Essential Insights on Managing Cholesterol for Heart Health
Learn essential facts about cholesterol, including its functions, types, and how lifestyle changes like diet, exercise, and weight management can improve your heart health. Understanding LDL and HDL levels helps guide effective strategies for maintaining healthy cholesterol and preventing cardiovascular disease.
Sponsored

Understanding Cholesterol: What You Need to Know
Cholesterol, derived from Greek roots meaning bile and solid, is a waxy, fat-like substance present in all body cells. It plays a vital role in producing hormones, vitamin D, and digestive substances. The body synthesizes all necessary cholesterol, but dietary intake also influences blood levels. Consuming excessive cholesterol-rich foods may elevate blood cholesterol, increasing cardiovascular risk. Cholesterol travels through the bloodstream via lipoproteins, primarily HDL (good) and LDL (bad). Regular blood testing helps monitor these levels to maintain heart health. A balanced diet emphasizing healthy fats, physical activity, and weight management is key to controlling cholesterol and reducing disease risk.
Excessive dietary cholesterol can lead to higher blood levels, raising the risk of arteriosclerosis and heart disease. It’s natural for everyone to have cholesterol in their bodies, essential for cell structure and hormone production.
Cholesterol is transported via lipoproteins—HDL and LDL. The LDL cholesterol, often called 'bad' cholesterol, can accumulate in arteries, causing blockages, while HDL helps remove excess cholesterol, promoting arterial health.
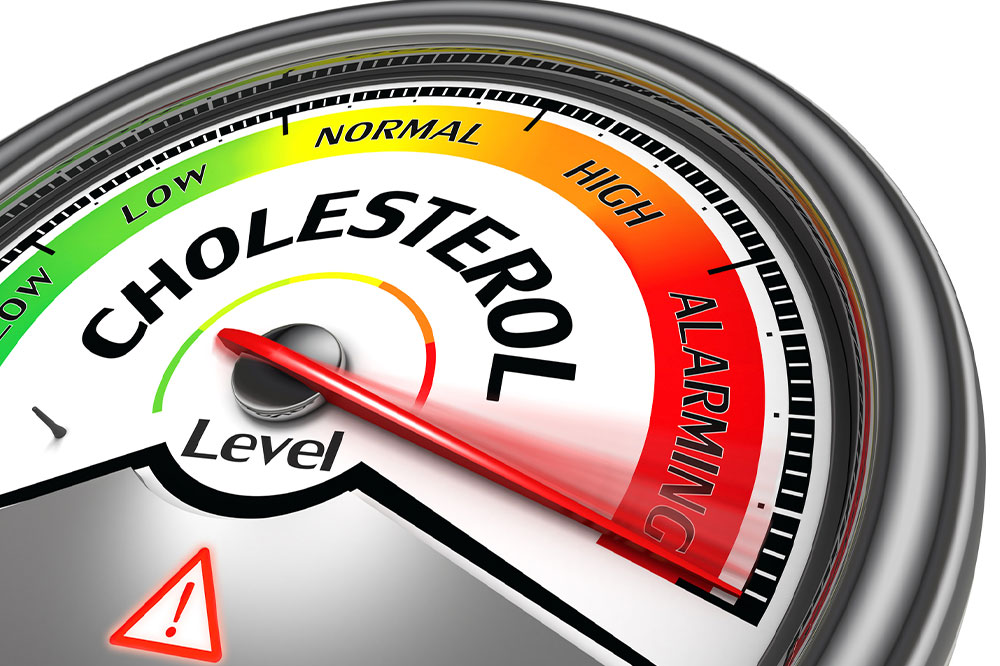
Blood tests measuring LDL and HDL levels are crucial—ideally, LDL should be below 100 mg/dL, and HDL should range between 40-60 mg/dL. Increasing HDL levels through lifestyle choices offers cardiovascular protection.
To improve cholesterol, adopt a diet rich in soluble fiber from oats, fruits, and vegetables, while reducing trans fats from processed foods. Moderate saturated fat intake from red meats and dairy is advised. Regular exercise, weight control, and incorporating heart-healthy foods like nuts, fish, and olive oil can boost HDL and reduce LDL.
Additional dietary tips include using spices like garlic and turmeric, enjoying moderate red wine, and choosing dark chocolates with high cocoa content. Substituting soy for fatty meats and consuming fiber-rich beans further supports heart health. For persistent issues, consult a healthcare provider for medical intervention options.