Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
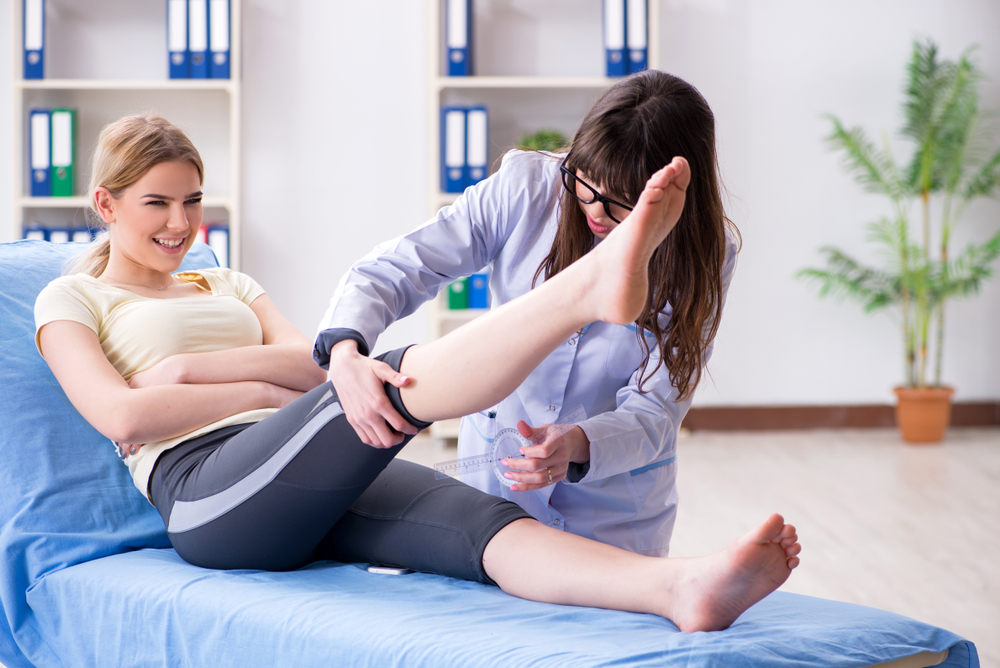
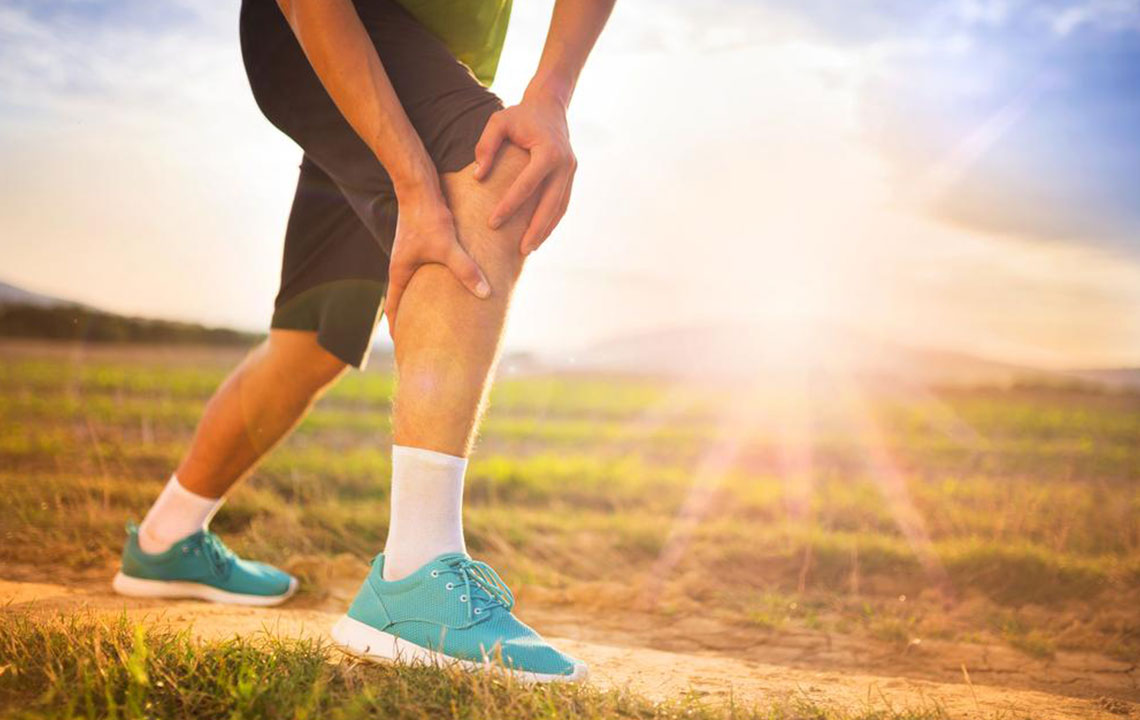
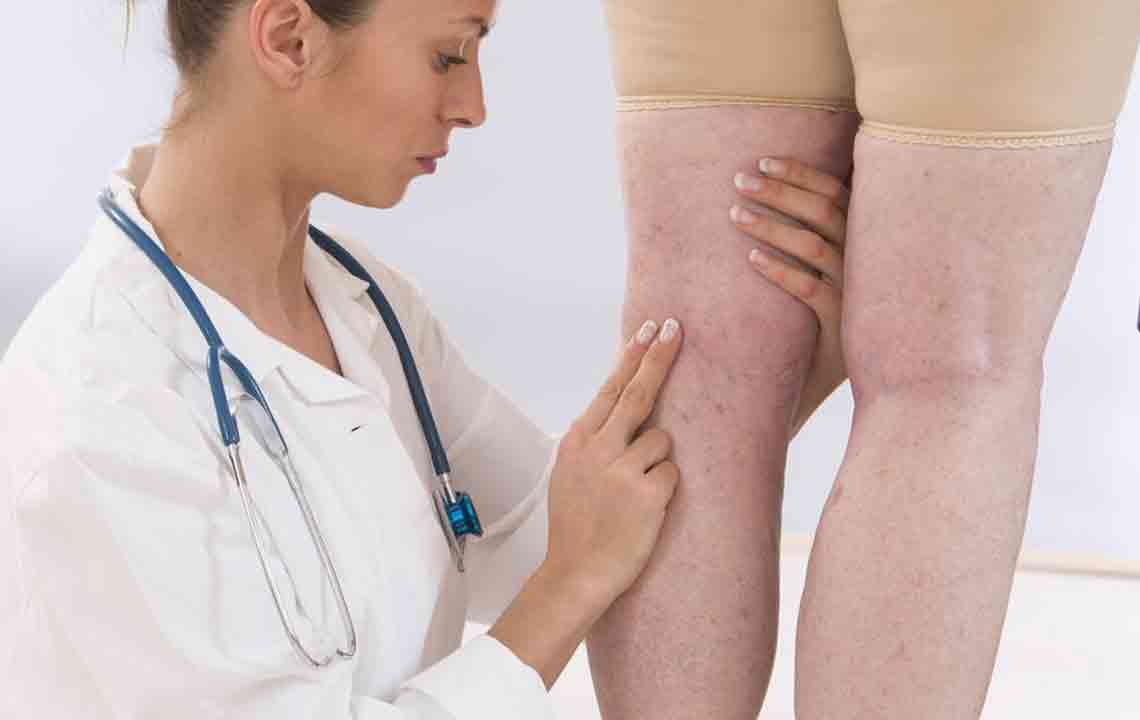
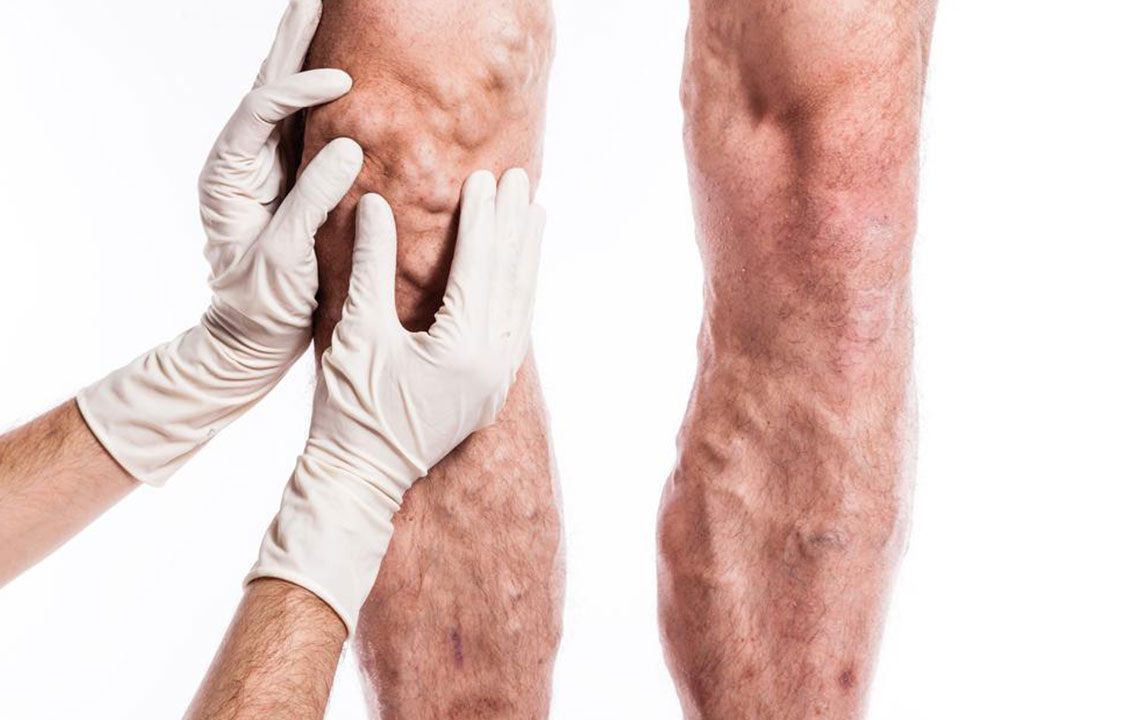
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition characterized by blood clots in deep veins, mainly in the legs. Risk factors include inactivity, injuries, pregnancy, and genetics. Symptoms often include leg swelling, pain, redness, and warmth. If untreated, DVT can lead to pulmonary embolism, a dangerous complication. Treatment involves anticoagulants such as Warfarin and Heparin to prevent clot growth and recurrence. Early detection and treatment are vital for preventing severe health consequences.
Sponsored
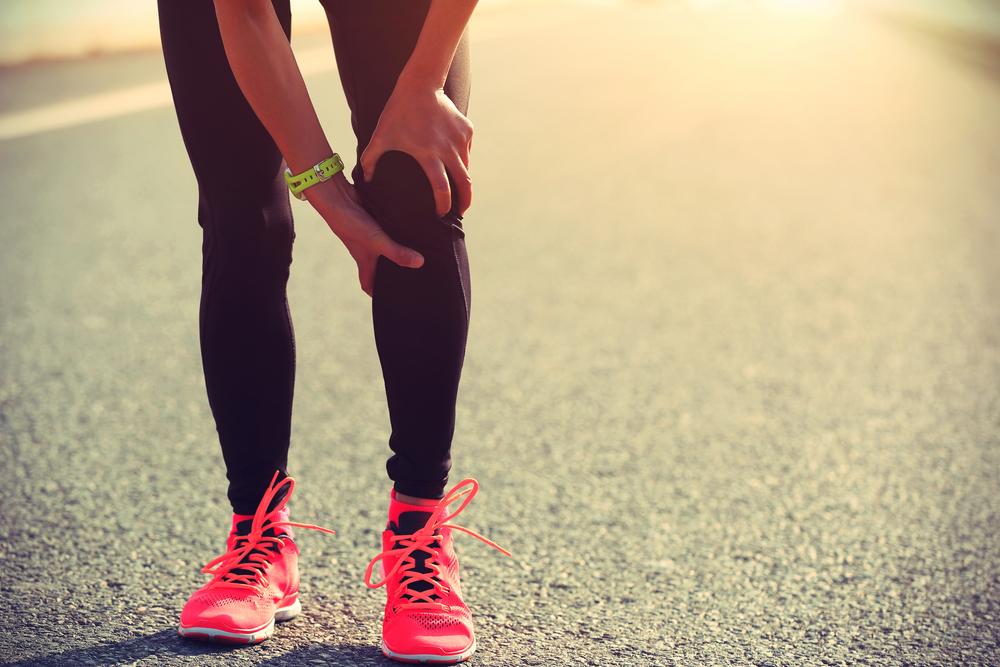

Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) involves blood clot formation within the deep veins, often in the legs. Conditions like prolonged inactivity, injury, or surgery increase the risk of clots developing. Age over 40, pregnancy, genetic factors, certain medications, and medical conditions such as cancer or heart disease also contribute. Symptoms include leg swelling, pain, warmth, and redness. If untreated, a clot can travel to the lungs, causing a life-threatening pulmonary embolism. Treatment primarily involves blood thinners like Warfarin and Heparin to prevent clot growth and recurrence.