Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Risks
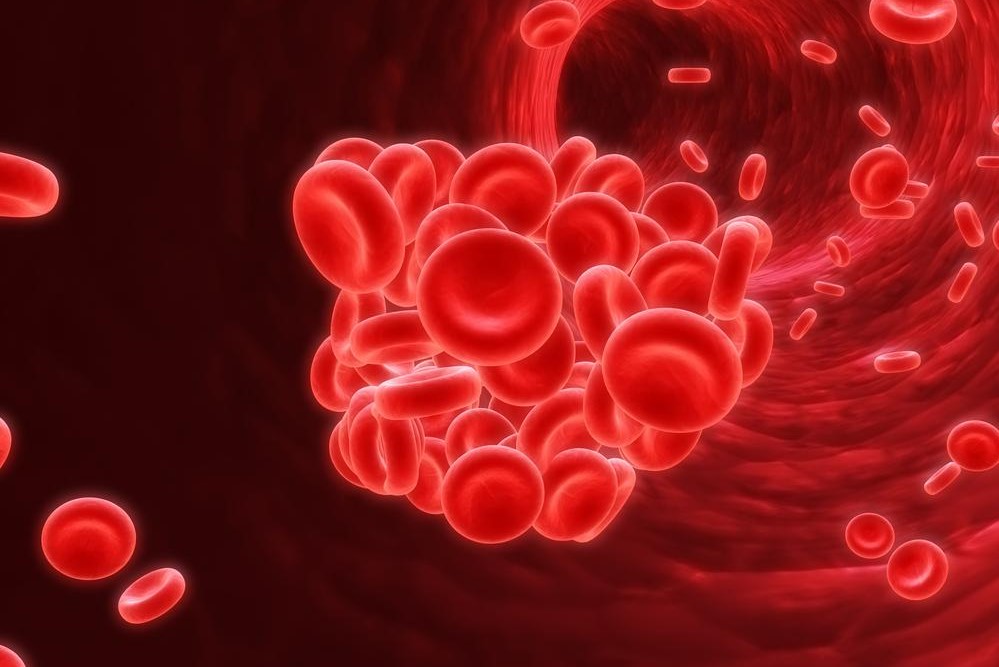
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can cause serious health issues if untreated. It involves blood clots forming in deep veins, mainly in the legs, with symptoms like pain, swelling, and warmth. Risk factors include age, immobility, pregnancy, obesity, and certain health conditions. Recognizing early signs and seeking prompt medical care can prevent complications like pulmonary embolism. Preventative measures include staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding prolonged inactivity. Anticoagulant therapy is commonly prescribed to manage DVT and reduce risks. Awareness and timely treatment are essential for health safety.
Sponsored

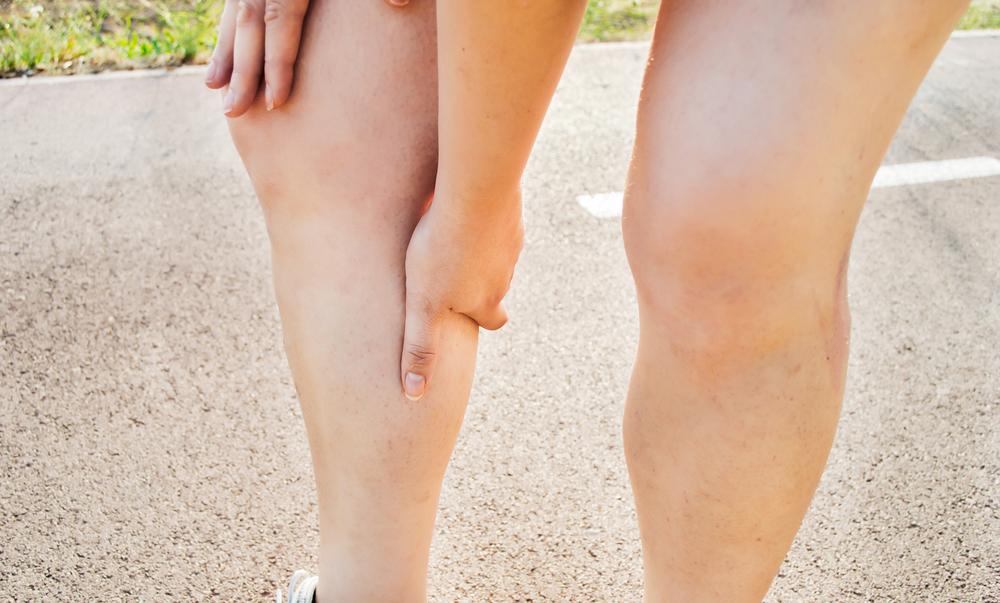
Prolonged immobility, whether during work or travel, can lead to deep vein thrombosis (DVT). This condition involves blood clots forming in deep veins, mainly in the thighs and lower legs, though other areas may be affected. Symptoms include leg pain, swelling, redness, warmth, or sometimes no signs at all. DVT occurs due to damage to blood vessel walls, increased clotting tendencies, and slow blood flow. If dislodged, clots can travel to the lungs, causing pulmonary embolism, which is life-threatening.
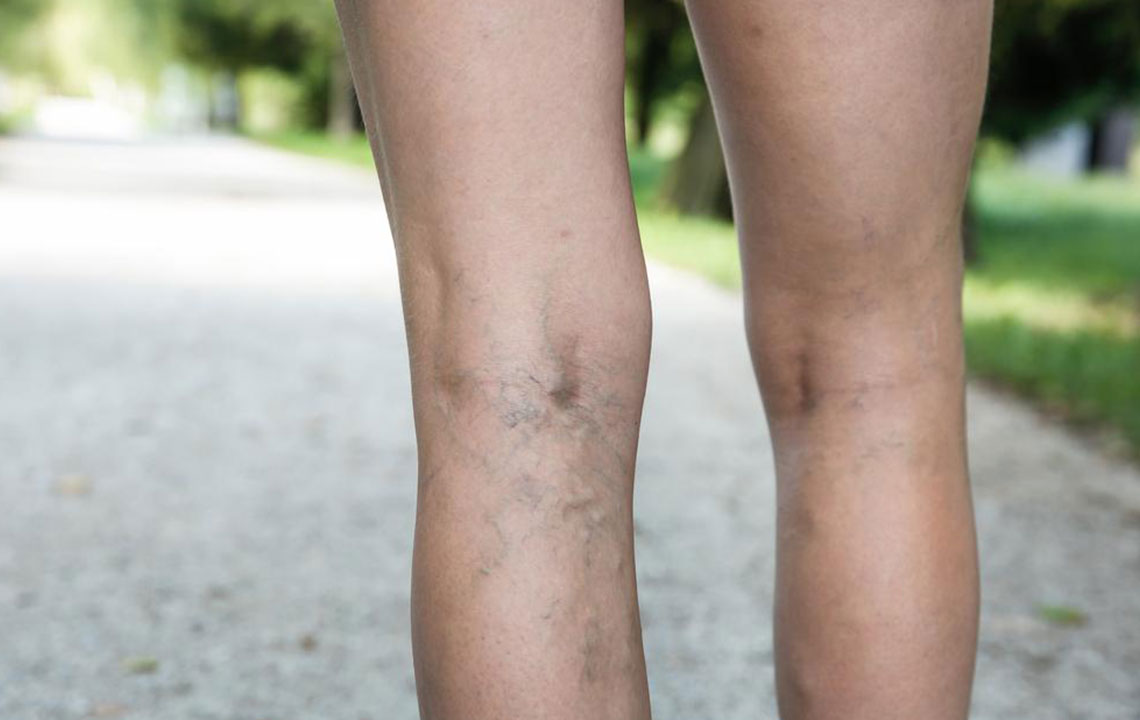
Common signs of DVT include intense leg pain, often starting in the calf and spreading upward. Swelling on one side of the leg or ankle, warmth, discoloration, and visible vein distention may also indicate DVT. Sometimes, symptoms are subtle or unnoticed, and the condition is only diagnosed after a pulmonary embolism occurs. Immediate medical attention is essential if you experience sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, coughing blood, dizziness, or fainting, as these may signal a life-threatening complication.
Individuals at higher risk include those over 60, with a family history of clotting disorders, or who experience prolonged immobility such as bed rest or long flights. Women taking contraceptives or pregnant women are also more vulnerable, especially postpartum. Obesity, smoking, heart disease, cancer, and other chronic illnesses further increase the likelihood of developing DVT. Preventative measures include maintaining an active lifestyle, healthy diet, and seeking prompt medical care if symptoms arise. Treatment typically involves anticoagulants to prevent clot growth and new clot formation.