Recognizing the Key Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
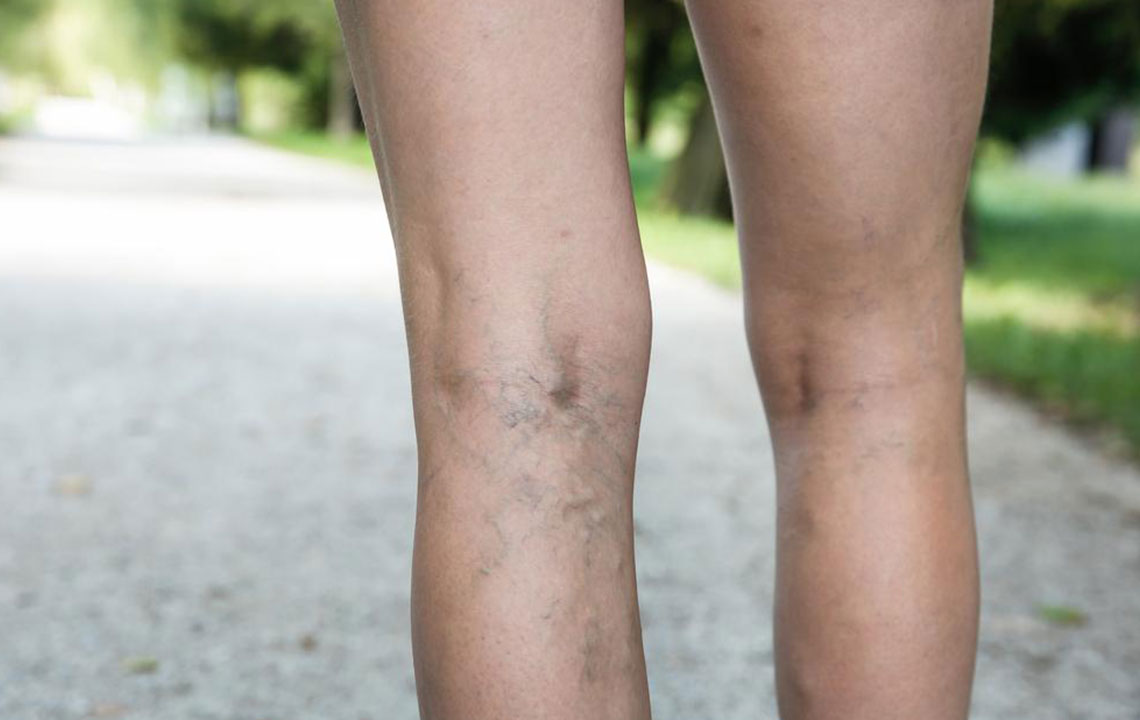
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) involves blood clots deep in veins, causing swelling, pain, and risk of embolism. Early detection through symptoms like leg swelling and warmth is essential for effective treatment and avoiding severe complications such as pulmonary embolism. Medical diagnosis and timely intervention with blood thinners or surgical options are crucial for patient safety.
Sponsored
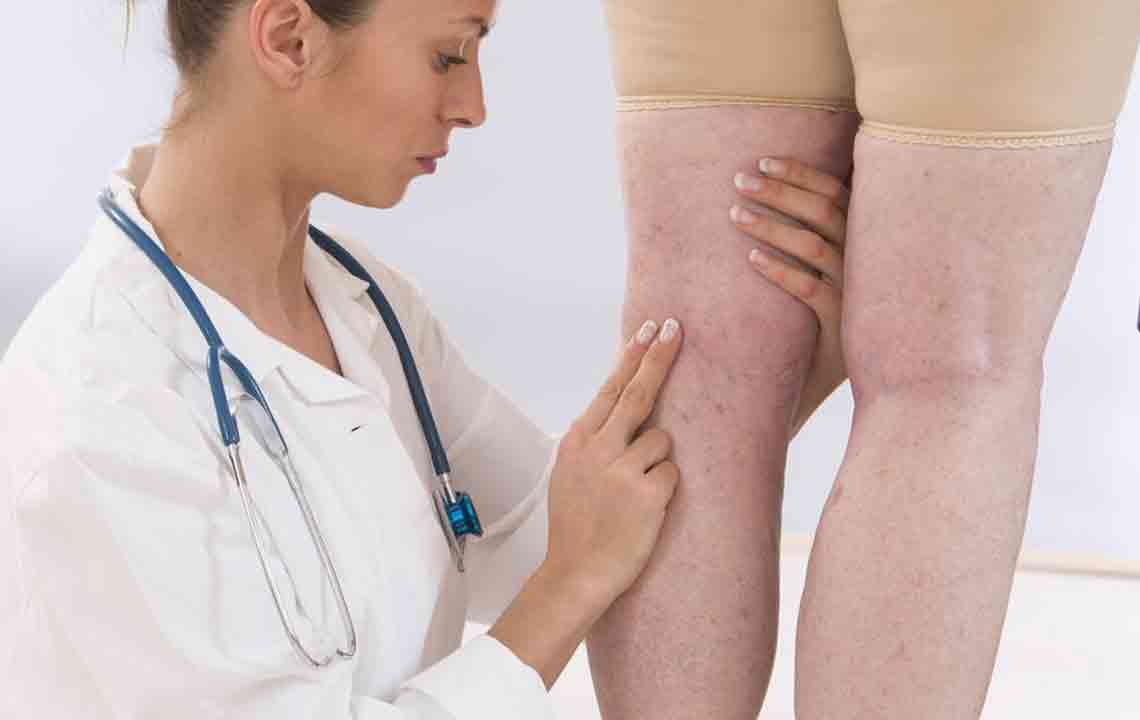
Understanding Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot forms in the deep veins, often in the legs or thighs. These clots are solid blood accumulations that can pose serious health risks. DVT is more common in individuals over fifty, influenced by blood flow and lifestyle factors. Common causes include previous vein injuries, obesity, genetic predisposition, hormonal treatments, smoking, prolonged immobility, and catheter placement. Recognizing symptoms early is crucial to prevent complications like pulmonary embolism, which can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and fainting.
Symptoms may include leg swelling, tenderness, warmth, and skin discoloration. Sometimes, patients remain symptom-free until a pulmonary embolism occurs, leading to severe breathing issues, chest pain, or collapse. DVT mostly affects one leg, with pain worsening when bending the knee or foot. If untreated, it can result in life-threatening embolisms. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical exams, and specific tests to differentiate DVT from other conditions. Prompt treatment, including blood thinners or filters, is vital to prevent complications.