Comprehensive Guide to Insulin Types and Delivery Devices for Diabetes Management
Explore various insulin types and administration devices essential for effective diabetes management. Learn about rapid-acting, long-acting, inhaled insulin, and how insulin pens simplify daily injections. Proper monitoring and appropriate insulin use can significantly enhance quality of life for diabetics.
Sponsored
Insulin Options and Delivery Devices for Effective Diabetes Control
According to the American Diabetes Association, diabetes encompasses several conditions characterized by elevated blood glucose levels. It occurs when the body either cannot produce enough insulin or cannot use it effectively. Insulin, a vital hormone, facilitates the transfer of food-derived glucose into cells for energy. Without sufficient insulin, glucose accumulates in the blood, potentially harming organs such as the kidneys, eyes, nerves, and heart over time.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune disorder destroying pancreatic beta cells that produce insulin, requiring multiple daily insulin injections. It accounts for approximately 5-10% of cases.
Type 2 Diabetes: The most prevalent form, representing 90-95% of cases. It develops when the body doesn't produce enough insulin or can't use it properly. Commonly affecting those over 40, but increasingly diagnosed in younger individuals due to lifestyle factors. Management includes diet, exercise, and medications like insulin pens.
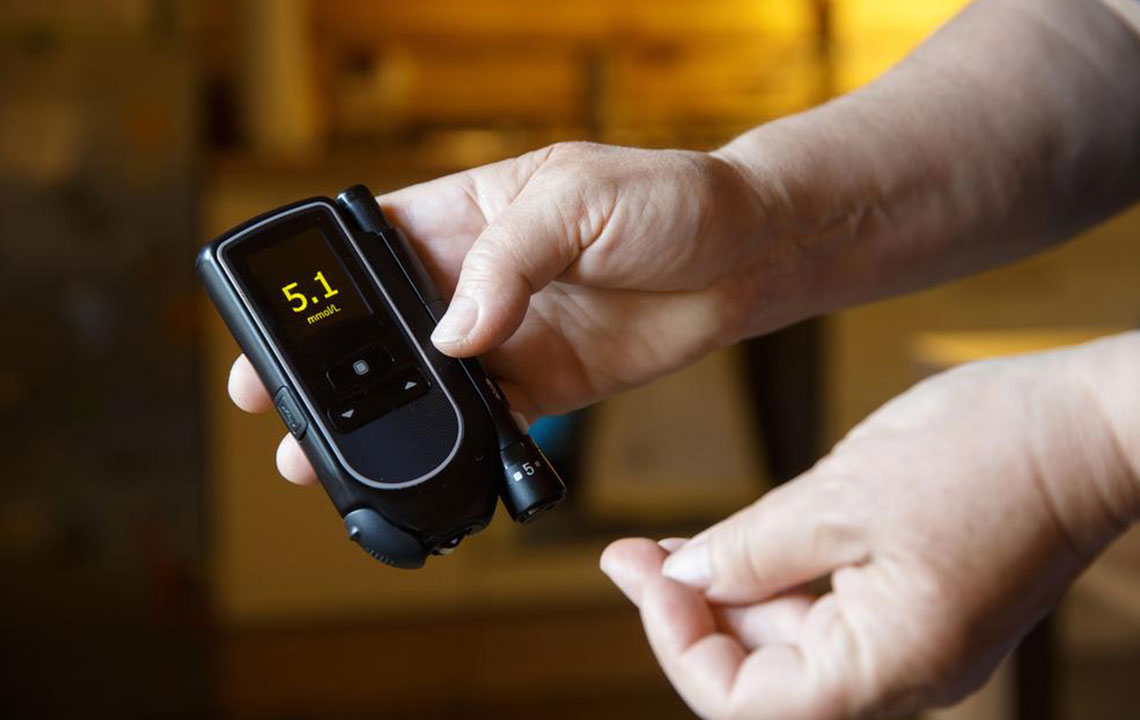
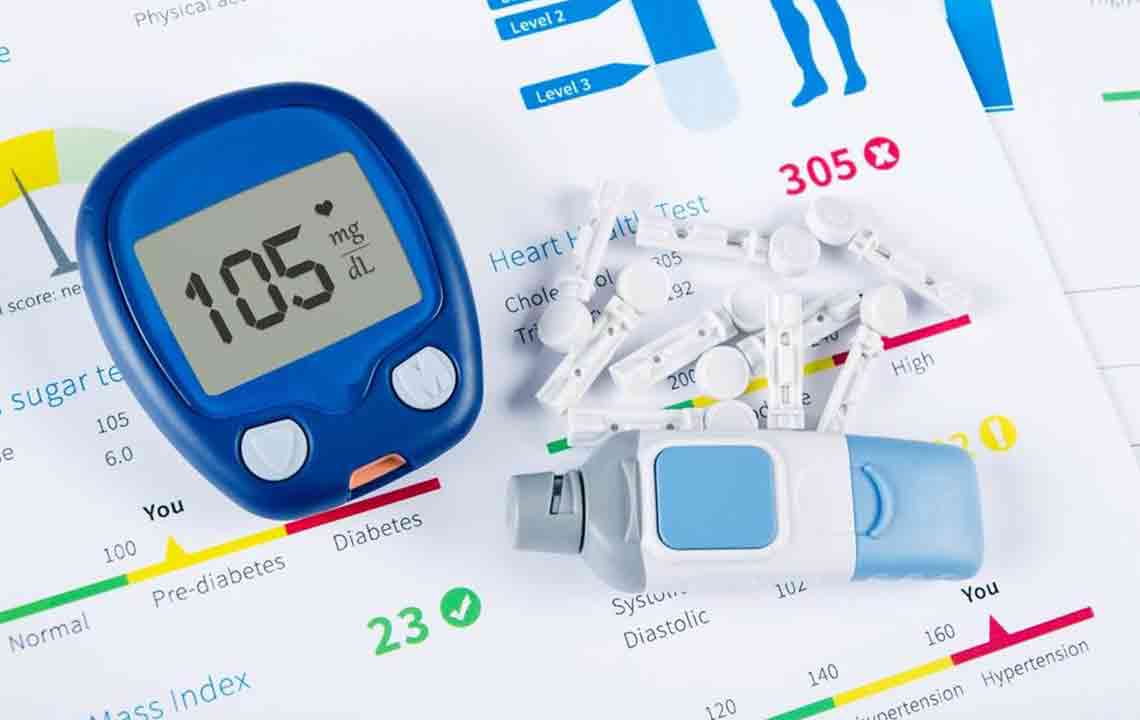
Monitoring blood glucose is essential; diabetic test strips are convenient tools for daily management, making life easier.
Insulin Variants
Rapid-acting insulin: Includes Insulin Glulisine (Apidra), Lispro (Humalog), and Aspart (NovoLog), beginning action within 15 minutes, peaking around an hour, and lasting 2-4 hours.
Regular or short-acting insulin: Humulin R and Novolin R are examples, starting to act within 30 minutes, peaking at 2-3 hours, and working for 3-4 hours.
Intermediate-acting insulin: NPH (Humulin N, Novolin N) reaches activity in 2-4 hours, peaks between 4-12 hours, and lasts about 12-18 hours.
Long-acting insulin: Insulin Detemir (Levemir) and Glargine (Lantus) provide steady glucose control over approximately 24 hours.
Inhaled insulin: Afrezza, using the Technosphere system, starts working within 12-15 minutes, peaks at 30 minutes, and exits in about 3 hours.
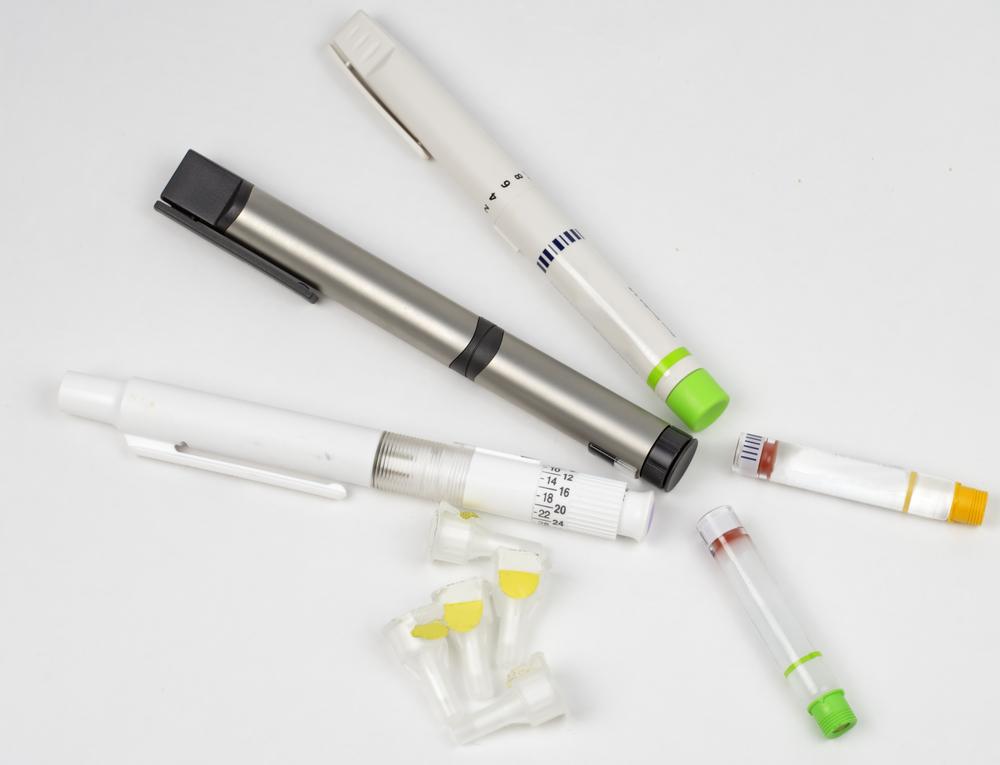
Insulin delivery is often via insulin pens, which contain pre-filled or cartridge-based insulin. The dose is dialed in, and insulin is administered through a needle, similar to syringes. Regularly checking insulin supplies is vital to prevent health complications.