Guide to Proper Ozempic Dosage and Usage
This comprehensive guide explains how to safely and effectively use Ozempic® for type 2 diabetes management. It covers dosage instructions, injection techniques, timing, and precautions to ensure optimal blood sugar control. Proper adherence and consultation with a healthcare provider are essential for safety and efficacy.
Sponsored
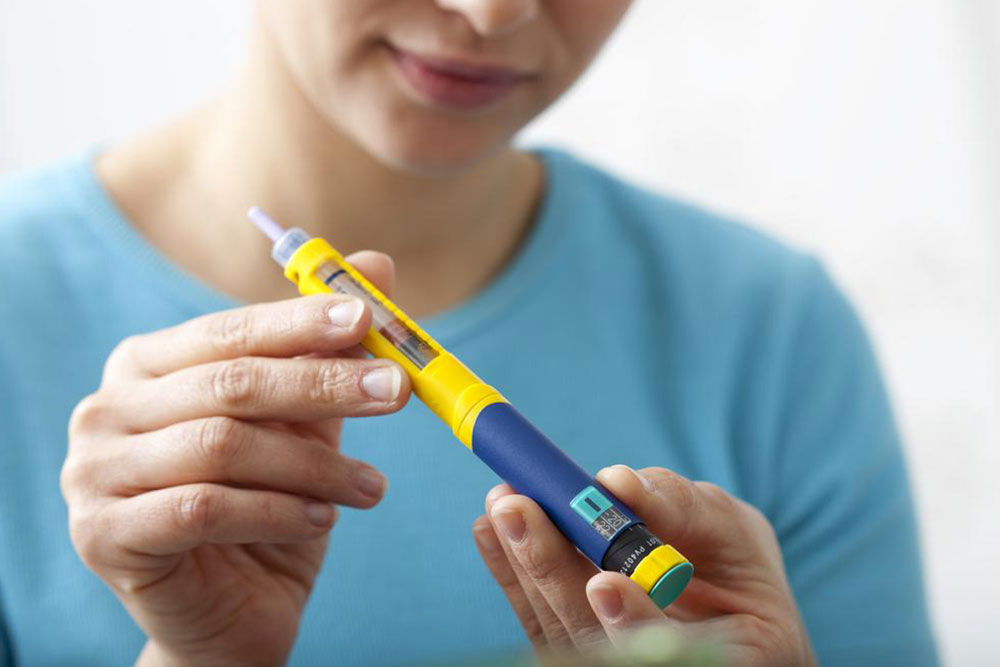
Ozempic® injections are typically reserved for type 2 diabetes patients when other treatments haven't achieved desired blood sugar control. This medication is a non-insulin injectable that mimics a natural hormone, reducing glucagon secretion and aiding in blood sugar regulation. Easy to administer via injection pens, following official guidelines ensures safe and effective use.
Key points about Ozempic® dosing include:
Ozempic® functions as a GLP-1 receptor agonist, helping manage blood glucose levels in type 2 diabetes patients.
Initial treatment usually starts with 0.25 mg weekly for four weeks, gradually stimulating insulin production and suppressing glucagon secretion.
Post four weeks, the dose may be increased to 0.5 mg weekly as per doctor’s advice.
If blood sugar remains uncontrolled, a further increase to 1 mg weekly might be recommended, but doses above this are uncommon.
When to take Ozempic®:
Select a consistent day each week for injection; timing relative to meals is flexible.
You can switch days with at least two days gap, and missed doses within five days can be taken later. Beyond this window, skip the dose and continue as scheduled.
Administration tips:
Avoid sharing the injection pen or needles; dispose of needles safely after use.
Inject into the upper arm, abdomen, or thigh, choosing different sites each week.
Check that the solution is clear and colorless before use; discard if it appears cloudy or has particles.
You may inject insulin into the same area, using separate needles and avoiding close proximity between injections.
Precautions:
Discuss any history of diabetic retinopathy, kidney or pancreatic issues with your doctor.
Women who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning pregnancy should consult their healthcare provider before use. While no direct harm is proven, caution is advised, and stopping Ozempic® two months prior to conception is recommended.
Note that Ozempic® is only for type 2 diabetes management and is not an insulin substitute. It’s most effective when combined with diet and exercise, and always follow your doctor’s guidance regarding dosage adjustments.