Effective Strategies for Managing Osteoporosis
Learn effective ways to manage osteoporosis through medications like EVENITY® and Prolia®, dietary adjustments rich in calcium and vitamin D, and safe, regular exercise routines. This guide provides practical tips to strengthen bones, prevent fractures, and improve overall health for those affected by osteoporosis.
Sponsored

Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones that become porous and brittle, significantly increasing fracture risk. Approximately 54 million individuals are affected by this condition worldwide. Although it impacts both genders, women, especially postmenopausal women, are more prone to developing osteoporosis. This article highlights practical management techniques to alleviate symptoms and improve bone health through various treatments and lifestyle adjustments.
Treatment Options
EVENITY® – A popular medication for postmenopausal osteoporosis, EVENITY® helps decrease fracture risk by limiting bone loss and promoting new bone growth. The standard dose is one injection every two weeks, showing notable improvements over time.
Prolia® – Containing denosumab, Prolia® is used to strengthen bone density and prevent fractures in individuals with low bone mass. Administered via a 1 ml pre-filled syringe every six months, this treatment slows bone deterioration effectively.
Nutritional Tips
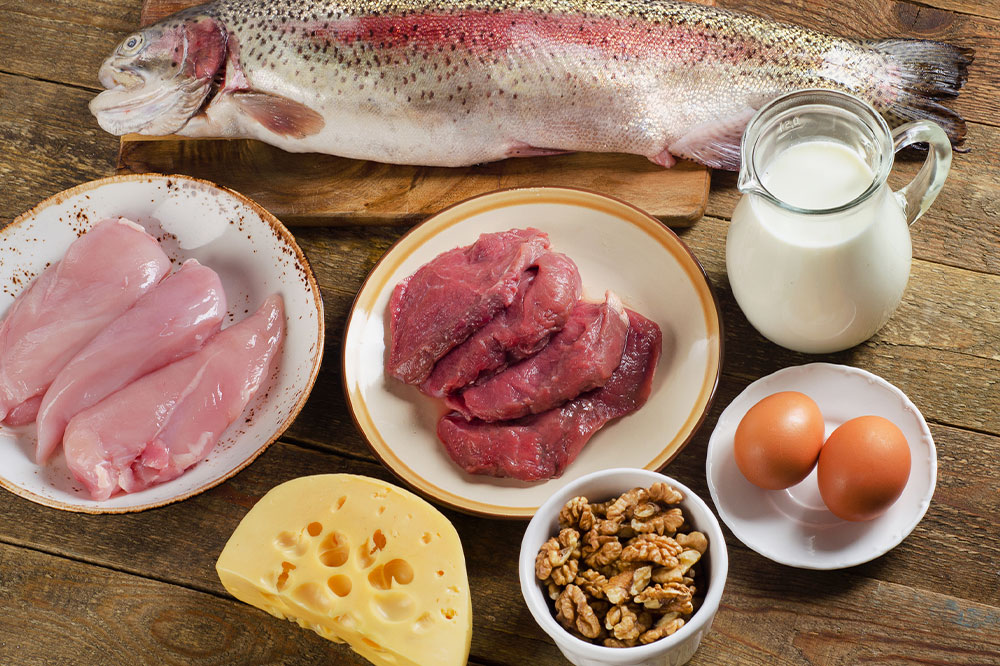
Patients are advised to incorporate calcium- and vitamin D-rich foods into their daily diet, as these nutrients are essential for bone health. Nut and seed snacks, dairy products, vegetables, and lean proteins should be staples. To avoid worsening osteoporosis, it’s important to limit foods high in refined sugars, sweets, and salty processed snacks.
Exercise Guidelines
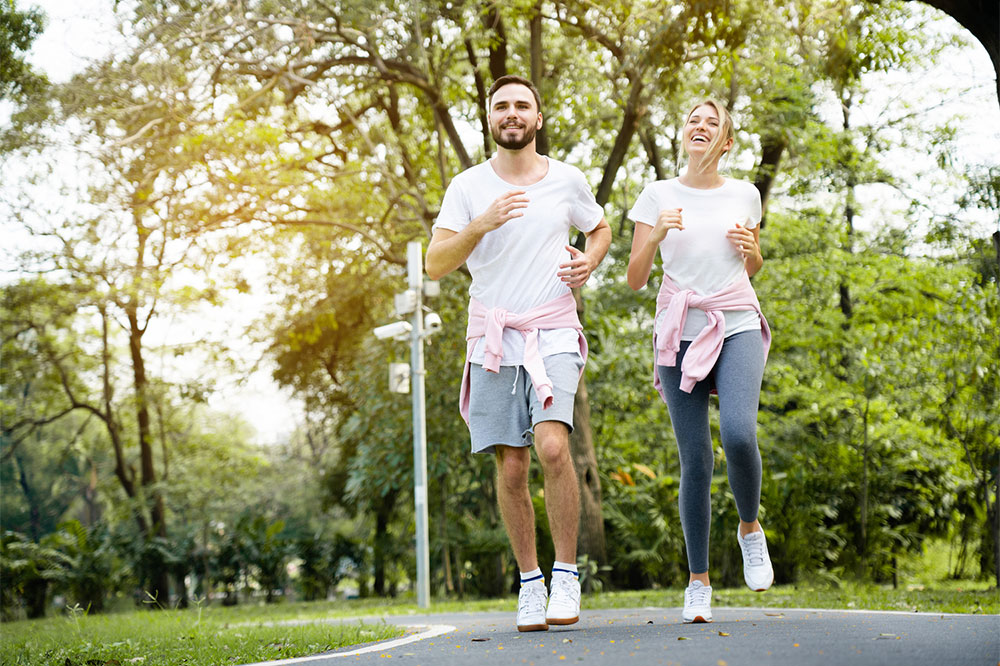
Engaging in regular physical activity is vital regardless of age. Low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, and jogging help maintain bone strength. For variety, activities like hiking or trekking can be beneficial. However, high-impact exercises such as weightlifting or intense workouts should be avoided to prevent joint strain or injury.