Understanding Eczema: Types, Signs, and Symptoms
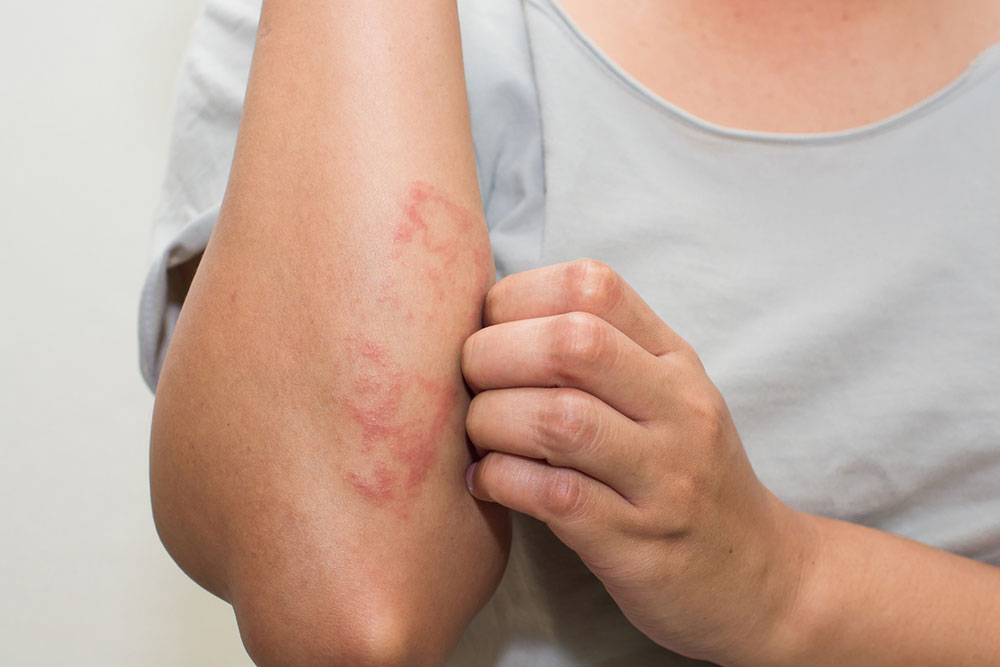
Eczema is a widespread skin condition characterized by inflammation, itching, and redness. It includes various types such as atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, and more. Recognizing the symptoms like dry, flaky skin, blisters, and rashes is essential for effective management. Factors like genetics, allergies, and environmental irritants contribute to its development. Understanding each type helps in targeted treatment, providing relief from discomfort and improving skin health. This comprehensive overview aids individuals in identifying and managing eczema effectively.
Sponsored
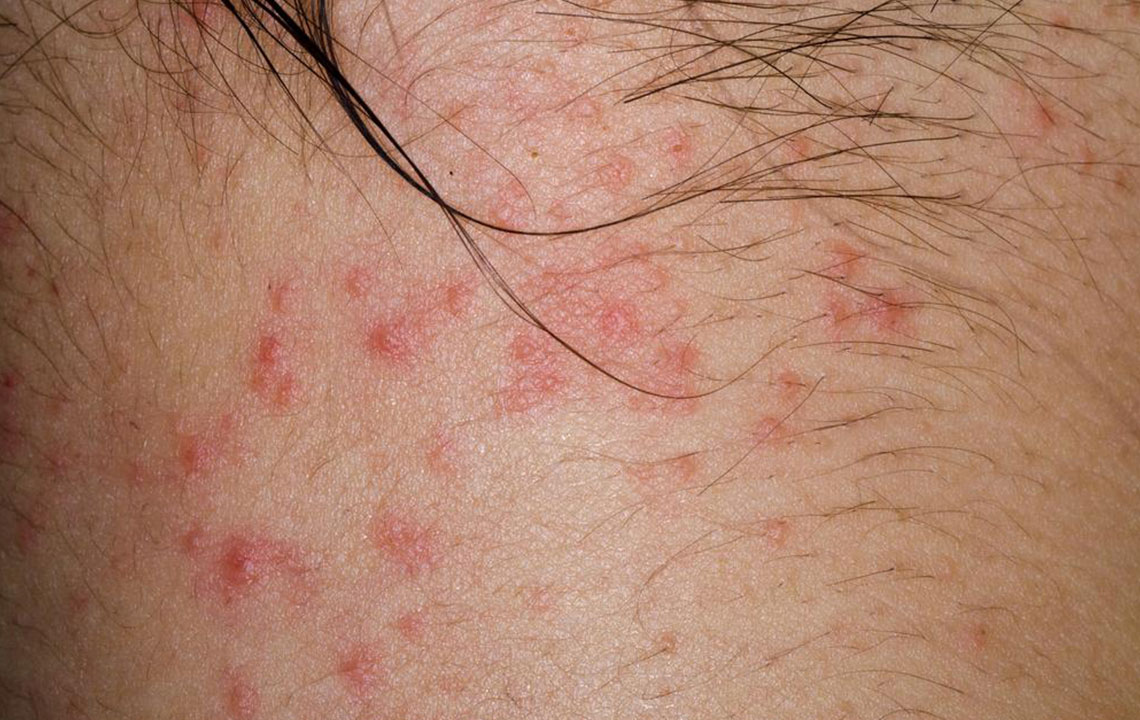
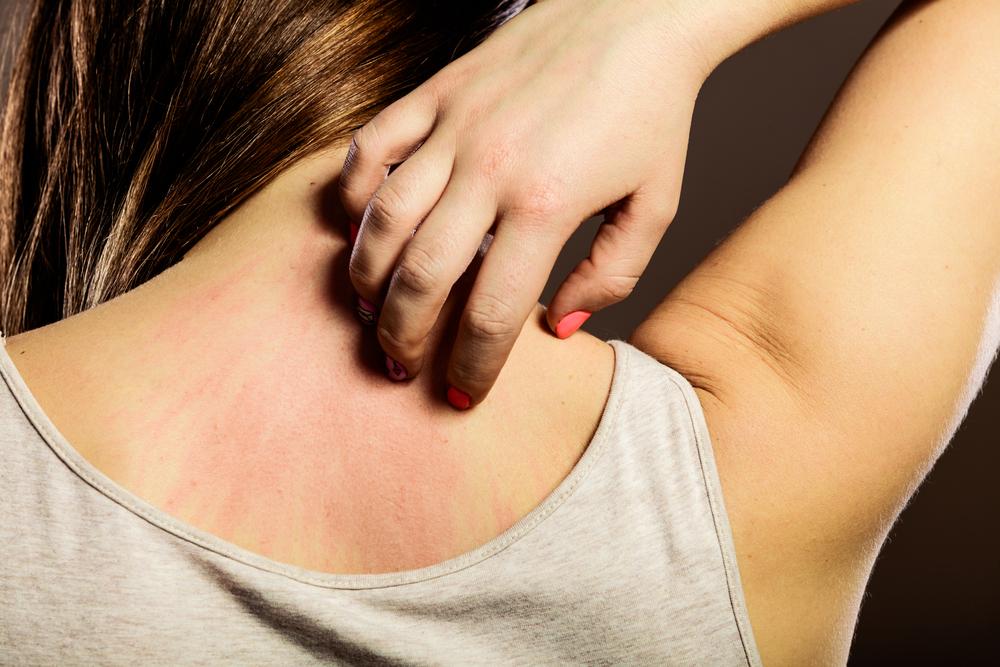
Eczema, also known as dermatitis, is a prevalent skin disorder marked by itchiness, redness, and inflammation. Affecting over 30 million individuals nationwide, this condition is non-contagious and often linked to genetic and environmental factors. It develops when allergic triggers impact the immune system and skin cells. Multiple types of eczema can occur simultaneously, each with distinct features. Symptoms include dry, flaky, and reddened skin, sometimes accompanied by oozing or cracking. Recognizing the specific type helps in effective management and treatment.
Among various forms, atopic dermatitis is the most common, often showing up as scratch marks behind the knees and on the face during childhood. Contact dermatitis results from skin contact with irritants like chemicals, soaps, or metals, causing redness and itching. Dyshidrotic eczema produces itchy blisters on hands and feet, often triggered by stress or allergies. Hand eczema arises from exposure to irritants and chemicals, presenting with dryness and cracks. Other types include neurodermatitis, nummular eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and their respective symptoms, which vary based on causes and affected areas.