Comprehensive Guide to Pain Types and Relief Strategies
This article provides an in-depth overview of various types of pain, their causes, and management methods. It covers medication options, therapy techniques, and the importance of medical consultation for effective pain relief. Suitable for patients seeking comprehensive pain management strategies.
Sponsored
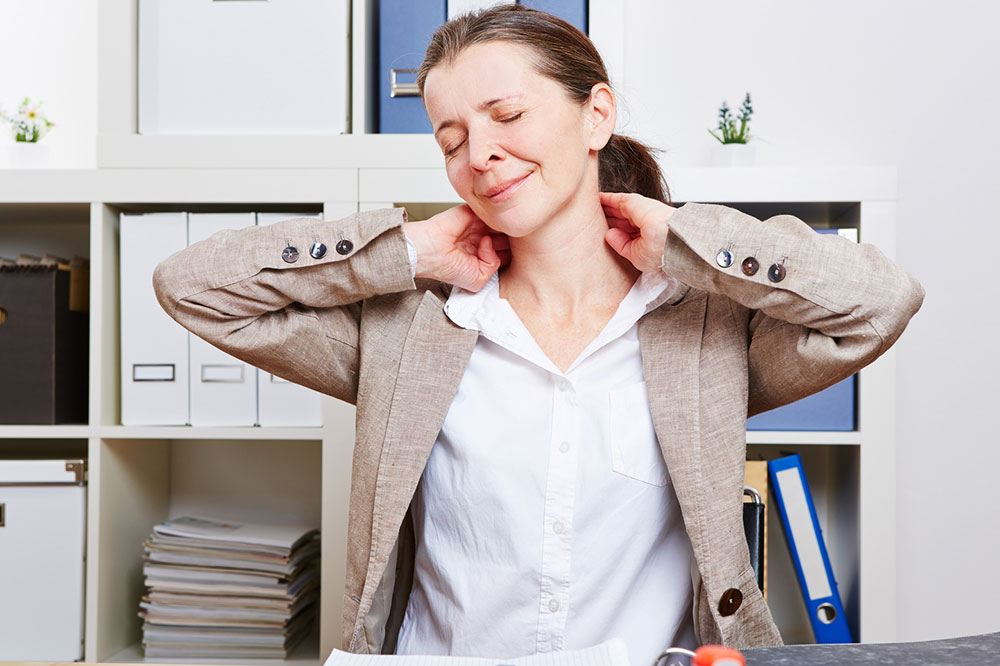

Understanding Different Pain Types and How to Manage Them
Effective pain relief depends on identifying its underlying cause. For example, nerve root compression from a herniated disc, which causes leg radiating pain, is often treated with epidural steroid injections. Conversely, severe issues like inflamed appendix may require surgery or invasive procedures. This article explores common pain causes and various management methods.
Common Causes of Pain
Cancer
Lateral epicondylitis
Plantar fasciitis
Piriformis syndrome
Torticollis
Myofasciitis
Post-herpetic neuralgia
Compression fractures
Coccydynia
Peripheral nerve damage
Infections, ulcers, or open wounds
Headaches
How Pain Management Is Achieved
Managing pain involves understanding its history, intensity, duration, and factors that improve or worsen it. Sharing complete details with healthcare providers ensures effective treatment.
Categories of Pain
Nociceptive pain: Results from tissue injury, can be sudden or persistent, affecting skin, muscles, or internal organs.
Neuropathic pain: Originates from nervous system damage or dysfunction, seen in conditions like shingles or diabetic neuropathy.
Approaches for Pain Relief
Psychological counseling
Physical and chiropractic therapies
Medication strategies
Interventional procedures
Medications for Pain Control
Adjuvant drugs: Such as antidepressants and muscle relaxants that support other treatments and reduce inflammation.
Strong opioids: Including morphine for managing moderate to severe pain in adults.
Combined opioids: Used with counseling or other therapies to minimize opioid reliance.
Weak opioids: Less potent than morphine, suitable for milder pain.
Non-opioid drugs: Like NSAIDs, aspirin, and acetaminophen—common OTC pain relievers.
Pain characteristics can vary with disease progression or treatment, requiring adjustments in management. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any medication to prevent complications.