Effective Strategies to Reduce Hemoglobin A1C Levels in Diabetes
This article outlines practical and effective methods for lowering A1C levels in diabetics, emphasizing consistent habits such as dietary regulation, regular exercise, hydration, weight management, and stress reduction. It provides actionable tips suitable for managing blood sugar over the long term, helping individuals improve their health status and prevent complications associated with high A1C levels.
Sponsored

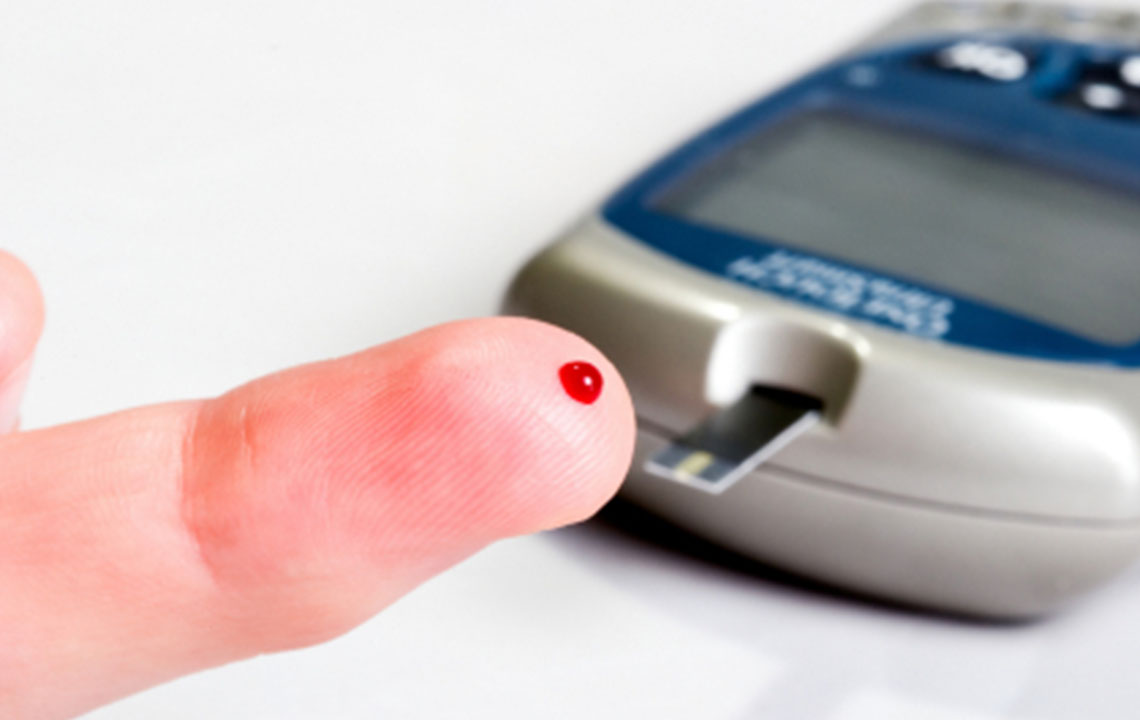
Modern lifestyles and busy schedules are impacting overall health, leading to issues such as obesity, hormone imbalances, and fluctuating blood sugar levels. Recent medical studies show a rising prevalence of type 2 diabetes across all ages and genders. To manage blood sugar over the past few months, healthcare providers recommend A1C testing. Unlike fasting or post-meal tests, A1C reflects long-term glucose control. While quick dietary changes may not significantly lower A1C, implementing consistent habits can make a difference. Below are practical tips to help lower your A1C effectively.
Maintain Regular Meal Times — Consistency in eating schedules is crucial for blood sugar management. Avoid skipping meals, especially breakfast, as irregular eating patterns can cause blood sugar spikes and fluctuations in A1C levels.
Adopt a Well-Balanced Diet — It's essential to consume a diet rich in carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, and minerals in appropriate proportions. If planning meals is challenging, consult a nutritionist and follow a tailored diet plan. Measuring servings helps prevent overeating, which can adversely affect blood sugar control.
Incorporate Fruits Daily — Fruits like berries, grapes, and cranberries are beneficial for diabetics. They help regulate blood glucose levels and support heart health without causing significant sugar spikes.
Avoid Processed and Junk Foods — Processed foods, sweets, fast foods, and sugary drinks can disrupt digestion and increase blood sugar. Limit or eliminate these from your diet to maintain stable A1C levels and overall health.
Keep Diabetic Snacks Handy — For busy individuals, having diabetic-friendly bars and shakes can prevent missed meals and help maintain balanced blood sugar levels during hectic routines.
Switch to Green Tea — Replacing sugary beverages with green tea can aid in controlling blood sugar and improving insulin sensitivity, making it a healthy alternative for diabetics.
Ensure Adequate Hydration — Drinking sufficient water is vital, especially since dehydration can result from frequent urination caused by high blood sugar. Proper hydration supports overall health and aids in lowering A1C.
Maintain Healthy Weight — Weight management is critical in controlling blood sugar. Obesity increases diabetes risk; hence, targeted weight loss can positively influence A1C levels. Regular BMI checks and healthy weight goals are recommended.
Engage in Regular Exercise — Physical activity like brisk walking, yoga, or light workouts enhances blood sugar regulation. Aim for at least 20-30 minutes daily to support long-term diabetes control.
Early diagnosis and lifestyle adjustments are key to managing diabetes effectively. Managing stress and monitoring blood sugar regularly are also important. Implement these strategies to achieve better A1C results and improve overall health.