Identifying Risk Factors for Receding Gums
This article explores the key risk factors for receding gums, including poor oral hygiene, smoking, teeth grinding, and genetics. Emphasizing the importance of good oral care and regular dental visits, it provides practical tips to prevent and manage gum recession, safeguarding both oral and overall health.
Sponsored
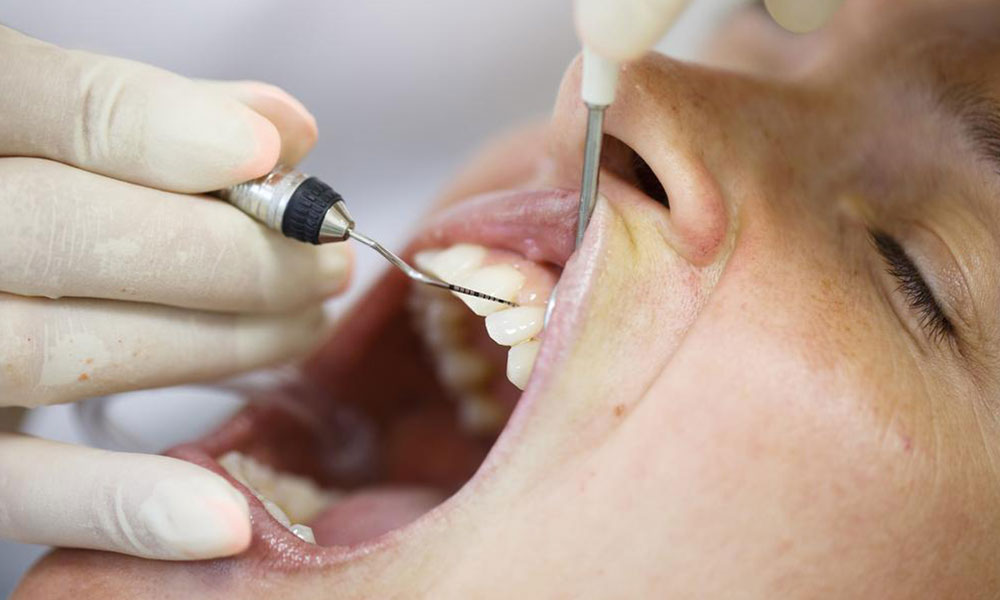
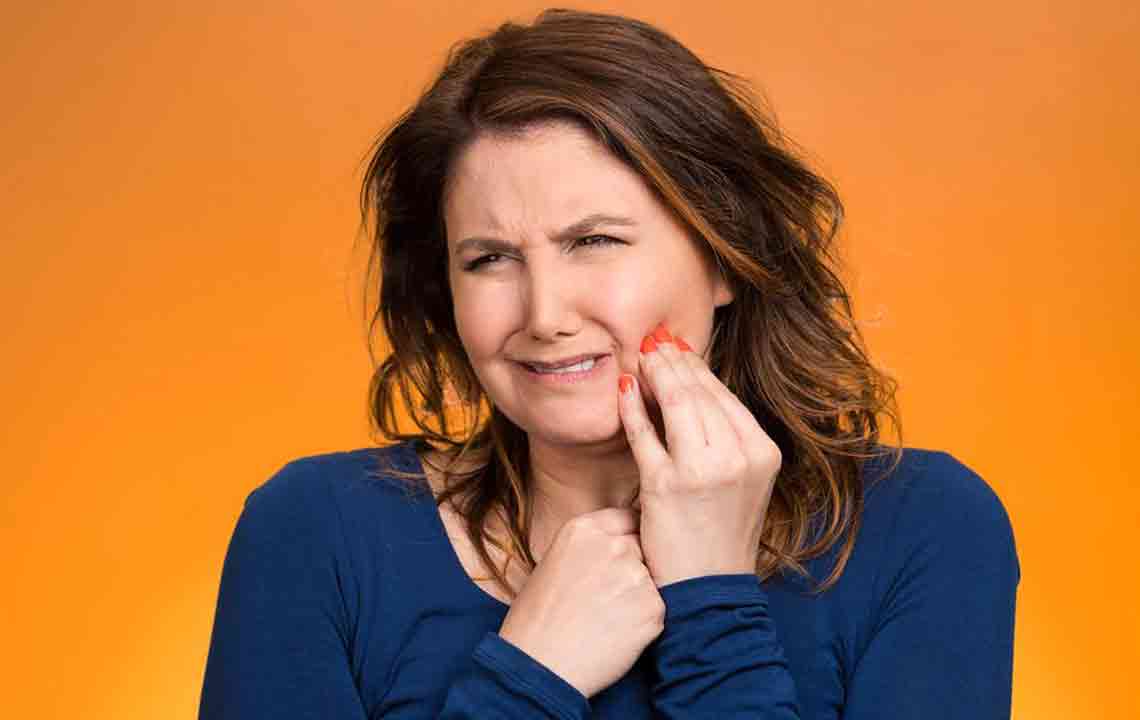
Understanding Who Is Prone to Receding Gums
Gums play a vital role in overall oral and systemic health. When food residues are not thoroughly cleaned from teeth, they can form plaque, producing toxins that irritate and cause inflammation of the gums. Persistent inflammation can lead to periodontal disease, affecting tissues like gums, tooth roots, ligaments, and bones. Such conditions increase the risk of cardiovascular and respiratory issues. Recognizing risk factors and maintaining proper oral hygiene are essential steps to prevent gum recession and protect overall well-being.
Smoking significantly contributes to gum recession. The chemicals in tobacco can deteriorate gum tissue, and if recession has begun, smoking may accelerate it, potentially leading to irreversible damage requiring costly surgical intervention. Additionally, frequent teeth grinding and clenching can exert excessive pressure on gums, promoting recession. Breaking these habits gradually can greatly help in reversing or preventing gum recession. Genetics may also play a role, but consistent oral care can mitigate risks.
Preventing gum recession involves attentive oral hygiene practices such as brushing twice daily with proper technique, flossing, rinsing after meals, and scheduling regular dental check-ups. Early detection and professional guidance can address emerging issues effectively, reducing the need for invasive procedures and maintaining healthy gums for overall health.