Key Insights Into Persistent Bronchitis-Related Cough
Explore essential facts about chronic bronchitis cough, including symptoms, diagnosis, prevention tips, effective home remedies, and measures to prevent spreading the illness. Learn how lifestyle changes and medical care can help manage this lung condition caused by smoking and pollution exposure.
Sponsored
A cough caused by bronchitis stems from inflammation within the bronchial tubes, which facilitate airflow to and from the lungs. The cough can be categorized as either acute or chronic, based on symptom duration. Acute bronchitis usually results from viral or bacterial infections, associated with colds and flu. Conversely, chronic bronchitis is primarily linked to smoking and prolonged exposure to pollutants, toxic gases, and airborne particles. This condition, common among smokers, leads to breathlessness, fatigue, and chest discomfort.
While complete cures are unavailable, medical treatments and lifestyle modifications can help ease symptoms. Learn about diagnosis methods, preventative strategies, home remedies, and precautions to stop disease spread.
Home remedies for managing chronic bronchitis cough
Eat foods rich in probiotics and anti-inflammatory properties, such as fresh fruits and vegetables, bone broth, yogurt, kefir, kombucha, sauerkraut, and coconut kefir to support immune health and reduce mucus production.
Avoid mucus-aggravating foods like processed sugar, fried items, and dairy products.
Boost your vitamin C intake by incorporating kale, oranges, strawberries, kiwis, bell peppers, and other citrus fruits into your diet.
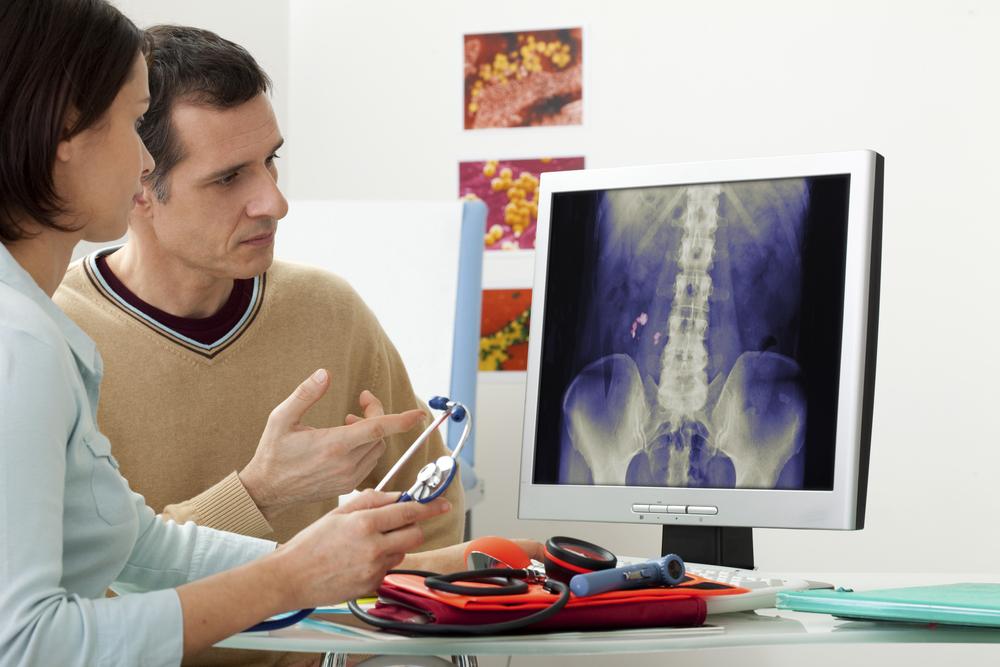
Diagnosing chronic bronchitis cough can be challenging initially due to overlapping symptoms with common colds. Healthcare providers often perform chest X-rays, especially in smokers or former smokers, to assess lung health. Sputum analysis and pulmonary function tests using spirometry are also instrumental in diagnosis, measuring airflow and lung capacity.
Prevention strategies for chronic bronchitis
Although there's no guaranteed way to prevent chronic bronchitis, quitting smoking significantly reduces risk; benefits increase over time, often after five years.
Minimize exposure to secondhand smoke, airborne fumes, dust, and pollutants that can harm lung health.
Annual flu and pneumonia vaccinations are recommended to prevent complications that could lead to bronchitis development.
Preventing disease transmission
Chronic bronchitis is not contagious, but precautions should be taken to prevent infection spread.
Avoid close contact with affected individuals and do not share personal items such as towels, utensils, or grooming tools.
Use gloves and masks when cleaning or handling items used by an infected person.
Wash hands thoroughly and refrain from touching face, eyes, or mouth to reduce infection risk.