Effective Strategies to Control Acid Reflux Symptoms
Discover practical strategies to control acid reflux effectively. This article covers dietary tips, lifestyle habits, natural remedies, and medical options to reduce symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Learn how small changes in daily routines and diet can provide long-term relief from acid reflux discomfort.
Sponsored

Reflux occurs when stomach acids travel back into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort, commonly known as heartburn. This digestive issue can be alleviated through simple lifestyle adjustments, dietary modifications, and natural remedies, offering long-term relief. Here's how to manage acid reflux effectively.
Home remedies for heartburn
Mild to moderate symptoms can often be eased with natural solutions at home.
Limit certain foods and drinks
Many everyday consumables—including coffee, carbonated drinks, acidic fruits, vegetables, fatty foods, and spicy dishes—can trigger reflux by increasing stomach acid. Reducing intake of these items helps minimize flare-ups.
Watch portion sizes
Overeating stresses the digestive system, leading to increased reflux. Eating smaller meals more frequently, pacing meals, and avoiding heavy eating sessions can significantly lessen symptoms.
Improve sleep habits
To prevent acid flow during sleep, avoid heavy meals before bedtime. Elevating your head with pillows and sleeping on your left side can reduce acid regurgitation, thanks to the natural shape of the digestive tract.
Manage stress levels
Elevated stress boosts cortisol, promoting hormonal imbalance and reflux episodes. Practices such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and relaxation techniques are highly recommended for stress reduction.
Medical treatment options
For mild to moderate cases, lifestyle changes and medications usually suffice. In rare, severe instances, endoscopic procedures or surgery may be necessary for persistent symptoms.
Medications
Antacids, histamine antagonists, proton pump inhibitors, and prokinetic drugs can help control symptoms. However, frequent antacid use might increase stomach acid production, so it should be monitored. Proton pump inhibitors are more powerful, often prescribed when esophageal damage is a concern, while histamine blockers are used to reduce acid production. Prokinetic agents may be combined with other treatments for efficiency.
Procedural interventions
Currently, minimally invasive endoscopic therapies are under study, offering quicker recovery and less pain than traditional surgery. The most common surgical option is Nissen fundoplication, where the upper stomach is wrapped around the esophagus to prevent acid reflux, providing lasting relief. This laparoscopic procedure is less invasive and effective.
Lifestyle modifications
Adjusting daily habits is key—avoiding harmful foods and beverages, maintaining a healthy weight, and reducing abdominal pressure can make a significant difference. Doctors may recommend weight loss and healthy BMI maintenance to lessen reflux triggers.
Foods promoting reflux relief
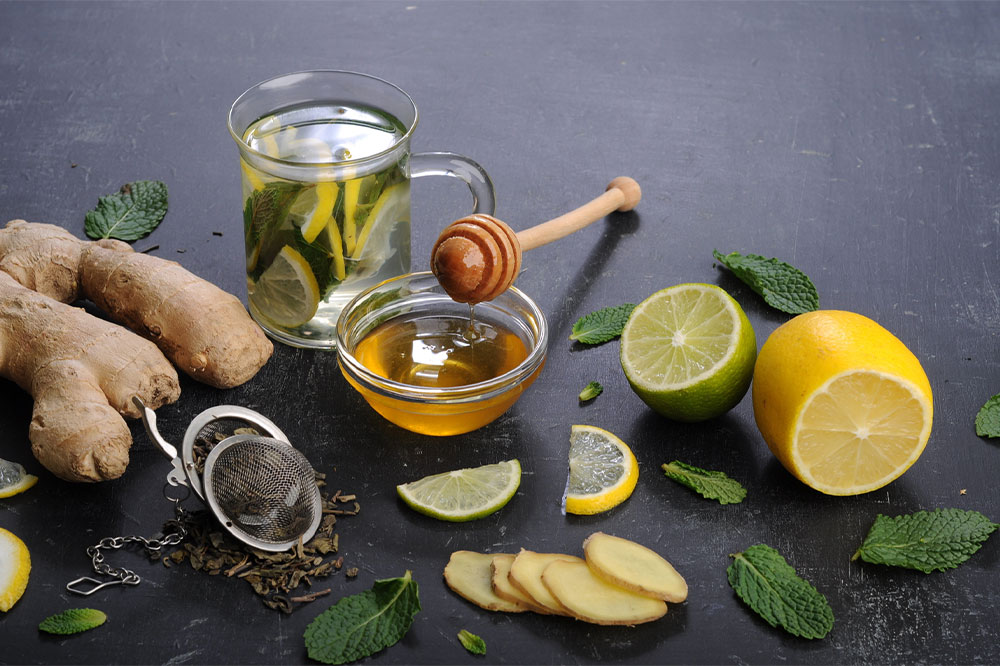
Incorporate fiber-rich foods such as broccoli, chickpeas, lentils, brown rice, whole wheat grains, and oats, as fiber aids digestion and mitigates reflux symptoms. Drinking decaffeinated herbal teas like chamomile, green, or fennel can soothe sudden discomforts. A low-carb diet helps prevent undigested carbs—which produce gas and bloating—from aggravating symptoms. Small dietary changes, coupled with lifestyle habits, can prevent severe flare-ups.