Recognizing the Key Indicators of Sarcoidosis
This article discusses the key signs and symptoms of sarcoidosis, an inflammatory disease affecting multiple organs. It highlights common symptoms like skin changes, respiratory issues, eye and heart problems, and explains the disease's nature, diagnosis, and prognosis. Recognizing these indicators can aid early detection and management, even though there is no definitive cure. The article serves as a comprehensive guide for understanding sarcoidosis's diverse manifestations and the importance of medical evaluation.
Sponsored

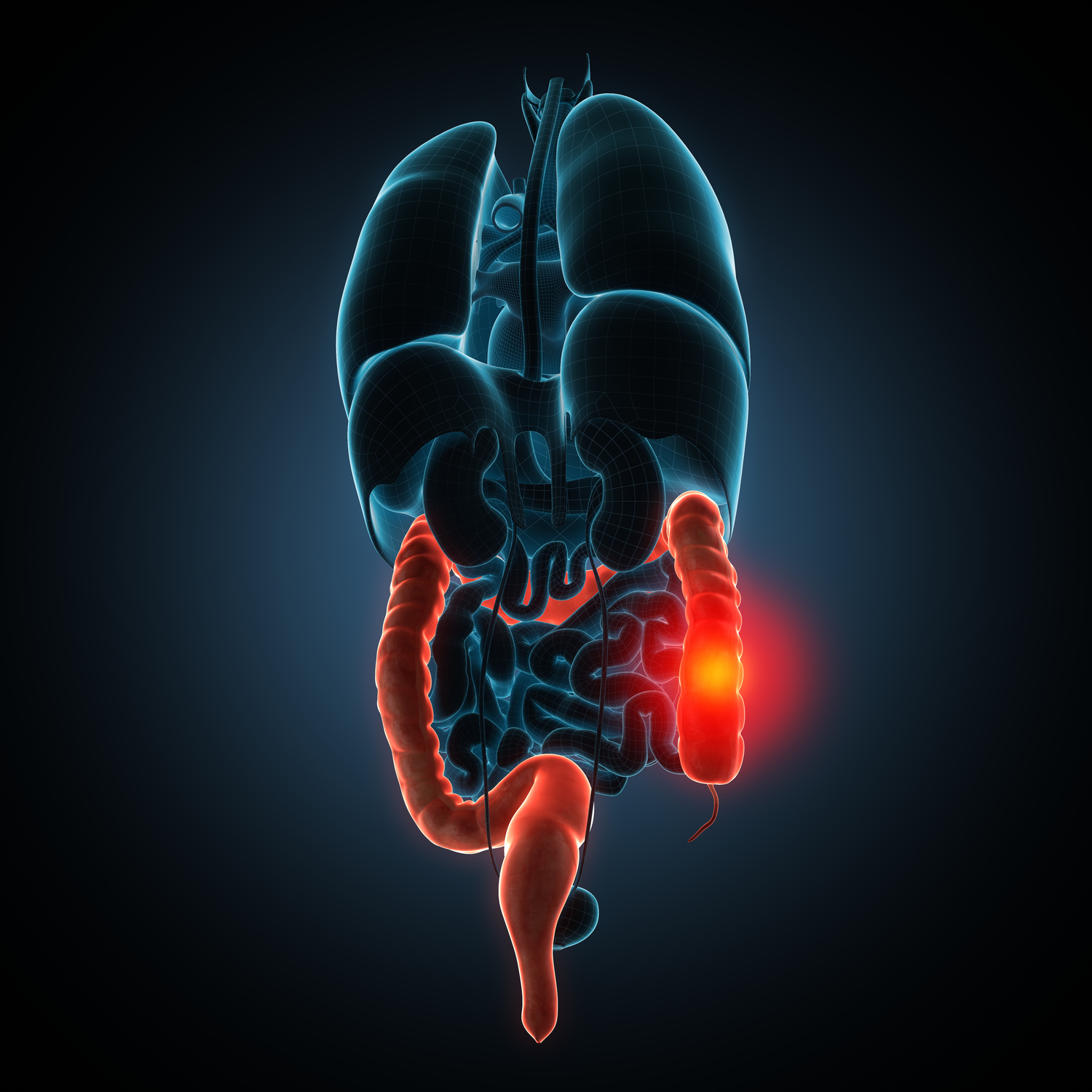
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory condition triggered by the immune system's reaction to foreign particles such as dust, bacteria, viruses, or chemicals. This disease leads to the formation of granulomas—clusters of inflammatory cells—in various organs, disrupting their normal functioning. Commonly affected areas include lymph nodes, eyes, skin, liver, spleen, brain, lungs, and heart. Symptoms vary based on the organ involved and can develop gradually or suddenly, sometimes remaining asymptomatic until discovered via imaging.
While there is no guaranteed cure, many cases see spontaneous resolution of granulomas without intervention. However, in rare instances, the disease becomes chronic, causing long-term damage. Typical symptoms often affect individuals between 20 and 40 years old but can vary widely.
Common symptoms include:
General symptoms: Fatigue, fever, joint discomfort, unexplained weight loss, dry mouth, nosebleeds, and swollen lymph nodes or abdominal swelling.
Respiratory issues: Chest pain, wheezing, persistent dry cough, and shortness of breath are frequent in lung involvement.
Skin changes: Tender red or purple bumps on shins or ankles, lesions on the face, darkening or lightening areas of skin, or nodules near tattoos or scars.
Eye problems: Often asymptomatic but may include redness, light sensitivity, blurred vision, or eye pain.
Heart symptoms: Fainting, irregular heartbeat, chest discomfort, fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling may indicate cardiac sarcoidosis.