Effective Strategies to Prevent and Manage Rheumatoid Arthritis
Learn effective methods to manage and prevent rheumatoid arthritis through exercise, relaxation, diet, and lifestyle adjustments. Discover foods to include and avoid to reduce inflammation and joint pain, alongside tips to minimize exposure to environmental triggers for better health outcomes.
Sponsored
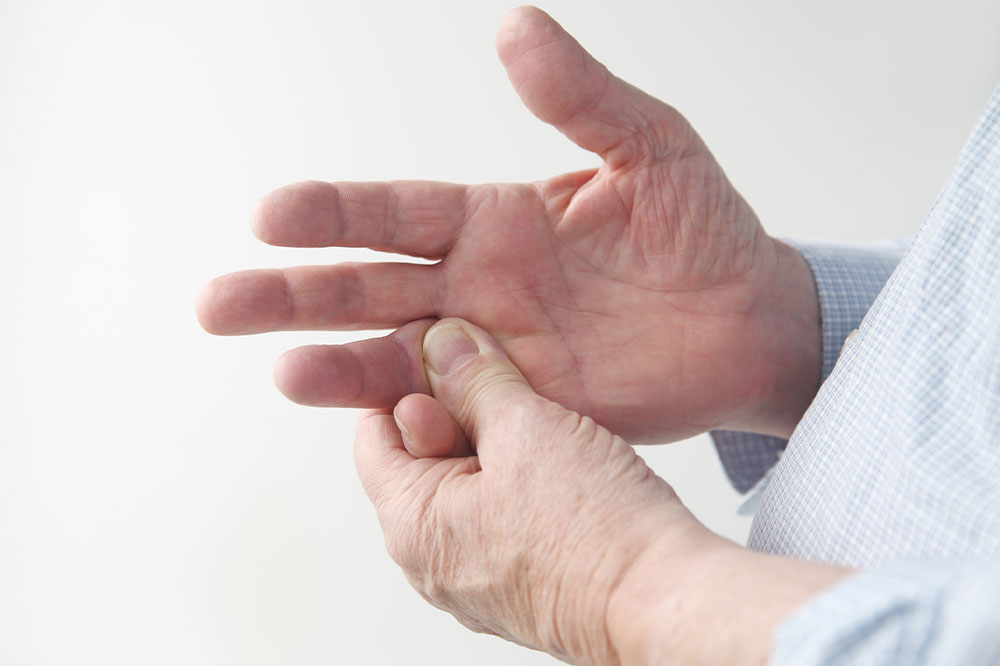
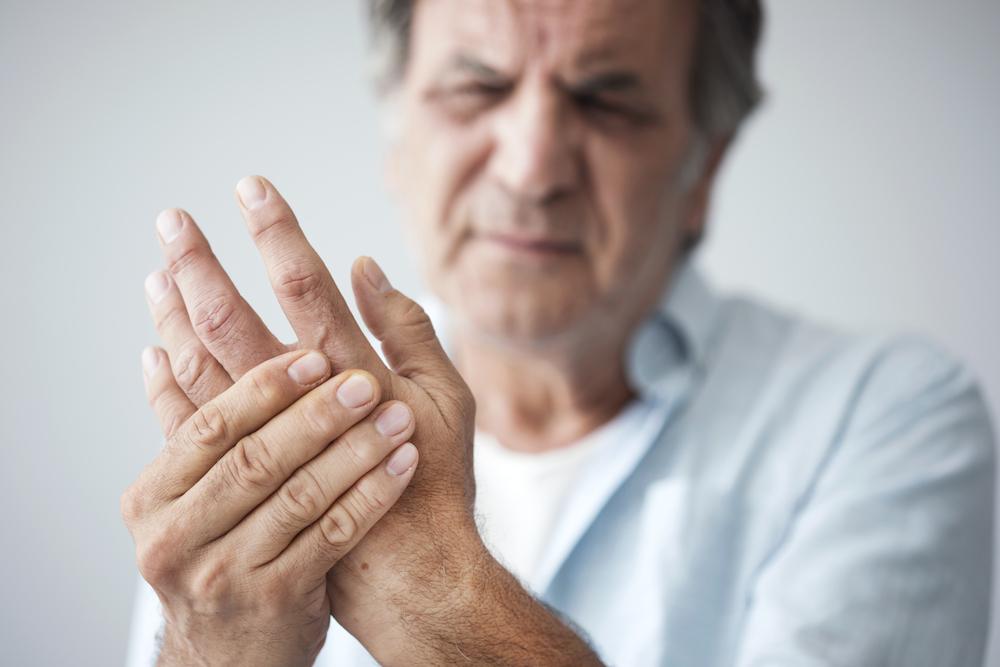
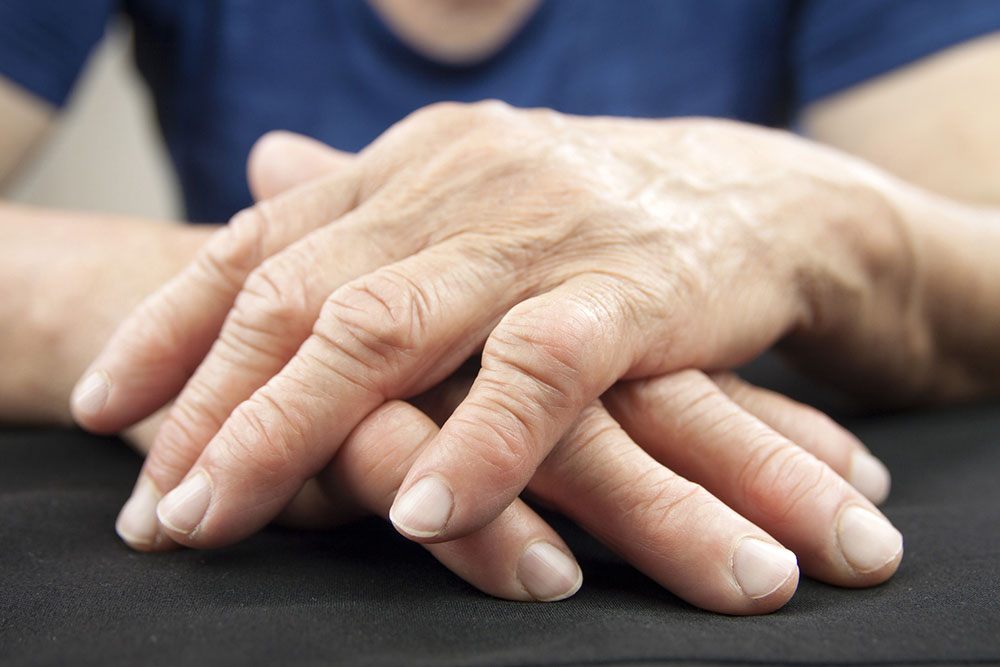
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a prevalent autoimmune disorder characterized by joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced mobility. While the exact cause remains uncertain, factors like genetics, environmental influences, and hormonal changes play a role. Some individuals experience temporary symptoms, while others develop persistent issues. Learning how to manage and prevent RA is essential. Regular physical activity tailored to your needs, relaxation techniques such as yoga, and adopting an anti-inflammatory diet can significantly improve quality of life.
Engage in Consistent Physical Activity
Performing gentle exercises regularly strengthens the muscles surrounding the joints. Consult your healthcare provider to identify suitable activities. Starting with walking or cycling can enhance muscular support and joint health.
Incorporate Relaxation Practices
Relaxation methods like guided imagery, muscle relaxation, and yoga help ease RA symptoms. These techniques reduce stress, which can exacerbate inflammation and joint discomfort.
Practice Tai Chi
Tai chi combines slow movements, stretching, and deep breathing, making it effective in managing stress and improving mood in RA sufferers. Ensure instruction from qualified teachers and avoid movements that increase pain.
Adopt an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Eating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, along with fruits and vegetables like walnuts, strawberries, oranges, kale, and spinach, can help reduce inflammation. Low-fat dairy also supports joint health.
Avoid Environmental Pollutants
Exposure to environmental toxins like industrial chemicals and cleaning agents may trigger or worsen RA in genetically susceptible individuals. Minimizing contact with harmful chemicals is advisable.
Foods That May Exacerbate RA Symptoms
Certain foods can increase inflammation and joint pain, including:
Red Meat: High in saturated fats and omega-6 fatty acids, which can worsen inflammation. Reducing red meat intake may lower joint discomfort.
Fried Foods: Contain unhealthy fats and additives that promote inflammation and obesity.
Processed Foods: Often include sugars, unhealthy fats, and refined ingredients that can aggravate RA symptoms.
Gluten-Rich Foods: Such as wheat, barley, and rye, which may increase RA risk, especially in individuals with celiac disease.