoskeletal issues. It highlights symptoms, diagnostic tests, and treatment options, emphasizing the importance of prompt medical attention for serious conditions like heart attacks and lung collapses, while offering insights into managing less severe causes effectively.
Sponsored
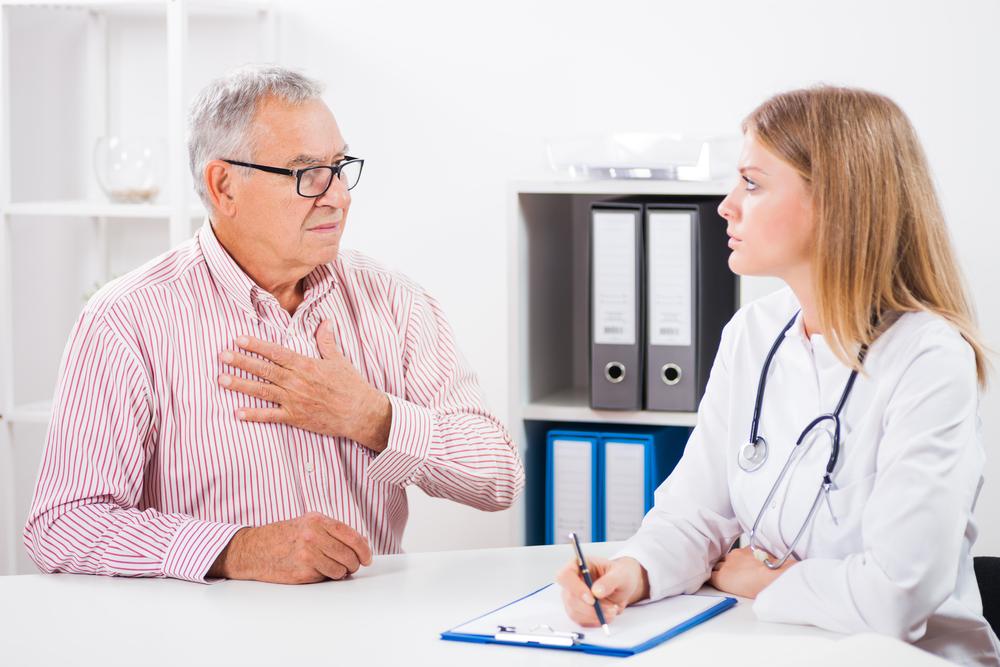

Chest pain, especially in the upper left region, often prompts concerns about a heart attack. While it can signal a cardiac event, there are numerous other causes. The discomfort can be felt from the neck to the upper abdomen and may present as dull, sharp, stabbing, burning, aching, or crushing sensations. Recognizing the type and origin of chest pain is crucial for proper treatment and prevention of serious health issues. Prompt medical attention is essential when experiencing chest pain.
Common causes of chest discomfort include:
Rib injuries: Fractures, bruises, or strains in the ribs can cause chest pain.
Muscle strain: Overexertion leading to inflammation in the chest muscles and tendons can result in pain, especially during activity.
Peptic ulcers: Sores in the stomach lining may cause chest discomfort, often resembling pain.
Asthma: Airway inflammation leads to chest tightness, coughing, and breathing difficulties.
Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD): Acid reflux causes burning sensations and sour taste in the mouth.
Pneumothorax: Lung collapse due to air buildup results in shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid heartbeat, and fatigue.
Esophageal hypersensitivity: Changes in pressure or acid in the esophagus can trigger chest pain.
Hiatal hernia: When part of the stomach protrudes into the chest, it often causes heartburn and pain after eating.
Tuberculosis: Lung infection symptoms include persistent cough, chest pain, and blood in sputum.
Mitral valve prolapse: Valve dysfunction leading to dizziness, palpitations, and chest discomfort.
Heart attack: Symptoms include chest pain, jaw or neck pain, weakness, arm and shoulder pain, and shortness of breath.
Angina: A squeezing chest pain linked to coronary artery issues, sometimes spreading to the back, neck, or shoulders.
When to seek immediate medical attention:
If chest pain occurs suddenly and on the right side or anywhere else.
If pain persists despite medication.
If pain radiates to the jaw, back, or left arm.
If accompanied by rapid breathing or heartbeat.
Diagnostic tests for chest pain include:
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Blood analysis
Chest X-ray
Echocardiogram
MRI scans
Stress testing
Coronary angiography
Types of chest pain based on causes:
Cardiac-related
Stress-induced
Rib injuries
High blood pressure issues
Nerve or muscle disorders
Bone-related chest pain
Psychological factors
Treatment options for chest pain:
Addressing the underlying cause is key to effective treatment.
Antacids help relieve acid reflux-related pain.
Stress management techniques are recommended for stress-related chest discomfort.
Rest and avoiding activities that strain muscles can alleviate pain.
Medications and, in some cases, surgical procedures are used for cardiac-related issues.
Surgical intervention may be necessary for collapsed lungs.