Comprehensive Guide to Deep Vein Thrombosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
This article explores deep vein thrombosis (DVT), highlighting its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of early detection to prevent severe complications like pulmonary embolism. Key risk factors include immobility, pregnancy, and obesity, with treatments such as blood thinners, compression stockings, and clot-busting medications. Understanding DVT aids in prevention and timely intervention, safeguarding health.
Sponsored

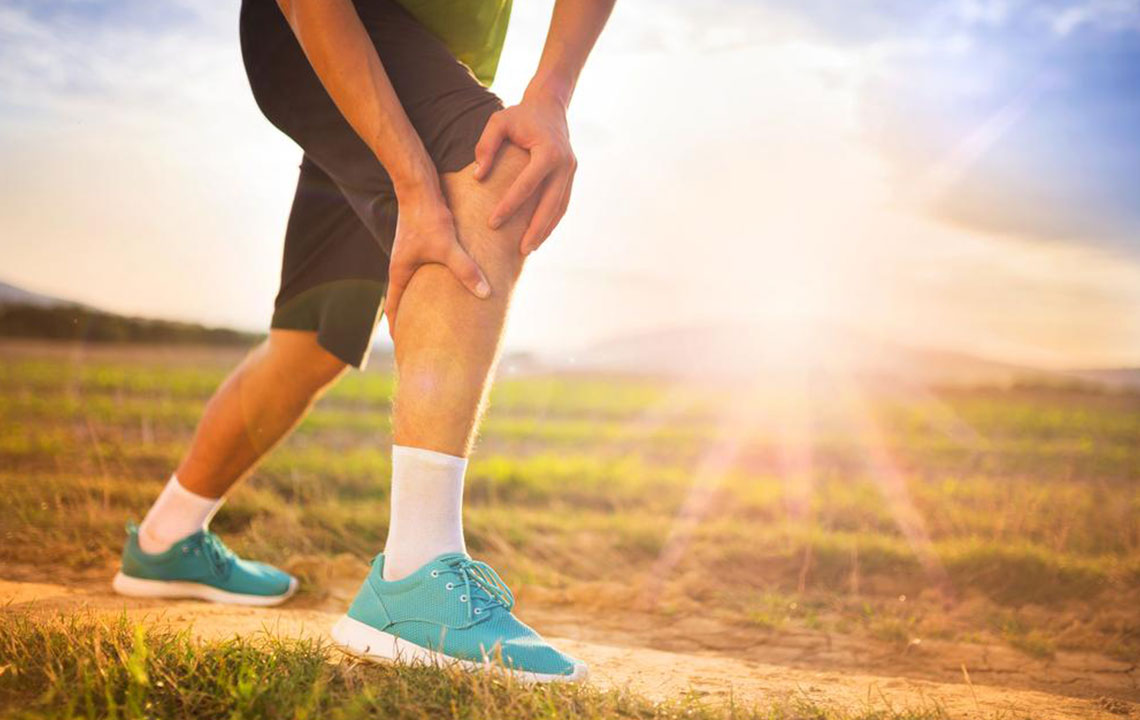
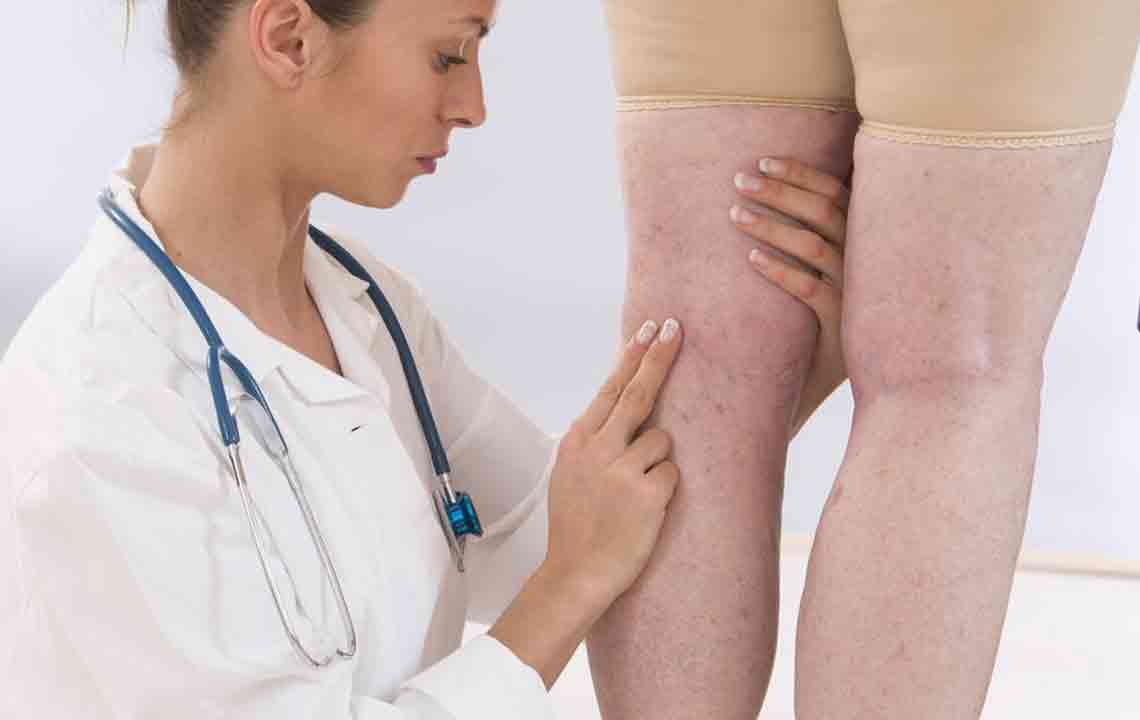
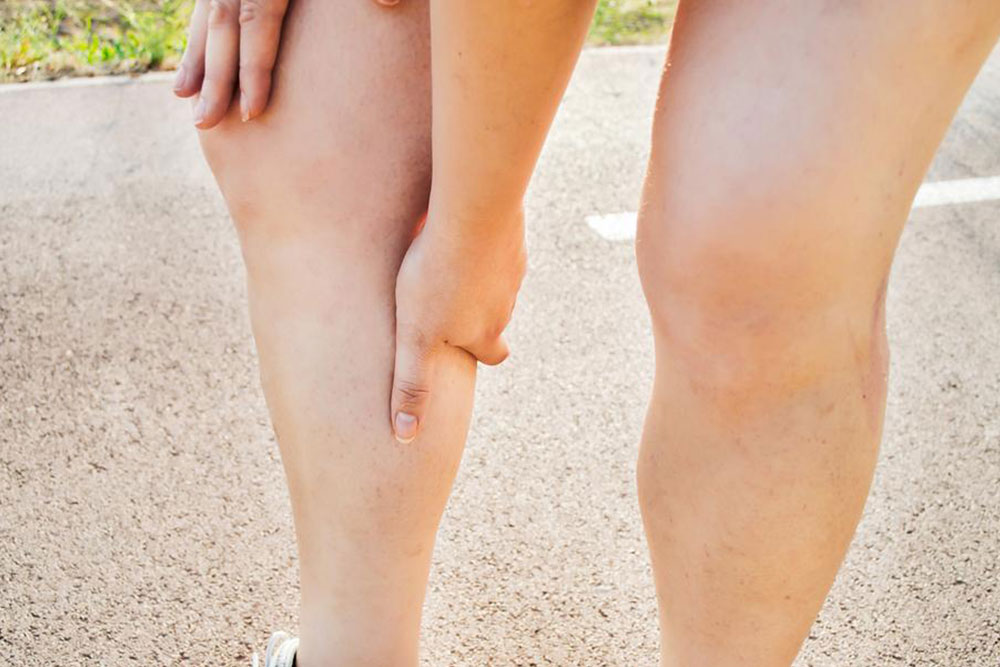
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) often goes unnoticed due to its subtle symptoms, but it involves the formation of blood clots within veins, frequently in the thigh area. This condition is linked to several health issues like post-thrombotic syndrome and thromboembolism. Causes include prolonged immobility, pregnancy, obesity, and genetic predisposition. Symptoms may include leg pain, swelling, discoloration, warmth, and tenderness, though they are often mild. Diagnosis involves blood tests, ultrasounds, CT scans, and venography. If untreated, DVT can lead to pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening complication. Treatment options include clot-busting drugs, compression stockings, and blood thinners, aimed at preventing clot growth and reducing symptoms. Awareness can help in early detection and prevention, especially through maintaining mobility and managing risk factors.